PD 158780Potent ErbB receptor family inhibitor CAS# 171179-06-9 |
- Calpain Inhibitor I, ALLN
Catalog No.:BCC1233
CAS No.:110044-82-1
- Calpeptin
Catalog No.:BCC2351
CAS No.:117591-20-5
- Acetyl-Calpastatin (184-210) (human)
Catalog No.:BCC2350
CAS No.:123714-50-1
- Calpain Inhibitor II, ALLM
Catalog No.:BCC1234
CAS No.:136632-32-1
- MDL 28170
Catalog No.:BCC2352
CAS No.:88191-84-8
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 171179-06-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 4707 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C14H12BrN5 | M.Wt | 330.18 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 21 mg/mL (63.60 mM; Need ultrasonic and warming) | ||
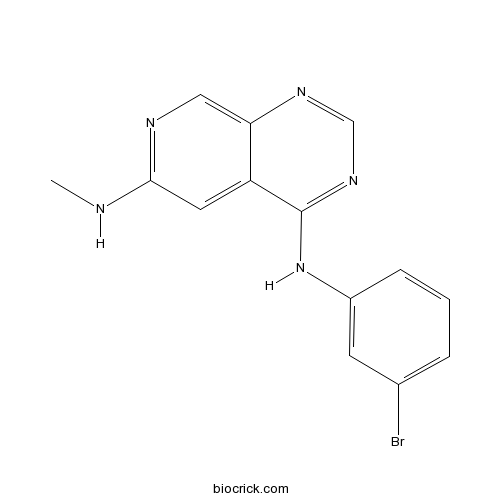
| Chemical Name | 4-N-(3-bromophenyl)-6-N-methylpyrido[3,4-d]pyrimidine-4,6-diamine | ||
| SMILES | CNC1=NC=C2C(=C1)C(=NC=N2)NC3=CC(=CC=C3)Br | ||
| Standard InChIKey | KFHMLBXBRCITHF-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C14H12BrN5/c1-16-13-6-11-12(7-17-13)18-8-19-14(11)20-10-4-2-3-9(15)5-10/h2-8H,1H3,(H,16,17)(H,18,19,20) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent inhibitor of ErbB receptor family tyrosine kinases (IC50 values are 0.008, 49 and 52 nM for EGFR, ErbB2 and ErbB2/ErbB4 respectively) that does not inhibit FGF or PDGF-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation. Induces G1 cell cycle arrest in MCF10A cells and is antiproliferative in A431 human epidermal carcinoma cells. |

PD 158780 Dilution Calculator

PD 158780 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.0287 mL | 15.1433 mL | 30.2865 mL | 60.573 mL | 75.7163 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6057 mL | 3.0287 mL | 6.0573 mL | 12.1146 mL | 15.1433 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3029 mL | 1.5143 mL | 3.0287 mL | 6.0573 mL | 7.5716 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0606 mL | 0.3029 mL | 0.6057 mL | 1.2115 mL | 1.5143 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0303 mL | 0.1514 mL | 0.3029 mL | 0.6057 mL | 0.7572 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
PD158780 is a potent EGFR family inhibitor with IC50s of 8 pM, 49, 52, 52 nM for EGFR, ErbB2, ErbB3, and ErbB4, respectively.
In Vitro:PD158780 inhibits EGF receptor autophosphorylation in A431 human epidermoid carcinoma with IC50 value of 13 nM. PD158780 is highly specific for the EGF receptor in Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts, inhibiting EGF-dependent receptor autophosphorylation and thymidine incorporation at low nanomolar concentrations while requiring micromolar levels for platelet-derived growth factor- and basic fibroblast growth factordependent processes. PD158780 inhibits heregulin-stimulated phosphorylation in the SK-BR-3 and MDAMB-453 breast carcinomas with IC50 values of 49 and 52 nM, respectively, suggesting that the compound is active against other members of the EGF receptor family[1].
In Vivo:PD158780 is active against clone formation in several breast tumors having different expression patterns of the ErbB family. PD158780 shows good therapeutic effect against the A431 epidermoid carcinoma when administered either intraperitoneally or orally. PD158780 produces measurable, significant effects against a mouse fibroblast transfected with human EGFR. PD158780 produces a significant therapeutic effect against the estrogendependent MCF-7 breast carcinoma at equitoxic dose levels[1].
References:
[1]. Fry DW, et al. Biochemical and antiproliferative properties of 4-[ar(alk)ylamino]pyridopyrimidines, a new chemical class of potent and specific epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Biochem Pharmacol. 1997 Oct 15;54(8):877-87.
- H-Ser(tBu)-OMe.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3033
CAS No.:17114-97-5
- EGLU
Catalog No.:BCC6871
CAS No.:170984-72-2
- Tetrindole mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC6763
CAS No.:170964-68-8
- Dihydroactinidiolide
Catalog No.:BCN6890
CAS No.:17092-92-1
- Donitriptan hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7742
CAS No.:170911-68-9
- Aburatubolactam A
Catalog No.:BCN1821
CAS No.:170894-24-3
- Persianone
Catalog No.:BCN7359
CAS No.:170894-20-9
- Cyasterone
Catalog No.:BCN5416
CAS No.:17086-76-9
- Sonepiprazole
Catalog No.:BCC7879
CAS No.:170858-33-0
- PNU 96415E
Catalog No.:BCC7467
CAS No.:170856-41-4
- (RS)-APICA
Catalog No.:BCC6925
CAS No.:170847-18-4
- E4CPG
Catalog No.:BCC6888
CAS No.:170846-89-6
- N-Methylquipazine dimaleate
Catalog No.:BCC6697
CAS No.:171205-17-7
- Posaconazole
Catalog No.:BCC1103
CAS No.:171228-49-2
- TAPI-1
Catalog No.:BCC5400
CAS No.:171235-71-5
- (RS)-AMPA hydrobromide
Catalog No.:BCC6926
CAS No.:171259-81-7
- Delphinidin-3-O-arabinoside chloride
Catalog No.:BCN3021
CAS No.:171370-55-1
- Ethyl 4-hydroxyphenylacetate
Catalog No.:BCN3792
CAS No.:17138-28-2
- Calcium Gluceptate
Catalog No.:BCC3743
CAS No.:17140-60-2
- Otophylloside B 4'''-O-alpha-L-cymaropyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN7511
CAS No.:171422-82-5
- Otophylloside B 4'''-O-beta-D-cymaropyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN7522
CAS No.:171422-85-8
- SLIGRL-NH2
Catalog No.:BCC3947
CAS No.:171436-38-7
- Dammarenediol II 3-O-caffeate
Catalog No.:BCN6519
CAS No.:171438-55-4
- Salprionin
Catalog No.:BCN3162
CAS No.:171439-43-3
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors. 14. Structure-activity relationships for methylamino-substituted derivatives of 4-[(3-bromophenyl)amino]-6-(methylamino)-pyrido[3,4-d]pyrimidine (PD 158780), a potent and specific inhibitor of the tyrosine kinase activity of receptors for the EGF family of growth factors.[Pubmed:9513602]
J Med Chem. 1998 Feb 26;41(5):742-51.
The 4-[(3-bromophenyl)amino]pyrido[3,4-d]pyrimidine PD 158780 is a very potent in vitro inhibitor of the tyrosine kinase activity of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) (IC50 0.08 nM), and other members of the erbB family, by competitive binding at the ATP site of these signal transduction enzymes. A series of analogues of PD 158780 bearing solubilizing functions off the 6-methylamino substituent were prepared by reaction of the 6-fluoro derivatives with appropriate amine nucleophiles. These were evaluated for their ability to inhibit the tyrosine phosphorylating action of EGF-stimulated full-length EGFR enzyme and for inhibition of autophosphorylation of the EGFR in A431 human epidermoid carcinoma cells in culture. The most effective analogues were those bearing weakly basic substituents through a secondary amine linkage, which proved water-soluble (> 10 mM) and potent (IC50S generally < 1 nM). No clear SAR could be discerned for these compounds with respect to amine base strength or the distance of the cationic center from the chromophore, suggesting that 6-substituents are in a favorable area of bulk tolerance in the enzyme binding site. More distinct SAR emerged for the ability of the compounds to inhibit EGFR autophosphorylation in A431 cells, where analogues bearing lipophilic weak bases were preferred. Representative analogues were evaluated for antitumor effectiveness against four in vivo tumor models. Significant in vivo activity was observed in estrogen-dependent MCF-7 breast and A431 epidermoid tumors. Marginal activity was seen in an EGFR-transfected tumor model, suggesting that while this cell line requires EGF for clone formation in soft agar, other growth factors may be able to replace EGF in vivo. Also, no activity was seen against the SK-OV-3 ovarian cancer model, which is known to express other EGF receptor family members (although it is not clear whether these are absolutely required for growth in vivo). While substantial growth delays were seen in A431 and MCF-7 tumor models, the treated tumors remained approximately the same size throughout therapy, suggesting that the compounds are cytostatic rather than cytotoxic under these test conditions. It remains to be determined if more prolonged therapy has cytotoxic effects in vivo, resulting in net tumor cell kill.
G1 cell cycle arrest due to the inhibition of erbB family receptor tyrosine kinases does not require the retinoblastoma protein.[Pubmed:15572027]
Exp Cell Res. 2005 Feb 1;303(1):56-67.
The erbB receptor family (EGFr, erbB-2, erbB-3, and erbB-4) consists of transmembrane glycoproteins that transduce extracellular signals to the nucleus when activated. erbB family members are widely expressed in epithelial, mesenchymal, and neuronal cells and contribute to the proliferation, differentiation, migration, and survival of these cell types. The present study evaluates the effects of erbB family signaling on cell cycle progression and the role that pRB plays in regulating this process. ErbB family RTK activity was inhibited by PD 158780 in the breast epithelial cell line MCF10A. PD 158780 (0.5 microM) inhibited EGF-stimulated and heregulin-stimulated autophosphorylation and caused a G1 cell cycle arrest within 24 h, which correlated with hypophosporylation of pRB. MCF10A cells lacking functional pRB retained the ability to arrest in G1 when treated with PD 158780. Both cell lines showed induction of p27(KIP1) protein when treated with PD 158780 and increased association of p27(KIP1) with cyclin E-CDK2. Furthermore, CDK2 kinase activity was dramatically inhibited with drug treatment. Changes in other pRB family members were noted with drug treatment, namely a decrease in p107 and an increase in p130. These findings show that the G1 arrest induced through inhibition of erbB family RTK activity does not require functional pRB.
Growth inhibition of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by EGF receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors.[Pubmed:10368634]
Anticancer Res. 1999 Mar-Apr;19(2A):919-24.
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is a malignancy of epithelial origin occurring with a high incidence in southern China and southeast Asia. Radiotherapy is the main treatment modality for NPC. No effective chemotherapy is available. Since prevention of EGF/EGFR binding by an EGFR specific monoclonal antibody suppressed the growth of NPC xenografts, we examined potential anti-NPC activity by a group of specific inhibitors of the EGFR family of tyrosine kinases. We found that HONE-T1 NPC cells expressed high levels of EGFR tyrosine kinase activity upon stimulation by EGF. The receptor tyrosine kinase activity was specifically inhibited by either reversible (PD158780) or irreversible (PD168393) inhibitors specific for EGFR family tyrosine kinases. This inhibition led to a dose-dependent suppression of anchorage-independent growth as determined by soft agar assays. A structural analog (PD159805) with no inhibitory activity against EGFR tyrosine kinase had no effect on HONE-T1 cell growth in agar. Furthermore, growth of HONE-T1 xenografts in SCID mice was also inhibited by treatment with PD158780 and PD 168393. This data provides an appealing application of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors for the treatment of nasopharyngeal carcinomas.
Biochemical and antiproliferative properties of 4-[ar(alk)ylamino]pyridopyrimidines, a new chemical class of potent and specific epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor.[Pubmed:9354588]
Biochem Pharmacol. 1997 Oct 15;54(8):877-87.
The tyrosine kinase inhibitors PD 69896, 153717, and 158780, which belong to the chemical class 4-[ar(alk)ylamino]pyridopyrimidines, have been characterized with respect to enzymology, target specificity, and antiproliferative effects in tumor cells. These compounds were competitive inhibitors with respect to ATP against purified epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor tyrosine kinase and inhibited EGF receptor autophosphorylation in A431 human epidermoid carcinoma with IC50 values of 2085, 110, and 13 nM, respectively. Onset of inhibition was immediate once cells were exposed to these compounds, whereas recovery of receptor autophosphorylation activity after the cells were washed free of the compound was dependent on inhibitory potency. Thus, full activity returned immediately after removal of PD 69896 but required 8 hr after exposure to PD 158780. PD 158780 was highly specific for the EGF receptor in Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts, inhibiting EGF-dependent receptor autophosphorylation and thymidine incorporation at low nanomolar concentrations while requiring micromolar levels for platelet-derived growth factor- and basic fibroblast growth factor-dependent processes. PD 158780 inhibited heregulin-stimulated phosphorylation in the SK-BR-3 and MDA-MB-453 breast carcinomas with IC50 values of 49 and 52 nM, respectively, suggesting that the compound was active against other members of the EGF receptor family. The antiproliferative effects of this series of compounds against A431 cells correlated precisely with the inhibitory potency against EGF receptor autophosphorylation. PD 158780 reduced clone formation in soft agar of fibroblasts transformed by EGF, EGF receptor, or the neu oncogene but not ras or raf, further demonstrating its high degree of specificity. Finally, this compound was active against clone formation in several breast tumors having different expression patterns of the erbB family, indicating an anticancer utility in tumors expressing these receptors.


