MK-5108 (VX-689)Aurora-A kinase inhibitor,highly selective CAS# 1010085-13-8 |
- MLN8237 (Alisertib)
Catalog No.:BCC2166
CAS No.:1028486-01-2
- CCT137690
Catalog No.:BCC2188
CAS No.:1095382-05-0
- Aurora A Inhibitor I
Catalog No.:BCC2182
CAS No.:1158838-45-9
- MLN8054
Catalog No.:BCC2170
CAS No.:869363-13-3
- MK-8745
Catalog No.:BCC3994
CAS No.:885325-71-3
- TAK-901
Catalog No.:BCC2180
CAS No.:934541-31-8
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1010085-13-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 24748204 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C22H21ClFN3O3S | M.Wt | 461.94 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | VX-689 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 12.5 mg/mL (27.06 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
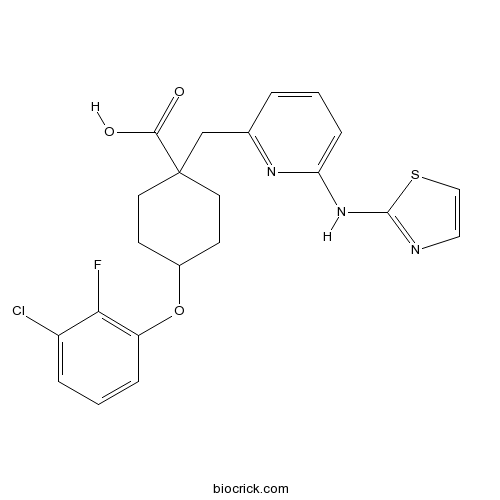
| Chemical Name | 4-(3-chloro-2-fluorophenoxy)-1-[[6-(1,3-thiazol-2-ylamino)pyridin-2-yl]methyl]cyclohexane-1-carboxylic acid | ||
| SMILES | C1CC(CCC1OC2=C(C(=CC=C2)Cl)F)(CC3=NC(=CC=C3)NC4=NC=CS4)C(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | LCVIRAZGMYMNNT-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C22H21ClFN3O3S/c23-16-4-2-5-17(19(16)24)30-15-7-9-22(10-8-15,20(28)29)13-14-3-1-6-18(26-14)27-21-25-11-12-31-21/h1-6,11-12,15H,7-10,13H2,(H,28,29)(H,25,26,27) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | MK-5108 is a highly selective inhibitor of Aurora-A kinase with 0.064 nM. | |||||
| Targets | Aurora-A | |||||
| IC50 | 0.064 nM | |||||
| Cell experiment: | |
| Cell lines | Tumor cell types (HCT116, LS174T, HL60, MDA-MB-231, ZR-75-1, MCF-7, PC3, MIA PaCa2, A375 and HeLa). |
| Preparation method | The solubility of this compound in DMSO is >10 mM. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37 °C for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20°C for several months. |
| Reacting condition | 48 h; IC50(15 nM-113 nM) |
| Applications | VX-680 caused accumulation of cells with 4 N DNA content and potently inhibited the proliferation of a wide variety of tumor cell types with half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) values ranging from 15 to 113 nM. These data are consistent with the prediction that the Aurora kinases are crucial for cell-cycle progression, and with the finding that overexpression of kinase-inactive Aurora-B disrupts cell division. |
| Animal experiment: | |
| Animal models | Female athymic NCr-nu mice |
| Dosage form | 75 mg/kg; b.i.d.i.p. |
| Application | VX-680 caused a marked reduction in tumor size in a human AML (HL-60) xenograft model. In nude mice treated with VX-680 at 75 mg/kg, twice a day intraperitoneally (b.i.d.i.p.) for 13 d, mean tumor volumes were reduced by 98% (P < 0.001) in comparison with the control group. |
| Other notes | Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
| References: [1] Harrington E A, Bebbington D, Moore J, et al. VX-680, a potent and selective small-molecule inhibitor of the Aurora kinases, suppresses tumor growth in vivo[J]. Nature medicine, 2004, 10(3): 262-267. | |

MK-5108 (VX-689) Dilution Calculator

MK-5108 (VX-689) Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1648 mL | 10.8239 mL | 21.6478 mL | 43.2957 mL | 54.1196 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.433 mL | 2.1648 mL | 4.3296 mL | 8.6591 mL | 10.8239 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2165 mL | 1.0824 mL | 2.1648 mL | 4.3296 mL | 5.412 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0433 mL | 0.2165 mL | 0.433 mL | 0.8659 mL | 1.0824 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0216 mL | 0.1082 mL | 0.2165 mL | 0.433 mL | 0.5412 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
MK-5108, also known as VX-689, is a novel, potent and selective inhibitor of Aurora A kinase (AAK) that competitively binds to the ATP binding site of AAK and hence potently inhibits the activity of AAK with 50% inhibition concentration IC50 value of 0.064 nM. MK-5108 also inhibits other members of Aurora kinase family, including Aurora B kinase (IC50 = 14 nM) and Aurora C kinase (IC50 = 12 nM), with a lesser potency. MK-5108 has been extensively studies and found to exhibit antitumor activity in a wide range of cancer types, including breast, cervix, colorectal, ovary and pancreas neoplasms.
Reference
Myke R. Green, BS, Pharm.D., BCOP, Joseph E. Woolery, BS, Pharm.D, and Daruka Mahadevan, MD, PhD. Update on Aurora Kinase Targeted Therapeutics in Oncology. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2008 November ; 3(3): 162–177.
- Bis[4-(dimethylamino)phenyl]methane
Catalog No.:BCC8889
CAS No.:101-61-1
- Hyoscyamine
Catalog No.:BCN1946
CAS No.:101-31-5
- Pyridostigmine Bromide
Catalog No.:BCC4579
CAS No.:101-26-8
- CY 208-243
Catalog No.:BCC6991
CAS No.:100999-26-6
- Levofloxacin
Catalog No.:BCC4791
CAS No.:100986-85-4
- CX-4945 (Silmitasertib)
Catalog No.:BCC3693
CAS No.:1009820-21-6
- NSC 687852 (b-AP15)
Catalog No.:BCC2389
CAS No.:1009817-63-3
- Thiamet G
Catalog No.:BCC4864
CAS No.:1009816-48-1
- Ebrotidine
Catalog No.:BCC1542
CAS No.:100981-43-9
- Rotundine
Catalog No.:BCN5983
CAS No.:10097-84-4
- 2,2-Bis(hydroxymethyl)butyric acid
Catalog No.:BCC8495
CAS No.:10097-02-6
- Stachyose
Catalog No.:BCN2566
CAS No.:10094-58-3
- Microcystin-LR
Catalog No.:BCC5339
CAS No.:101043-37-2
- Larixinol
Catalog No.:BCN6484
CAS No.:101046-79-1
- Tenovin-3
Catalog No.:BCC3889
CAS No.:1011301-27-1
- 3,8'-Biapigenin
Catalog No.:BCN5825
CAS No.:101140-06-1
- Milnacipran HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4922
CAS No.:101152-94-7
- Odoriflavene
Catalog No.:BCN8240
CAS No.:101153-41-7
- Tenovin-6
Catalog No.:BCC3667
CAS No.:1011557-82-6
- Momordicoside P
Catalog No.:BCN3275
CAS No.:1011726-62-7
- Longipedlactone J
Catalog No.:BCN6644
CAS No.:1011762-93-8
- CUDC-101
Catalog No.:BCC2149
CAS No.:1012054-59-9
- IRAK inhibitor 4
Catalog No.:BCC1657
CAS No.:1012104-68-5
- Picrasidine Q
Catalog No.:BCN3182
CAS No.:101219-61-8
Aurora kinase inhibitor patents and agents in clinical testing: an update (2011 - 2013).[Pubmed:24965505]
Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2014 Sep;24(9):1021-38.
INTRODUCTION: Aurora kinase A, B and C, members of serine/threonine kinase family, are key regulators of mitosis. As Aurora kinases are overexpressed in many of the human cancers, small-molecule inhibitors of Aurora kinase have emerged as a possible treatment option for cancer. AREAS COVERED: In 2009 and 2011, the literature pertaining to Aurora kinase inhibitors and their patents was reviewed. Here, the aim is to update the information for Aurora kinase inhibitors in clinical trials and the patents filed between the years 2011 and 2013. Pubmed, Scopus(R), Scifinder(R), USPTO, EPO and www.clinicaltrials.gov databases were used for searching the literature and patents for Aurora kinase inhibitors. EXPERT OPINION: Even though both Aurora sub-type selective as well as pan-selective inhibitors show preclinical and clinical efficacy, so far no Aurora kinase inhibitor has been approved for clinical use. Particularly, dose-limiting toxicity (neutropenia) is a key issue that needs to be addressed. Preliminary evidence suggests that the use of selective Aurora A inhibitors could avoid Aurora B-mediated neutropenia in clinical settings. Also, use of adjunctive agents such as granulocyte stimulating factor to overcome neutropenia associated with Aurora B inhibition could be an answer to overcome the toxicity and bring Aurora inhibitors to market in the future.
Long residence times revealed by Aurora A kinase-targeting fluorescent probes derived from inhibitors MLN8237 and VX-689.[Pubmed:24403173]
Chembiochem. 2014 Feb 10;15(3):443-50.
We report the development of three fluorescent probes for protein kinase Aurora A that are derived from the well-known inhibitors MLN8237 and VX-689 (MK-5108). Two of these probes target the ATP site of Aurora A, and one targets simultaneously the ATP and substrate sites of the kinase. The probes were tested in an assay with fluorescence polarisation/anisotropy readout, and we demonstrated slow association kinetics and long residence time of the probes (kon 10(5)-10(7) M(-1) s(-1), koff 10(-3)-10(-4) s(-1); residence time 500-3000 s). The presence of the Aurora A activator TPX2 caused a significant reduction in the on-rate and increase in the off-rate of fluorescent probes targeting ATP site. These observations were supported by Aurora A inhibition assays with MLN8237 and VX-689. Overall, our results emphasise the importance of rational design of experiments with these compounds and correct interpretation of the obtained data.


