PSB 06126NTPDase 3 inhibitor CAS# 1052089-16-3 |
- PSI
Catalog No.:BCC1124
CAS No.:158442-41-2
- Salinosporamide A (NPI-0052, Marizomib)
Catalog No.:BCC2094
CAS No.:437742-34-2
- Aclacinomycin A
Catalog No.:BCC1232
CAS No.:57576-44-0
- E-64
Catalog No.:BCC1222
CAS No.:66701-25-5
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1052089-16-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 24868313 | Appearance | Powder |
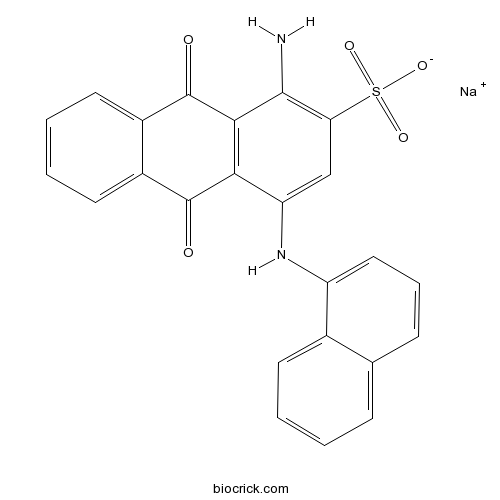
| Formula | C24H15N2NaO5S | M.Wt | 466.44 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in DMSO and to 50 mM in ethanol | ||
| Chemical Name | sodium;1-amino-4-(naphthalen-1-ylamino)-9,10-dioxoanthracene-2-sulfonate | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC=C2C(=C1)C=CC=C2NC3=CC(=C(C4=C3C(=O)C5=CC=CC=C5C4=O)N)S(=O)(=O)[O-].[Na+] | ||
| Standard InChIKey | BLOBABILSRPNHR-UHFFFAOYSA-M | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C24H16N2O5S.Na/c25-22-19(32(29,30)31)12-18(26-17-11-5-7-13-6-1-2-8-14(13)17)20-21(22)24(28)16-10-4-3-9-15(16)23(20)27;/h1-12,26H,25H2,(H,29,30,31);/q;+1/p-1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Nucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase 3 (NTPDase 3) inhibitor. Reported to inhibit rat NTPDase 3 at low micromolar concentrations and display selectivity over NTPDase 1 and NTPDase 2. |

PSB 06126 Dilution Calculator

PSB 06126 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1439 mL | 10.7195 mL | 21.439 mL | 42.878 mL | 53.5975 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4288 mL | 2.1439 mL | 4.2878 mL | 8.5756 mL | 10.7195 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2144 mL | 1.0719 mL | 2.1439 mL | 4.2878 mL | 5.3597 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0429 mL | 0.2144 mL | 0.4288 mL | 0.8576 mL | 1.0719 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0214 mL | 0.1072 mL | 0.2144 mL | 0.4288 mL | 0.536 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- PSB 0739
Catalog No.:BCC6095
CAS No.:1052087-90-7
- Q94 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6281
CAS No.:1052076-77-3
- 9-Oxoageraphorone
Catalog No.:BCN5866
CAS No.:105181-06-4
- AC 264613
Catalog No.:BCC3952
CAS No.:1051487-82-1
- GSK1349572 sodiuM salt
Catalog No.:BCC6407
CAS No.:1051375-19-9
- S/GSK1349572
Catalog No.:BCC2138
CAS No.:1051375-16-6
- GSK744 (S/GSK1265744)
Catalog No.:BCC3888
CAS No.:1051375-10-0
- Ligucyperonol
Catalog No.:BCN6638
CAS No.:105108-20-1
- Moellendorffilin
Catalog No.:BCN3546
CAS No.:105099-87-4
- Ro 51
Catalog No.:BCC6157
CAS No.:1050670-85-3
- 1-Ketoaethiopinone
Catalog No.:BCN3219
CAS No.:105062-36-0
- GPR120 modulator 2
Catalog No.:BCC1600
CAS No.:1050506-87-0
- WEB 2086
Catalog No.:BCC7335
CAS No.:105219-56-5
- Virosine B
Catalog No.:BCN6742
CAS No.:1052228-70-2
- SBE 13 HCl
Catalog No.:BCC6408
CAS No.:1052532-15-6
- 5'-Methoxylariciresinol
Catalog No.:BCN7012
CAS No.:105256-12-0
- 3'-Deoxy-4-O-methylepisappanol
Catalog No.:BCN3676
CAS No.:1052714-12-1
- Ganodermatriol
Catalog No.:BCC8177
CAS No.:105300-28-5
- Aloeresin D
Catalog No.:BCN2850
CAS No.:105317-67-7
- Neocaesalpin O
Catalog No.:BCN7266
CAS No.:1053189-53-9
- 5,7,4'-Tri-O-methylcatechin
Catalog No.:BCN3951
CAS No.:105330-59-4
- Tanshinlactone
Catalog No.:BCN5867
CAS No.:105351-70-0
- Tyrphostin 9
Catalog No.:BCC4471
CAS No.:10537-47-0
- Shuterin
Catalog No.:BCN8068
CAS No.:105377-77-3
The A2b adenosine receptor antagonist PSB-603 promotes oxidative phosphorylation and ROS production in colorectal cancer cells via adenosine receptor-independent mechanism.[Pubmed:27693637]
Cancer Lett. 2016 Dec 1;383(1):135-143.
PURPOSE: Adenosine is a multifaceted regulator of tumor progression. It modulates immune cell activity as well as acting directly on tumor cells. The A2b adenosine receptor (A2b-AR) is thought to be an important mediator of these effects. In this study we sought to analyze the contribution of the A2b-AR to the behavior of colorectal cancer cells. PRINCIPAL RESULTS: The A2b-AR antagonist PSB-603 changed cellular redox state without affecting cellular viability. Quantification of cellular bioenergetics demonstrated that PSB-603 increased basal oxygen consumption rates, indicative of enhanced mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation. Unexpectedly, pharmacological and genetic approaches to antagonize AR-related signalling of PSB-603 did not abolish the response, suggesting that it was AR-independent. PSB-603 also induced acute increases in reactive oxygen species, and PSB-603 synergized with chemotherapy treatment to increase colorectal cancer cell death, consistent with the known link between cellular metabolism and chemotherapy response. MAJOR CONCLUSIONS: PSB-603 alters cellular metabolism in colorectal cancer cells and increases their sensitivity to chemotherapy. Although requiring more mechanistic insight into its A2b-AR-independent activity, our results show that PSB-603 may have clinical value as an anti-colorectal cancer therapeutic.
Production, purification, and characterization of metalloprotease from Candida kefyr 41 PSB.[Pubmed:27717786]
Int J Biol Macromol. 2017 Jan;94(Pt A):106-113.
A thermostable metalloprotease, produced from an environmental strain of Candida kefyr 41 PSB, was purified 16 fold with a 60% yield by cold ethanol precipitation and affinity chromatography (bentonite-acrylamide-cysteine microcomposite). The purified enzyme appeared as a single protein band at 43kDa. Its optimum pH and temperature points were found to be 7.0 and 105 degrees C, respectively. Km and Vmax values of the enzyme were determined to be 3.5mg/mL and 4.4mumolmL(-1)min(-1), 1.65mg/mL and 6.1mumolmL(-1)min(-1), using casein and gelatine as the substrates, respectively. The activity was inhibited by using ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA), indicating that the enzyme was a metalloprotease. Stability of the enzyme was investigated by using thermodynamic and kinetic parameters. The thermal inactivation profile of the enzyme conformed to the first order kinetics. The half life of the enzyme at 95, 105, 115, 125 and 135 degrees C was 1310, 610, 220, 150, and 86min, respectively.
A novel PSB-EDI system for high ammonia wastewater treatment, biomass production and nitrogen resource recovery: PSB system.[Pubmed:27508366]
Water Sci Technol. 2016;74(3):616-24.
A novel process coupling photosynthetic bacteria (PSB) with electrodeionization (EDI) treatment was proposed to treat high ammonia wastewater and recover bio-resources and nitrogen. The first stage (PSB treatment) was used to degrade organic pollutants and accumulate biomass, while the second stage (EDI) was for nitrogen removal and recovery. The first stage was the focus in this study. The results showed that using PSB to transform organic pollutants in wastewater into biomass was practical. PSB could acclimatize to wastewater with a chemical oxygen demand (COD) of 2,300 mg/L and an ammonia nitrogen (NH4(+)-N) concentration of 288-4,600 mg/L. The suitable pH was 6.0-9.0, the average COD removal reached 80%, and the biomass increased by an average of 9.16 times. The wastewater COD removal was independent of the NH4(+)-N concentration. Moreover, the PSB functioned effectively when the inoculum size was only 10 mg/L. The PSB-treated wastewater was then further handled in an EDI system. More than 90% of the NH4(+)-N was removed from the wastewater and condensed in the concentrate, which could be used to produce nitrogen fertilizer. In the whole system, the average NH4(+)-N removal was 94%, and the average NH4(+)-N condensing ratio was 10.0.
Natural light-micro aerobic condition for PSB wastewater treatment: a flexible, simple, and effective resource recovery wastewater treatment process.[Pubmed:28278105]
Environ Technol. 2018 Jan;39(1):74-82.
Photosynthetic bacteria (PSB) have two sets of metabolic pathways. They can degrade pollutants through light metabolic under light-anaerobic or oxygen metabolic pathways under dark-aerobic conditions. Both metabolisms function under natural light-microaerobic condition, which demands less energy input. This work investigated the characteristics of PSB wastewater treatment process under that condition. Results showed that PSB had very strong adaptability to chemical oxygen demand (COD) concentration; with F/M of 5.2-248.5 mg-COD/mg-biomass, the biomass increased three times and COD removal reached above 91.5%. PSB had both advantages of oxygen metabolism in COD removal and light metabolism in resource recovery under natural light-microaerobic condition. For pollutants' degradation, COD, total organic carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus removal reached 96.2%, 91.0%, 70.5%, and 92.7%, respectively. For resource recovery, 74.2% of C in wastewater was transformed into biomass. Especially, coexistence of light and oxygen promote N recovery ratio to 70.9%, higher than with the other two conditions. Further, 93.7% of N-removed was synthesized into biomass. Finally, CO2 emission reduced by 62.6% compared with the traditional process. PSB wastewater treatment under this condition is energy-saving, highly effective, and environment friendly, and can achieve pollution control and resource recovery.


