EbrotidineH2-receptor antagonist,competitive CAS# 100981-43-9 |
- Metiamide
Catalog No.:BCC1742
CAS No.:34839-70-8
- Famotidine
Catalog No.:BCC4529
CAS No.:76824-35-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 100981-43-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 65869 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C14H17BrN6O2S3 | M.Wt | 477.42 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | FI3542 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 100 mg/mL (209.46 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
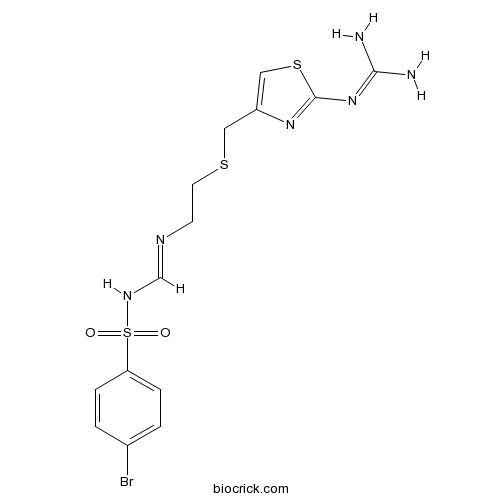
| Chemical Name | N-(4-bromophenyl)sulfonyl-N'-[2-[[2-(diaminomethylideneamino)-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]methylsulfanyl]ethyl]methanimidamide | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC(=CC=C1S(=O)(=O)NC=NCCSCC2=CSC(=N2)N=C(N)N)Br | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ZQHFZHPUZXNPMF-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C14H17BrN6O2S3/c15-10-1-3-12(4-2-10)26(22,23)19-9-18-5-6-24-7-11-8-25-14(20-11)21-13(16)17/h1-4,8-9H,5-7H2,(H,18,19)(H4,16,17,20,21) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Ebrotidine(FI 3542) is a competitive H2-receptor antagonist (Ki= 127.5 nM) with a potent antisecretory activity and evidenced gastroprotection.
IC50 Value: 127.5 nM (Ki)[1]; 0.21mg/kg (ED50, histamine- stimulated acid secretion) [2]
Target: H2 receptor
in vitro: Ebrotidine displaced 3H-thiotidine specific binding to histamine H2-receptors (Ki: 127.5 nmol/l), showing a higher affinity (p < 0.05) than ranitidine (Ki: 190.0 nmol/l) and cimetidine (Ki: 246.1 nmol/l) [1].
in vivo: Following intravenous administration to rats, ebrotidine inhibited histamine- and pentagastrin-stimulated acid secretion in a dose-dependent manner, ED50 being 0.21 and 0.44 mg/kg, respectively [2]. The mean number of gastric erosions seen at endoscopy after treatment with ebrotidine plus ASA (2.0 +/- 0.3) was significantly lower than that after placebo plus ASA (3.7 +/- 0.2). This reduction in lesion core by ebrotidine was accompanied by a significant increase in gastric blood flow (by 15% in corpus and 26% in antrum), by a rise in transmucosal potential difference (by 12%), and by a decrease of mucosal microbleeding [3]. Results of macroscopic assessment revealed that ebrotidine at doses of 50mg and higher/kg body weight effectively prevented mucosal injury, and that the maximal protective effect was achieved by 1h. Physicochemical analysis established that ebrotidine evoked 30% increase in mucus gel dimension, and showed 20% increase in phospholipids, and the content of sulfo- (18%) and sialomucins (21%) [4]. References: | |||||
| Cell experiment: [1] | |
| Cell lines | Helicobacter. pylori |
| Preparation method | The solubility of this compound in DMSO is >10 mM. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37 °C for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20°C for several months. |
| Reacting condition | MIC: 75 micrograms/ml, 5 days |
| Applications | Ebrotidine gave a mean MIC value of 75 micrograms/ml. Ebrotidine at 100 micrograms/ml enhanced the activity of the antimicrobials studied as follows: erythromycin 3 times, tetracycline 1.1 times, amoxicillin 3 times, metronidazole-sensitive strains 9 times and clarithromycin 5 times. |
| Animal experiment: [2] | |
| Animal models | Sprague-Dawley rats with chronic gastric ulcers |
| Dosage form | Intragastric route100 mg/kg, twice daily for 14 days |
| Application | Treatment with ebrotidine resulted in an accelerated ulcer healing. A 40% decrease in ulcer area was observed by the third day and a 71% decrease by the fifth day; the ulcers were essentially healed by the seventh day. |
| Other notes | Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
| References: [1] Palacin C, Tarrago C, Sacristan A, et al. In vitro anti-Helicobacter pylori activity of ebrotidine. Arzneimittel-Forschung, 1997, 47(4A): 471-474. [2] Slomiany B L, Piotrowski J, Slomiany A. Cell cycle progression during gastric ulcer healing by ebrotidine and sucralfate. General Pharmacology: The Vascular System, 1997, 29(3): 367-370. | |

Ebrotidine Dilution Calculator

Ebrotidine Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0946 mL | 10.473 mL | 20.9459 mL | 41.8918 mL | 52.3648 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4189 mL | 2.0946 mL | 4.1892 mL | 8.3784 mL | 10.473 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2095 mL | 1.0473 mL | 2.0946 mL | 4.1892 mL | 5.2365 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0419 mL | 0.2095 mL | 0.4189 mL | 0.8378 mL | 1.0473 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0209 mL | 0.1047 mL | 0.2095 mL | 0.4189 mL | 0.5236 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Ebrotidine is a selective antagonist of histamine H2-receptor with Ki value of 127.5 nM [1].
Ebrotidine inhibited the secretion of gastric acid through competing with histamine for the combination with H2-receptor. It was found to have gastroprotective effect via abating the hyperplastic effects in gastric enteroendocrine cells and interfering the proteolytic and lipolytic activities and the urease of Helicobacter pylori. Besides that, ebrotidine promoted the proliferation of the epithelial cells and alleviated the effects brought by stress, ethanol and aspirin. Unlike other H2 inhibitors, ebrotidine showed no carcinogenic risk enterochromaffin-like cells of mice [1 and 2].
Ebrotidine showed about 10-fold higher anti-secretory effects than cimetidine. Its affinity for H2-receptor was 1.5- and 2-fold higher than that of ranitidine and cimetidine, respectively. In the in vitro assays, ebrotidine promoted the phospholipid secretion of gastric mucosa and maintained the calcium balance of mucosal cells through suppressing EGF-induced phosphorylation of calcium channel proteins. Ebrotidine exerted anti- Helicobacter pylori potency with MIC90 value of 256 mg/L. It inhibited 57% of the proteolytic activity and 93% of the lipolytic activity of the bacteria at concentrations of 35 and 60 mg/L, respectively. In addition, ebrotidine displayed inhibition effects on the urease at a low concentration of 2.1 μM by 77% [1].
The administration of 1 to 100 mg/kg ebrotidine dose-dependently inhibited gastric acid secretion in rats. The effects could last for about 8 hours when the dose was 100 mg/kg. Ebrotidine was also found to have the ability of helping healing ulcer [1].
References:
[1]. Patel S S, Wilde M I. Ebrotidine. Drugs, 1996, 51(6): 974-80; discussion 981.
[2]. Romero A, Gómez F, Villamayor F, et al. Study of the population of enterochromaffin-like cells in mouse gastric mucosa after long-term treatment with ebrotidine. Toxicologic pathology, 1996, 24(2): 160-165.
- Rotundine
Catalog No.:BCN5983
CAS No.:10097-84-4
- 2,2-Bis(hydroxymethyl)butyric acid
Catalog No.:BCC8495
CAS No.:10097-02-6
- Stachyose
Catalog No.:BCN2566
CAS No.:10094-58-3
- Caulophyllumine A
Catalog No.:BCN7928
CAS No.:1009318-60-8
- AZD2014
Catalog No.:BCC3732
CAS No.:1009298-59-2
- AZD8055
Catalog No.:BCC3629
CAS No.:1009298-09-2
- Panamycin 607
Catalog No.:BCN1813
CAS No.:100905-89-3
- Piceatannol
Catalog No.:BCN5824
CAS No.:10083-24-6
- (RS)-CPP
Catalog No.:BCC6561
CAS No.:100828-16-8
- 4,4'-Bis(α,α-dimethylbenzyl)diphenylamine
Catalog No.:BCC8661
CAS No.:10081-67-1
- Chlorahololide C
Catalog No.:BCN7256
CAS No.:1007859-25-7
- (R)-5-Hydroxy-1,7-diphenyl-3-heptanone
Catalog No.:BCN3591
CAS No.:100761-20-4
- Thiamet G
Catalog No.:BCC4864
CAS No.:1009816-48-1
- NSC 687852 (b-AP15)
Catalog No.:BCC2389
CAS No.:1009817-63-3
- CX-4945 (Silmitasertib)
Catalog No.:BCC3693
CAS No.:1009820-21-6
- Levofloxacin
Catalog No.:BCC4791
CAS No.:100986-85-4
- CY 208-243
Catalog No.:BCC6991
CAS No.:100999-26-6
- Pyridostigmine Bromide
Catalog No.:BCC4579
CAS No.:101-26-8
- Hyoscyamine
Catalog No.:BCN1946
CAS No.:101-31-5
- Bis[4-(dimethylamino)phenyl]methane
Catalog No.:BCC8889
CAS No.:101-61-1
- MK-5108 (VX-689)
Catalog No.:BCC2176
CAS No.:1010085-13-8
- Microcystin-LR
Catalog No.:BCC5339
CAS No.:101043-37-2
- Larixinol
Catalog No.:BCN6484
CAS No.:101046-79-1
- Tenovin-3
Catalog No.:BCC3889
CAS No.:1011301-27-1
Determination of ebrotidine metabolites in overlapping peaks from capillary zone electrophoresis using chemometric methods.[Pubmed:11197182]
Electrophoresis. 2001 Jan;22(1):71-6.
This paper illustrates the possibilities of chemometric methods in the resolution and quantification of various compounds in overlapping peaks from capillary electrophoresis. Ebrotidine and most of its metabolites were efficiently separated by capillary zone electrophoresis (CZE) in a fused-silica capillary. However, the procedure was not suitable for the physical separation of the three less ionizable metabolites, which comigrated and overlapped with the electroosmotic flow signal. Multivariate curve resolution based on an alternating least squares procedure was used for their mathematical resolution. For such a purpose, data obtained in the CZE system with a diode array detector, which consisted of UV spectra registered over time, were analyzed. The Ebrotidine metabolites were successfully resolved and quantified in synthetic mixtures and urine samples.
Determination of ebrotidine and its metabolites by capillary electrophoresis with UV and mass spectrometry detection.[Pubmed:10949494]
J Chromatogr A. 2000 Aug 4;888(1-2):281-92.
This study describes the application of capillary electrophoresis (CE) to the analysis of Ebrotidine and its metabolites as an alternative analytical technique to liquid chromatography. Comparison between UV-diode array spectroscopy and mass spectrometry (MS) using an ion-trap system with electrospray ionization as detection systems has been performed. The quality parameters of the UV detection method were established, obtaining linear calibration curves over the range studied (8-200 mg ml(-1)), limits of detection between 3.4 and 4.3 microg ml(-1), and run-to-run and day-to-day precision lower than 14%. For these compounds the protonated species [M+H]+ and, in some cases, sodium adducts were observed in the MS spectra. Using MS coupled to CE, limits of detection were between 0.5 and 2.6 microg ml(-1).


