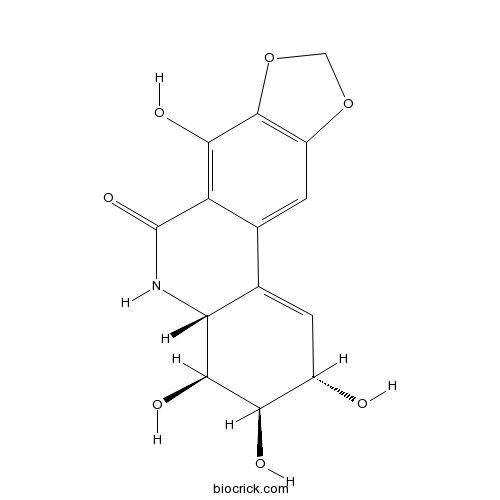
NarciclasineModulates the Rho/ROCK/LIM kinase/cofilin pathway CAS# 29477-83-6 |
- Fasudil (HA-1077) HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2542
CAS No.:105628-07-7
- chroman 1
Catalog No.:BCC1480
CAS No.:1273579-40-0
- RKI-1447
Catalog No.:BCC1903
CAS No.:1342278-01-6
- Y-27632 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1273
CAS No.:129830-38-2
- ROCK inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC1905
CAS No.:867017-68-3
- SLx-2119
Catalog No.:BCC1954
CAS No.:911417-87-3
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 29477-83-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 72376 | Appearance | White powder |
| Formula | C14H13NO7 | M.Wt | 307.25 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Lycoricidinol | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 26 mg/mL (84.62 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | (2S,3R,4S,4aR)-2,3,4,7-tetrahydroxy-3,4,4a,5-tetrahydro-2H-[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-j]phenanthridin-6-one | ||
| SMILES | C1OC2=C(O1)C(=C3C(=C2)C4=CC(C(C(C4NC3=O)O)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | LZAZURSABQIKGB-AEKGRLRDSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C14H13NO7/c16-6-1-5-4-2-7-13(22-3-21-7)11(18)8(4)14(20)15-9(5)12(19)10(6)17/h1-2,6,9-10,12,16-19H,3H2,(H,15,20)/t6-,9+,10+,12-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Narciclasine displays marked proapoptotic and cytotoxic activity, as does pancratistatin, and significant in vivo anticancer effects in various experimental models, but it is also associated with severe toxic side effects. 2. Narciclasine acts on the auxin signaling pathway upstream of TIR1, which modulates Aux/IAA protein degradation, and thereby affects the auxin-mediated responses in Arabidopsis roots, inhibits the root hair development of lettuce seedlings. 3. The alkaloid Narciclasine is the bioactive compound responsible for the anti-inflammatory action of HCE. |
| Targets | Immunology & Inflammation related |

Narciclasine Dilution Calculator

Narciclasine Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.2547 mL | 16.2734 mL | 32.5468 mL | 65.0936 mL | 81.367 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6509 mL | 3.2547 mL | 6.5094 mL | 13.0187 mL | 16.2734 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3255 mL | 1.6273 mL | 3.2547 mL | 6.5094 mL | 8.1367 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0651 mL | 0.3255 mL | 0.6509 mL | 1.3019 mL | 1.6273 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0325 mL | 0.1627 mL | 0.3255 mL | 0.6509 mL | 0.8137 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Narciclasine
Description:
IC50: The mean IC50 of about 50 nmol/L calculated on the 6 human glioblastoma multiforme was similar to the value previously reported for 6 carcinoma cell lines and consistent with National Cancer Institute data, which also reveal a mean IC50 value of 47 nmol/L for the compound across a panel of 60 cancer cell lines [1].
Narciclasine is a toxic alkaloid found in various Amaryllidaceae species, modulatting the Rho/ROCK/LIM kinase/cofilin pathway, stimulating RhoA activation and inducing actin polymerization. The cytostatic activity of Narciclasine involves the impairment of actin cytoskeleton organization by targeting GTPases, including RhoA and the elongation factor eEF1A. Thus, Narciclasine is a potentially promising agent for the treatment of primary brain cancers and various brain metastases.
In vitro: In a MM46 cell in-vitro study, authors examined the inhibitory activities of Amaryllidaceae alkaloids, namely, lycoricidinol (narciclasine), hippeastrine and ungerine against the cytotoxicity of calprotectin. It was found that lycoricidinol (narciclasine) inhibited calprotectin-induced cytotoxicity at more than 10-fold lower concentration (IC50=0.001-0.01 μ/ml) than lycorine, while the effects of the latter two alkaloids were very weak [2].
In vivo: In an in-vivo study, the authors checked the prophylactic effect of lycorine and lycoricidinol (narciclasine) on the adjuvant arthritis model in rats. Results showed that lycoricidinol (narciclasine), rather than lycorine, significantly suppressed the degree of swelling of adjuvant-treated as well as untreated feet, suggesting that lycoricidinol (narciclasine) might be a candidate as a the drug having marked suppressive activity for inflammation which might be influenced by calprotectin [2].
Clinical trial: Up to now, Narciclasine is still in the preclinical development stage and are planned to move toward clinical trials in oncology within a 3-4 year period in order to help patients with brain cancers, including gliomas, as well as brain metastases, which was said by Robert Kiss, Ph.D., co-author of the study from the Laboratory of Toxicology at the Institute of Pharmacy at the Université Libre de Bruxelles in Brussels, Belgium.
Reference:
[1] Lefranc F, Sauvage S, Van Goietsenoven G, Mégalizzi V, Lamoral-Theys D, Debeir O, Spiegl-Kreinecker S, Berger W, Mathieu V, Decaestecker C, Kiss R. Narciclasine, a plant growth modulator, activates Rho and stress fibers in glioblastoma cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 2009;8(7):1739-50.
[2] Mikami M, Kitahara M, Kitano M, Ariki Y, Mimaki Y, Sashida Y, Yamazaki M, Yui S. Suppressive activity of lycoricidinol (narciclasine) against cytotoxicity of neutrophil-derived calprotectin, and its suppressive effect on rat adjuvant arthritis model. Biol Pharm Bull. 1999;22(7):674-8.
- Ganoderic acid Z
Catalog No.:BCN2440
CAS No.:294674-09-2
- L 006235
Catalog No.:BCC2361
CAS No.:294623-49-7
- Ticarcillin sodium
Catalog No.:BCC4737
CAS No.:29457-07-6
- Sophorabioside
Catalog No.:BCN7838
CAS No.:2945-88-2
- Pseudolycorine
Catalog No.:BCN5371
CAS No.:29429-03-6
- 4',7-Di-O-methylnaringenin
Catalog No.:BCN5197
CAS No.:29424-96-2
- 7-Nitroindazole
Catalog No.:BCC6713
CAS No.:2942-42-9
- Cyclen
Catalog No.:BCN8441
CAS No.:294-90-6
- Secoisolariciresinol
Catalog No.:BCN5196
CAS No.:29388-59-8
- Anhydrosecoisolariciresinol
Catalog No.:BCN7521
CAS No.:29388-33-8
- Ro 90-7501
Catalog No.:BCC7351
CAS No.:293762-45-5
- Thevetiaflavone
Catalog No.:BCN4024
CAS No.:29376-68-9
- Cypellocarpin C
Catalog No.:BCN7556
CAS No.:294856-66-9
- Valerosidate
Catalog No.:BCN6750
CAS No.:29505-31-5
- MNI-caged-L-glutamate
Catalog No.:BCC7086
CAS No.:295325-62-1
- Eupatoletin
Catalog No.:BCN3605
CAS No.:29536-44-5
- Olivil
Catalog No.:BCN5198
CAS No.:2955-23-9
- Negletein
Catalog No.:BCN8085
CAS No.:29550-13-8
- (E)-N-Caffeoylputrescine
Catalog No.:BCC8391
CAS No.:29554-26-5
- Sakuranetin
Catalog No.:BCN5199
CAS No.:2957-21-3
- 2-Amino-2',5-dichlorobenzophenone
Catalog No.:BCC8520
CAS No.:2958-36-3
- Gynuramide II
Catalog No.:BCN5200
CAS No.:295803-03-1
- Friedelin 3,4-lactone
Catalog No.:BCN6449
CAS No.:29621-75-8
- 13-Oxo-9E,11E-octadecadienoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN8173
CAS No.:29623-29-8
Synthesis and biological evaluation of unnatural derivatives of narciclasine: 7-aza-nornarciclasine and its N-oxide.[Pubmed:25108300]
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2014 Sep 1;24(17):4236-8.
Several unnatural derivatives of Narciclasine were prepared in which the C-7 carbon was replaced with nitrogen. The 7-aza derivative and its N-oxide were prepared by the coupling of iodopicolinic acid with a conduramine unit derived chemoenzymatically from bromobenzene. Intramolecular Heck reaction was used to construct the isocarbostyryl ring system. The compounds were submitted to biological screening against cancer cell lines. Full experimental and spectra data are provided for all new compounds.
Haemanthus coccineus extract and its main bioactive component narciclasine display profound anti-inflammatory activities in vitro and in vivo.[Pubmed:25754537]
J Cell Mol Med. 2015 May;19(5):1021-32.
Haemanthus coccineus extracts (HCE) have traditionally been used to treat a variety of diseases, like febrile colds or asthma. Since new therapeutic options against inflammatory processes are still urgently needed, we aimed to pharmacologically characterise the anti-inflammatory potential of HCEin vitro and in vivo and to identify the underlying bioactive component(s). The action of HCE on oedema formation and leucocyte infiltration were analysed in two murine models of inflammation (dermal oedema induced by arachidonic acid and croton oil; kidney injury caused by unilateral ureteral obstruction). The interaction of leucocytes with endothelial cells (ECs) as well as the activation parameters of these two cell types were analysed. Moreover, the nuclear factor kappaB (NFkappaB) pathway was investigated in detail in ECs. Using different fractions of HCE, the bioactive principle was identified. In vivo, HCE (450 mg/kg orally or 2 mg/kg intraperitoneally) inhibited oedema formation, leucocyte infiltration and cytokine synthesis. In vitro, HCE (100-300 ng/ml) blocked leucocyte-EC interaction as well as the activation of isolated leucocytes (cytokine synthesis and proliferation) and of primary ECs (adhesion molecule expression). HCE suppressed NFkappaB-dependent gene transcription in the endothelium, but did not interfere with the NFkappaB activation cascade (IkappaB degradation, p65 nuclear translocation and NFkappaB DNA-binding activity). The alkaloid Narciclasine was elucidated as the bioactive compound responsible for the anti-inflammatory action of HCE. Our study highlights HCE and its main alkaloid Narciclasine as novel interesting approach for the treatment of inflammation-related disorders.
Narciclasine as well as other Amaryllidaceae isocarbostyrils are promising GTP-ase targeting agents against brain cancers.[Pubmed:22419031]
Med Res Rev. 2013 Mar;33(2):439-55.
The anticancer activity of Amaryllidaceae isocarbostyrils is well documented. At pharmacological concentrations, that is, approximately 1 muM in vitro and approximately 10 mg/kg in vivo, Narciclasine displays marked proapoptotic and cytotoxic activity, as does pancratistatin, and significant in vivo anticancer effects in various experimental models, but it is also associated with severe toxic side effects. At physiological doses, that is, approximately 50 nM in vitro and approximately 1 mg/kg in vivo, Narciclasine is not cytotoxic but cytostatic and displays marked anticancer activity in vivo in experimental models of brain cancer (including gliomas and brain metastases), but it is not associated with toxic side effects. The cytostatic activity of Narciclasine involves the impairment of actin cytoskeleton organization by targeting GTPases, including RhoA and the elongation factor eEF1A. We have demonstrated that chronic treatments of Narciclasine (1 mg/kg) significantly increased the survival of immunodeficient mice orthotopically xenografted with highly invasive human glioblastomas and apoptosis-resistant brain metastases, including melanoma- and non-small-cell-lung cancer- (NSCLC) related brain metastases. Thus, Narciclasine is a potentially promising agent for the treatment of primary brain cancers and various brain metastases. To date, efforts to develop synthetic analogs with anticancer properties superior to those of Narciclasine have failed; thus, research efforts are now focused on Narciclasine prodrugs.
Inhibition of root growth by narciclasine is caused by DNA damage-induced cell cycle arrest in lettuce seedlings.[Pubmed:24482192]
Protoplasma. 2014 Sep;251(5):1113-24.
Narciclasine (NCS) is an Amaryllidaceae alkaloid isolated from Narcissus tazetta bulbs. Its phytotoxic effects on plant growth were examined in lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) seedlings. Results showed that high concentrations (0.5-5 muM) of NCS restricted the growth of lettuce roots in a dose-dependent manner. In NCS-treated lettuce seedlings, the following changes were detected: reduction of mitotic cells and cell elongation in the mature region, inhibition of proliferation of meristematic cells, and cell cycle. Moreover, comet assay and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) assay indicated that higher levels NCS (0.5-5 muM) induced DNA damage in root cells of lettuce. The decrease in meristematic cells and increase in DNA damage signals in lettuce roots in responses to NCS are in a dose-dependent manner. NCS-induced reactive oxygen species accumulation may explain an increase in DNA damage in lettuce roots. Thus, the restraint of root growth is due to cell cycle arrest which is caused by NCS-induced DNA damage. In addition, it was also found that NCS (0.5-5 muM) inhibited the root hair development of lettuce seedlings. Further investigations on the underlying mechanism revealed that both auxin and ethylene signaling pathways are involved in the response of root hairs to NCS.
Narciclasine inhibits the responses of Arabidopsis roots to auxin.[Pubmed:22476291]
Planta. 2012 Aug;236(2):597-612.
The plant hormone auxin plays a central role in the regulation of plant growth and development, as well as in responses to environmental stimuli. Narciclasine (NCS, an Amaryllidaceae alkaloid) isolated from Narcissus tazetta bulbs has a broad range of inhibitory effects on plants. In this study, the role of NCS in responses to auxin in Arabidopsis thaliana roots was investigated. We demonstrated the inhibitory effects of NCS on auxin-inducible lateral root formation, root hair formation, primary root growth, and the expression of primary auxin-inducible genes in Arabidopsis roots using DR5::GUS reporter gene, native auxin promoters (IAA12::GUS, IAA13::GUS), and quantitative reverse transcription PCR analysis. Results also showed that NCS did not affect the expression of cytokinin-inducible ARR5::GUS reporter gene. NCS relieved the auxin-enhanced degradation of the Aux/IAA repressor modulated by the SCFTIR1 ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. In addition, NCS did not alter the auxin-stimulated interaction between IAA7/AXR2 (Aux/IAA proteins) and the F-box protein TIR1 activity of the proteasome. Taken together, these results suggest that NCS acts on the auxin signaling pathway upstream of TIR1, which modulates Aux/IAA protein degradation, and thereby affects the auxin-mediated responses in Arabidopsis roots.
Structure-activity relationship analysis of novel derivatives of narciclasine (an Amaryllidaceae isocarbostyril derivative) as potential anticancer agents.[Pubmed:19199649]
J Med Chem. 2009 Feb 26;52(4):1100-14.
Narciclasine (1) is a plant growth regulator that has been previously demonstrated to be proapoptotic to cancer cells at high concentrations (> or = 1 microM). Data generated in the present study show that Narciclasine displays potent antitumor effects in apoptosis-resistant as well as in apoptosis-sensitive cancer cells by impairing the organization of the actin cytoskeleton in cancer cells at concentrations that are not cytotoxic (IC(50) values of 30-90 nM). The current study further revealed that any chemical modification to the Narciclasine backbone generally led to compounds of variable stability, weaker activity, or even the complete loss of antiproliferative effects in vitro. However, one hemisynthetic derivative of Narciclasine, compound 7k, demonstrated by both the intravenous and oral routes higher in vivo antitumor activity in human orthotopic glioma models in mice when compared to Narciclasine at nontoxic doses. Narciclasine and compound 7k may therefore be of potential use to combat brain tumors.
Narciclasine, a plant growth modulator, activates Rho and stress fibers in glioblastoma cells.[Pubmed:19531573]
Mol Cancer Ther. 2009 Jul;8(7):1739-50.
Cell motility and resistance to apoptosis characterize glioblastoma multiforme growth and malignancy. Narciclasine, a plant growth modulator, could represent a powerful new weapon targeting the Achilles' heel of glioblastoma multiforme and may offer the potential to better combat these devastating malignancies. The in vitro effects of Narciclasine on cell proliferation, morphology, actin cytoskeleton organization, and the Rho/Rho kinase/LIM kinase/cofilin pathway and its antitumor activity in vivo have been determined in models of human glioblastoma multiforme. Narciclasine impairs glioblastoma multiforme growth by markedly decreasing mitotic rates without inducing apoptosis. The compound also modulates the Rho/Rho kinase/LIM kinase/cofilin signaling pathway, greatly increasing GTPase RhoA activity as well as inducing actin stress fiber formation in a RhoA-dependent manner. Lastly, the treatment of human glioblastoma multiforme orthotopic xenograft- bearing mice with nontoxic doses of Narciclasine significantly increased their survival. Narciclasine antitumor effects were of the same magnitude as those of temozolomide, the drug associated with the highest therapeutic benefits in treating glioblastoma multiforme patients. Our results show for the first time that Narciclasine, a plant growth modulator, activates Rho and stress fibers in glioblastoma multiforme cells and significantly increases the survival of human glioblastoma multiforme preclinical models. This statement is made despite the recognition that to date, irrespective of treatment, no single glioblastoma multiforme patient has been cured.
The Amaryllidaceae isocarbostyril narciclasine induces apoptosis by activation of the death receptor and/or mitochondrial pathways in cancer cells but not in normal fibroblasts.[Pubmed:17898872]
Neoplasia. 2007 Sep;9(9):766-76.
Our study has shown that the Amaryllidaceae isocarbostyril Narciclasine induces marked apoptosis-mediated cytotoxic effects in human cancer cells but not in normal fibroblasts by triggering the activation of the initiator caspases of the death receptor pathway (caspase-8 and caspase-10) at least in human MCF-7 breast and PC-3 prostate carcinoma cells. The formation of the Fas and death receptor 4 (DR4) death-inducing signaling complex was clearly evidenced in MCF-7 and PC-3 cancer cells. Caspase-8 was found to interact with Fas and DR4 receptors on Narciclasine treatment. However, Narciclasine-induced downstream apoptotic pathways in MCF-7 cells diverged from those in PC-3 cells, where caspase-8 directly activated effector caspases such as caspase-3 in the absence of any further release of mitochondrial proapoptotic effectors. In contrast, in MCF-7 cells, the apoptotic process was found to require an amplification step that is mitochondria-dependent, with Bid processing, release of cytochrome c, and caspase-9 activation. It is postulated that the high selectivity of Narciclasine to cancer cells might be linked, at least in part, to this activation of the death receptor pathway. Normal human fibroblasts appear approximately 250-fold less sensitive to Narciclasine, which does not induce apoptosis in these cells probably due to the absence of death receptor pathway activation.


