HPI 1Hh signaling inhibitor CAS# 599150-20-6 |
- Cyclopamine
Catalog No.:BCN2964
CAS No.:4449-51-8
- Purmorphamine
Catalog No.:BCC3641
CAS No.:483367-10-8
- GANT61
Catalog No.:BCC1090
CAS No.:500579-04-4
- GANT 58
Catalog No.:BCC1587
CAS No.:64048-12-0
- GDC-0449 (Vismodegib)
Catalog No.:BCC1285
CAS No.:879085-55-9
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 599150-20-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 2926768 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C27H29NO6 | M.Wt | 463.52 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in DMSO and to 100 mM in ethanol | ||
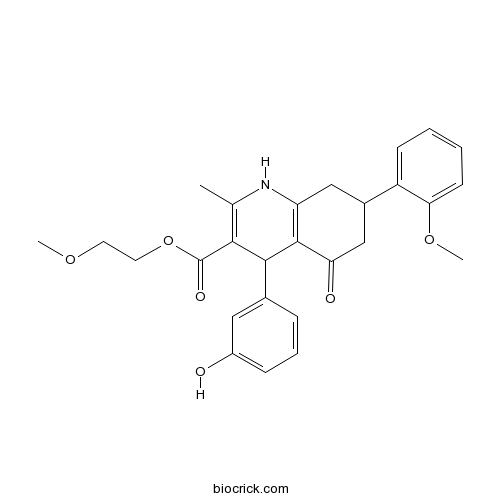
| Chemical Name | 2-methoxyethyl 4-(3-hydroxyphenyl)-7-(2-methoxyphenyl)-2-methyl-5-oxo-4,6,7,8-tetrahydro-1H-quinoline-3-carboxylate | ||
| SMILES | CC1=C(C(C2=C(N1)CC(CC2=O)C3=CC=CC=C3OC)C4=CC(=CC=C4)O)C(=O)OCCOC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ZXSWZQSYZYMZKS-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C27H29NO6/c1-16-24(27(31)34-12-11-32-2)25(17-7-6-8-19(29)13-17)26-21(28-16)14-18(15-22(26)30)20-9-4-5-10-23(20)33-3/h4-10,13,18,25,28-29H,11-12,14-15H2,1-3H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Hedgehog (Hh) signaling inhibitor. Inhibits Sonic hedgehog (Shh)-, SAG- and Gli-induced Hh pathway activation in Shh-LIGHT2 cells (IC50 values are 1.5, 1.5, 4 and 6 μM for Shh-, SAG-, Gli2- and Gli1-induced activation). Also inhibits Hh pathway activation in SmoM2-LIGHT cells (IC50 = 2.5 μM); inhibits the proliferation of cerebellar granule neuron precursors expressing SmoM2. Does not inhibit Wnt signaling. |

HPI 1 Dilution Calculator

HPI 1 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1574 mL | 10.787 mL | 21.574 mL | 43.1481 mL | 53.9351 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4315 mL | 2.1574 mL | 4.3148 mL | 8.6296 mL | 10.787 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2157 mL | 1.0787 mL | 2.1574 mL | 4.3148 mL | 5.3935 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0431 mL | 0.2157 mL | 0.4315 mL | 0.863 mL | 1.0787 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0216 mL | 0.1079 mL | 0.2157 mL | 0.4315 mL | 0.5394 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Hedgehog (Hh) signaling inhibitor. Inhibits Sonic hedgehog (Shh)-, SAG- and Gli-induced Hh pathway activation in Shh-LIGHT2 cells (IC50 values are 1.5, 1.5, 4 and 6 μM for Shh-, SAG-, Gli2- and Gli1-induced activation). Also inhibits Hh pathway activation
- Vicenin -3
Catalog No.:BCN3014
CAS No.:59914-91-9
- 3-Hydroxy-8,9-methylenedioxypterocarpene
Catalog No.:BCN1407
CAS No.:59901-98-3
- Sulfasalazine
Catalog No.:BCC2545
CAS No.:599-79-1
- 3,3'-Sulfonyldianiline
Catalog No.:BCC8595
CAS No.:599-61-1
- Medicagenic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3893
CAS No.:599-07-5
- Mesopsin
Catalog No.:BCN8050
CAS No.:5989-16-2
- Loliolid
Catalog No.:BCN3655
CAS No.:5989-02-6
- 7-hydroxy-4-benzopyrone
Catalog No.:BCC9209
CAS No.:59887-89-7
- ent-7alpha,9-Dihydroxy-15-oxokaur-16-en-19,6bet-olide
Catalog No.:BCN7401
CAS No.:59885-89-1
- N-Formyl-Met-Leu-Phe
Catalog No.:BCC7205
CAS No.:59880-97-6
- L-Dihydroorotic acid
Catalog No.:BCC9007
CAS No.:5988-19-2
- Glabridin
Catalog No.:BCN1221
CAS No.:59870-68-7
- Vindesine sulfate
Catalog No.:BCC8266
CAS No.:59917-39-4
- Vicriviroc maleate
Catalog No.:BCC2038
CAS No.:599179-03-0
- 3',4'-dihydro-3'-hydroxy-Xanthyletin
Catalog No.:BCN3680
CAS No.:5993-18-0
- Malotilate
Catalog No.:BCC1196
CAS No.:59937-28-9
- Carlinoside
Catalog No.:BCN2853
CAS No.:59952-97-5
- Tagitinin F
Catalog No.:BCN4101
CAS No.:59979-57-6
- Tagitinin A
Catalog No.:BCN4102
CAS No.:59979-61-2
- EDTA
Catalog No.:BCC7493
CAS No.:60-00-4
- Guanethidine Sulfate
Catalog No.:BCC3789
CAS No.:60-02-6
- H-Tyr-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3123
CAS No.:60-18-4
- Acetylcholine chloride
Catalog No.:BCN2197
CAS No.:60-31-1
- (6-)ε-Aminocaproic acid
Catalog No.:BCC4888
CAS No.:60-32-2
Effects of therapy using a helicase-primase inhibitor (HPI) in mice infected with deliberate mixtures of wild-type HSV-1 and an HPI-resistant UL5 mutant.[Pubmed:20420855]
Antiviral Res. 2010 Jul;87(1):67-73.
Point mutations in the HSV-1 UL5 (helicase) gene confer resistance to helicase-primase inhibitors (HPIs), e.g. BAY 57-1293. Such mutations normally occur at a frequency of < or =10(-6)PFU. However, individual HSV-1 laboratory strains and some clinical isolates contained resistance mutations (e.g. UL5: Lys356Asn) at 10(-4)PFU. To address the possibility that pre-existing mutants at high frequency might have an impact on therapy using HPIs, deliberate mixtures were prepared to contain the SC16 UL5: Lys356Asn mutant in SC16 wild-type in the proportion of 1/500 or 1/50PFU. Mice were infected in the neck-skin with 5x10(4)PFU/mouse of wt alone, mutant alone, or the respective mixture. The mutant could not be detected in infectious virus yields from mice inoculated with the 1/500 mixture. However, resistant mutant was recovered from some treated mice inoculated with the 1/50 mixture. All mice inoculated with mixtures remained responsive to BAY 57-1293-therapy with no increase in clinical signs compared to treatment of wt-infected mice.
Bis{2-[(phenylimino)ethyl]-1H-pyrrol-1-ido-kappa(2)N,N'}nickel(II): a supramolecular structure formed by C-Hpi hydrogen bonds.[Pubmed:23907874]
Acta Crystallogr C. 2013 Aug;69(Pt 8):851-4.
In the title compound, [Ni(C(1)(2)H(1)(1)N(2))(2)], the NiII cation lies on an inversion centre and has a square-planar coordination geometry. This transition metal complex is composed of two deprotonated N,N'-bidentate 2-[(phenylimino)ethyl]-1H-pyrrol-1-ide ligands around a central NiII cation, with the pyrrolide rings and imine groups lying trans to each other. The Ni-N bond lengths range from 1.894 (3) to 1.939 (2) A and the bite angle is 83.13 (11) degrees . The Ni-N(pyrrolide) bond is substantially shorter than the Ni-N(imino) bond. The planes of the phenyl rings make a dihedral angle of 78.79 (9) degrees with respect to the central NiN(4) plane. The molecules are linked into simple chains by an intermolecular C-Hpi interaction involving a phenyl beta-C atom as donor. Intramolecular C-Hpi interactions are also present.
Polymeric nanoparticle-encapsulated hedgehog pathway inhibitor HPI-1 (NanoHHI) inhibits systemic metastases in an orthotopic model of human hepatocellular carcinoma.[Pubmed:21868763]
Clin Cancer Res. 2012 Mar 1;18(5):1291-302.
PURPOSE: To illustrate the prognostic significance of hedgehog (Hh) signaling in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and to evaluate the efficacy of a novel nanoparticle-encapsulated inhibitor of the Hh transcription factor, Gli1 (NanoHHI) using in vitro and in vivo models of human HCCs. EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN: Patched1 (Ptch1) expression was detected in tumor tissue microarrays of 396 patients with HCC who underwent curative surgical resection during February 2000 to December 2002. Prognostic significance was assessed using Kaplan-Meier survival estimates and log-rank tests. The effects of NanoHHI alone and in combination with sorafenib were investigated on HCC cell lines. Primary HCC tumor growth and metastasis were examined in vivo using subcutaneous and orthotopic HCC xenografts in nude mice. RESULTS: Elevated expression of Ptch1 in HCC tissues was significantly related to disease recurrence, as well as a shorter time to recurrence in patients with HCC. In vitro, NanoHHI significantly inhibited the proliferation and invasion of HCC cell lines. NanoHHI potently suppressed in vivo tumor growth of HCC xenografts in both subcutaneous and orthotopic milieus, and in contrast to sorafenib, resulted in significant attenuation of systemic metastases in the orthotopic setting. Furthermore, NanoHHI significantly decreased the population of CD133-expressing HCC cells, which have been implicated in tumor initiation and metastases. CONCLUSION: Downstream Hh signaling has prognostic significance in patients with HCC as it predicts early recurrence. Gli inhibition through NanoHHI has profound tumor growth inhibition and antimetastatic effects in HCC models, which may provide a new strategy in the treatment of patients with HCC and prevention post-operative recurrence.
Small-molecule inhibitors reveal multiple strategies for Hedgehog pathway blockade.[Pubmed:19666565]
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Aug 18;106(33):14132-7.
Inappropriate activation of the Hedgehog (Hh) signaling pathway has been implicated in a diverse spectrum of cancers, and its pharmacological blockade has emerged as an anti-tumor strategy. While nearly all known Hh pathway antagonists target the transmembrane protein Smoothened (Smo), small molecules that suppress downstream effectors could more comprehensively remediate Hh pathway-dependent tumors. We report here four Hh pathway antagonists that are epistatic to the nucleocytoplasmic regulator Suppressor of Fused [Su(fu)], including two that can inhibit Hh target gene expression induced by overexpression of the Gli transcription factors. Each inhibitor has a unique mechanism of action, and their phenotypes reveal that Gli processing, Gli activation, and primary cilia formation are pharmacologically targetable. We further establish the ability of certain compounds to block the proliferation of cerebellar granule neuron precursors expressing an oncogenic form of Smo, and we demonstrate that Hh pathway inhibitors can have tissue-specific activities. These antagonists therefore constitute a valuable set of chemical tools for interrogating downstream Hh signaling mechanisms and for developing chemotherapies against Hh pathway-related cancers.


