GNF 2Bcr-Abl inhibitor CAS# 778270-11-4 |
- Imatinib Mesylate (STI571)
Catalog No.:BCC1115
CAS No.:220127-57-1
- Dasatinib (BMS-354825)
Catalog No.:BCC1281
CAS No.:302962-49-8
- Saracatinib (AZD0530)
Catalog No.:BCC1166
CAS No.:379231-04-6
- Bosutinib (SKI-606)
Catalog No.:BCC1167
CAS No.:380843-75-4
- DPH
Catalog No.:BCC1538
CAS No.:484049-04-9
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 778270-11-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5311510 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C18H13F3N4O2 | M.Wt | 374.32 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (267.15 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
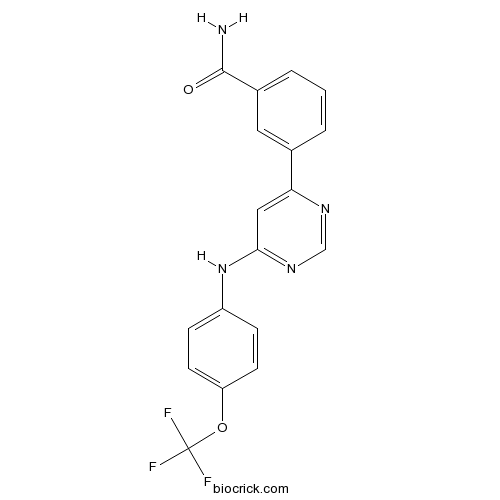
| Chemical Name | 3-[6-[4-(trifluoromethoxy)anilino]pyrimidin-4-yl]benzamide | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC(=CC(=C1)C(=O)N)C2=CC(=NC=N2)NC3=CC=C(C=C3)OC(F)(F)F | ||
| Standard InChIKey | WEVYNIUIFUYDGI-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C18H13F3N4O2/c19-18(20,21)27-14-6-4-13(5-7-14)25-16-9-15(23-10-24-16)11-2-1-3-12(8-11)17(22)26/h1-10H,(H2,22,26)(H,23,24,25) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Allosteric inhibitor of Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase activity (IC50 = 267 nM); inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in Bcr-Abl-expressing cells. Selective for Bcr-Abl over a panel of serine, threonine and tyrosine kinases. Non-ATP-competitive. |

GNF 2 Dilution Calculator

GNF 2 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6715 mL | 13.3576 mL | 26.7151 mL | 53.4302 mL | 66.7878 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5343 mL | 2.6715 mL | 5.343 mL | 10.686 mL | 13.3576 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2672 mL | 1.3358 mL | 2.6715 mL | 5.343 mL | 6.6788 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0534 mL | 0.2672 mL | 0.5343 mL | 1.0686 mL | 1.3358 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0267 mL | 0.1336 mL | 0.2672 mL | 0.5343 mL | 0.6679 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
GNF-2 is a highly selective non-ATP competitive inhibitor of Bcr-Abl with an IC50 value of 100 to 300 nM in various cell lines.
BCR-ABL gene is fused by the BCR and ABL1 genes [1]. BCR-ABL increased production of tyrosine kinase and played an essential role in the pathogenesis of chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) [2].
Unlike imatinib® that competitively inhibited the ATP-binding site of BCR-ABL kinase activity [3], GNF-2 allosterically inhibited (through binding the myristate-binding site of ABL[4]) the proliferation of BCR-ABL positive cell and induces cell apoptosis. In Ba/F3.p210 Bcr-abl–expressing cells, 48 h treatment of GNF-2 was able to inhibit the proliferation of cells with an IC50 value of 138 nM [5]. In addition, GNF-2 has been found to inhibit E255V and Y253H mutant Ba/F3 cells cell growth, with an IC50 value of 268 and 194 nM, respectively [5]. GNF-2 also caused growth inhibition of K562 and SUP-B15 with an IC50 value of 273 nM and 268 nM, respectively[5].
Injecting with BCR-ABL–expressing Ba/F3-p210 cells, 4 % lymphocytes reduction in eperipheral blood was induced [6].
References:
[1].REDDY, K. S. & GROVE, B. 1998. A Philadelphia-Negative Chronic Myeloid Leukemia with a BCR/ABL Fusion Gene on Chromosome 9. Cancer Genetics and Cytogenetics, 107, 48-50.
[2].RUMPOLD, H. & WEBERSINKE, G. 2011. Molecular pathogenesis of Philadelphia-positive chronic myeloid leukemia - is it all BCR-ABL? Curr Cancer Drug Targets, 11, 3-19.
[3].SEGGEWISS, R., LORE, K., GREINER, E., MAGNUSSON, M. K., PRICE, D. A., DOUEK, D. C., DUNBAR, C. E. & WIESTNER, A. 2005. Imatinib inhibits T-cell receptor-mediated T-cell proliferation and activation in a dose-dependent manner. Blood, 105, 2473-2479.
[4].FABBRO, D., MANLEY, P. W., JAHNKE, W., LIEBETANZ, J., SZYTTENHOLM, A., FENDRICH, G., STRAUSS, A., ZHANG, J., GRAY, N. S., ADRIAN, F., WARMUTH, M., PELLE, X., GROTZFELD, R., BERST, F., MARZINZIK, A., COWAN-JACOB, S. W., FURET, P. & MESTAN, J. 2010. Inhibitors of the Abl kinase directed at either the ATP- or myristate-binding site. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Proteins and Proteomics, 1804, 454-462.
[5].ADRIAN, F. J., DING, Q., SIM, T., VELENTZA, A., SLOAN, C., LIU, Y., ZHANG, G., HUR, W., DING, S., MANLEY, P., MESTAN, J., FABBRO, D. & GRAY, N. S. 2006. Allosteric inhibitors of Bcr-abl-dependent cell proliferation. Nat Chem Biol, 2, 95-102.
[6]. ADRIAN, F. J., DING, Q., SIM, T., VELENTZA, A., SLOAN, C., LIU, Y., ZHANG, G., HUR, W., DING, S., MANLEY, P., MESTAN, J., FABBRO, D. & GRAY, N. S. 2006. Allosteric inhibitors of Bcr-abl-dependent cell proliferation. Nat Chem Biol, 2, 95-102.
- Carasinol B
Catalog No.:BCN8226
CAS No.:777857-86-0
- Dehydrocrebanine
Catalog No.:BCN4328
CAS No.:77784-22-6
- Potassium phosphate monobasic
Catalog No.:BCC7583
CAS No.:7778-77-0
- 1,2-Dihydrotanshinquinone
Catalog No.:BCN2477
CAS No.:77769-21-2
- 1,7-Dihydroxy-3-methoxy-2-prenylxanthone
Catalog No.:BCN1354
CAS No.:77741-58-3
- (-)-Toddanol
Catalog No.:BCN3429
CAS No.:77715-99-2
- Arctigenin
Catalog No.:BCN6291
CAS No.:7770-78-7
- 6'''-Feruloylspinosin
Catalog No.:BCN2802
CAS No.:77690-92-7
- Enoximone
Catalog No.:BCC7155
CAS No.:77671-31-9
- ent-11,16-Epoxy-15-hydroxykauran-19-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1355
CAS No.:77658-46-9
- ent-9-Hydroxy-15-oxo-19-kauranoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1356
CAS No.:77658-45-8
- ent-9-Hydroxy-15-oxo-16-kauren-19-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1357
CAS No.:77658-39-0
- GNF 5
Catalog No.:BCC3892
CAS No.:778277-15-9
- Nelumol A
Catalog No.:BCN4749
CAS No.:77836-86-3
- (1R)-(+)-Alpha-Pinene
Catalog No.:BCC8275
CAS No.:7785-70-8
- Oglemilast
Catalog No.:BCC1817
CAS No.:778576-62-8
- Isopulegol
Catalog No.:BCN4974
CAS No.:7786-67-6
- Beta-Lipotropin (1-10), porcine
Catalog No.:BCC1009
CAS No.:77875-68-4
- Doxazosin Mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC1257
CAS No.:77883-43-3
- Dinaciclib (SCH727965)
Catalog No.:BCC3765
CAS No.:779353-01-4
- Longikaurin E
Catalog No.:BCN4329
CAS No.:77949-42-9
- Z-Glycinol
Catalog No.:BCC3095
CAS No.:77987-49-6
- Secologanin dimethyl acetal
Catalog No.:BCN4581
CAS No.:77988-07-9
- Mulberrofuran C
Catalog No.:BCN4032
CAS No.:77996-04-4
Expanding the structural diversity of Bcr-Abl inhibitors: Hybrid molecules based on GNF-2 and Imatinib.[Pubmed:26298495]
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2015 Oct 1;25(19):4164-8.
In order to expand the structural diversity of Bcr-Abl inhibitors, twenty hybrids (series E and P) have been synthesized and characterized based on Imatinib and GNF-2. Their biological activities were evaluated in vitro against human leukemia cells. Most compounds exhibited potent antiproliferative activity against K562 cells, especially for compounds E4, E5 and E7. Furthermore, these new hybrids were also screened for Abl kinase inhibitory activity, and some of them inhibited Abl kinase with low micromolar IC50 values. In particular, compound P3 displayed the most potent activity with IC50 value of 0.017 muM comparable with that of Imatinib. Molecular docking studies indicated that these novel hybrids fitted well with the active site of Bcr-Abl. These results suggested the great potential of these compounds as novel Bcr-Abl inhibitors.
The tyrosine kinase inhibitor GNF-2 suppresses osteoclast formation and activity.[Pubmed:24130113]
J Leukoc Biol. 2014 Feb;95(2):337-45.
GNF-2, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor, was developed to overcome imatinib-resistant mutations found in CML patients. Osteoclasts are the principal bone-resorbing cells that are responsible for bone diseases, such as osteoporosis, tumor-induced osteolysis, and metastatic cancers. In this study, we investigated the effect of GNF-2 on osteoclast development induced by RANKL and M-CSF. We found that GNF-2 inhibited osteoclast differentiation from BMMs. GNF-2 suppressed RANKL-induced NF-kappaB transcriptional activity and the induction of c-Fos and NFATc1, which are two key transcription factors in osteoclastogenesis. We also observed that GNF-2 dose-dependently inhibited the proliferation of osteoclast precursors through the suppression of the M-CSFR c-Fms. In addition, GNF-2 accelerated osteoclast apoptosis by inducing caspase-3 and Bim expression. Furthermore, GNF-2 interfered with actin cytoskeletal organization and subsequently blocked the bone-resorbing activity of mature osteoclasts. In agreement with its in vitro effects, GNF-2 reduced osteoclast number and bone loss in a mouse model of LPS-induced bone destruction. Taken together, our data reveal that GNF-2 possesses anti-bone-resorptive properties, suggesting that GNF-2 may have therapeutic value for the treatment of bone-destructive disorders that can occur as a result of excessive osteoclastic bone resorption.
Overcoming Bcr-Abl T315I mutation by combination of GNF-2 and ATP competitors in an Abl-independent mechanism.[Pubmed:23186157]
BMC Cancer. 2012 Nov 27;12:563.
BACKGROUND: Philadelphia positive leukemias are characterized by the presence of Bcr-Abl fusion protein which exhibits an abnormal kinase activity. Selective Abl kinase inhibitors have been successfully established for the treatment of Ph (+) leukemias. Despite high rates of clinical response, Ph (+) patients can develop resistance against these kinase inhibitors mainly due to point mutations within the Abl protein. Of special interest is the 'gatekeeper' T315I mutation, which confers complete resistance to Abl kinase inhibitors. Recently, GNF-2, Abl allosteric kinase inhibitor, was demonstrated to possess cellular activity against Bcr-Abl transformed cells. Similarly to Abl kinase inhibitors (AKIs), GNF-2 failed to inhibit activity of mutated Bcr-Abl carrying the T315I mutation. METHODS: Ba/F3 cells harboring native or T315I mutated Bcr-Abl constructs were treated with GNF-2 and AKIs. We monitored the effect of GNF-2 with AKIs on the proliferation and clonigenicity of the different Ba/F3 cells. In addition, we monitored the auto-phosphorylation activity of Bcr-Abl and JAK2 in cells treated with GNF-2 and AKIs. RESULTS: In this study, we report a cooperation between AKIs and GNF-2 in inhibiting proliferation and clonigenicity of Ba/F3 cells carrying T315I mutated Bcr-Abl. Interestingly, cooperation was most evident between Dasatinib and GNF-2. Furthermore, we showed that GNF-2 was moderately active in inhibiting the activity of JAK2 kinase, and presence of AKIs augmented GNF-2 activity. CONCLUSIONS: Our data illustrated the ability of allosteric inhibitors such as GNF-2 to cooperate with AKIs to overcome T315I mutation by Bcr-Abl-independent mechanisms, providing a possibility of enhancing AKIs efficacy and overcoming resistance in Ph+ leukemia cells.
GNF-2 Inhibits Dengue Virus by Targeting Abl Kinases and the Viral E Protein.[Pubmed:27105280]
Cell Chem Biol. 2016 Apr 21;23(4):443-52.
Dengue virus infects more than 300 million people annually, yet there is no widely protective vaccine or drugs against the virus. Efforts to develop antivirals against classical targets such as the viral protease and polymerase have not yielded drugs that have advanced to the clinic. Here, we show that the allosteric Abl kinase inhibitor GNF-2 interferes with dengue virus replication via activity mediated by cellular Abl kinases but additionally blocks viral entry via an Abl-independent mechanism. To characterize this newly discovered antiviral activity, we developed disubstituted pyrimidines that block dengue virus entry with structure-activity relationships distinct from those driving kinase inhibition. We demonstrate that biotin- and fluorophore-conjugated derivatives of GNF-2 interact with the dengue glycoprotein, E, in the pre-fusion conformation that exists on the virion surface, and that this interaction inhibits viral entry. This study establishes GNF-2 as an antiviral compound with polypharmacological activity and provides "lead" compounds for further optimization efforts.
Targeting Bcr-Abl by combining allosteric with ATP-binding-site inhibitors.[Pubmed:20072125]
Nature. 2010 Jan 28;463(7280):501-6.
In an effort to find new pharmacological modalities to overcome resistance to ATP-binding-site inhibitors of Bcr-Abl, we recently reported the discovery of GNF-2, a selective allosteric Bcr-Abl inhibitor. Here, using solution NMR, X-ray crystallography, mutagenesis and hydrogen exchange mass spectrometry, we show that GNF-2 binds to the myristate-binding site of Abl, leading to changes in the structural dynamics of the ATP-binding site. GNF-5, an analogue of GNF-2 with improved pharmacokinetic properties, when used in combination with the ATP-competitive inhibitors imatinib or nilotinib, suppressed the emergence of resistance mutations in vitro, displayed additive inhibitory activity in biochemical and cellular assays against T315I mutant human Bcr-Abl and displayed in vivo efficacy against this recalcitrant mutant in a murine bone-marrow transplantation model. These results show that therapeutically relevant inhibition of Bcr-Abl activity can be achieved with inhibitors that bind to the myristate-binding site and that combining allosteric and ATP-competitive inhibitors can overcome resistance to either agent alone.
Allosteric inhibitors of Bcr-abl-dependent cell proliferation.[Pubmed:16415863]
Nat Chem Biol. 2006 Feb;2(2):95-102.
Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) is a myeloproliferative disorder characterized at the molecular level by the expression of Bcr-abl, a 210-kDa fusion protein with deregulated tyrosine kinase activity. Encouraged by the clinical validation of Bcr-abl as the target for the treatment of CML by imatinib, we sought to identify pharmacological agents that could target this kinase by a distinct mechanism. We report the discovery of a new class of Bcr-abl inhibitors using an unbiased differential cytotoxicity screen of a combinatorial kinase-directed heterocycle library. Compounds in this class (exemplified by GNF-2) show exclusive antiproliferative activity toward Bcr-abl-transformed cells, with potencies similar to imatinib, while showing no inhibition of the kinase activity of full-length or catalytic domain of c-abl. We propose that this new class of compounds inhibits Bcr-abl kinase activity through an allosteric non-ATP competitive mechanism.


