Psora 4Kv1.3 blocker CAS# 724709-68-6 |
- MLN9708
Catalog No.:BCC2091
CAS No.:1201902-80-8
- MG-132
Catalog No.:BCC1227
CAS No.:133407-82-6
- Clasto-Lactacystin β-lactone
Catalog No.:BCC1224
CAS No.:154226-60-5
- Bortezomib (PS-341)
Catalog No.:BCC1238
CAS No.:179324-69-7
- CEP-18770
Catalog No.:BCC2093
CAS No.:847499-27-8
- AM 114
Catalog No.:BCC3589
CAS No.:856849-35-9
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 724709-68-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 6603977 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C21H18O4 | M.Wt | 334.37 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 50 mM in DMSO and to 10 mM in ethanol | ||
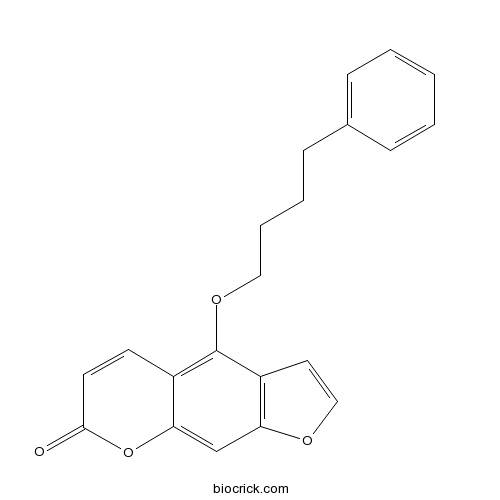
| Chemical Name | 4-(4-phenylbutoxy)furo[3,2-g]chromen-7-one | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC=C(C=C1)CCCCOC2=C3C=CC(=O)OC3=CC4=C2C=CO4 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | JJAWGNIQEOFURP-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C21H18O4/c22-20-10-9-16-19(25-20)14-18-17(11-13-23-18)21(16)24-12-5-4-8-15-6-2-1-3-7-15/h1-3,6-7,9-11,13-14H,4-5,8,12H2 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent KV1.3 channel blocker (EC50 = 3 nM). Preferentially binds the C-type inactivated state of the channel, similar to the activity of CP 339818. Displays 17- to 70-fold selectivity over closely-related KV1 channels (KV1, KV2, KV4 and KV7); exhibits activity at KV1.5 (IC50 = 7.7 nM). Suppresses proliferation of human and rat myelin-specific effector memory T cells (EC50 values are 25 and 60 nM respectively). |

Psora 4 Dilution Calculator

Psora 4 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.9907 mL | 14.9535 mL | 29.907 mL | 59.814 mL | 74.7675 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5981 mL | 2.9907 mL | 5.9814 mL | 11.9628 mL | 14.9535 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2991 mL | 1.4953 mL | 2.9907 mL | 5.9814 mL | 7.4767 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0598 mL | 0.2991 mL | 0.5981 mL | 1.1963 mL | 1.4953 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0299 mL | 0.1495 mL | 0.2991 mL | 0.5981 mL | 0.7477 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
EC50: 3 nM
Psora 4 is a Kv1.3 blocker.
The voltage-gated Kv1.3 channel and the Ca2+-activated IKCa1 channel has been reported to promote and sustain Ca2+ signaling in human T cells via providing the driving force for Ca2+ entry through voltage-independent Ca2+ channels. Selective blockade of Kv1.3 and/or IKCa1 leads to membrane depolarization, reduced Ca2+ entry, as well as diminished cytokine proliferation and production.
In vitro: Psora-4 could block Kv1.3 in a dose-dependent manner. Psora-4 was found to be the most potent small-molecule Kv1.3 blocker known. Psora-4 exhibited 17- to 70-fold selectivity for Kv1.3 over Kv1-family channels including Kv1.1, Kv1.2, Kv1.4, and Kv1.7 and also showed no effect on human ether-a-go-go-related channel, Kv3.1, or the neuronal NaV1.2 channel. In addition, Psora-4 could suppress the proliferation of rat and human myelin-specific effector memory T cells with EC50 values of 60 and 25 nM, respectively, without persistently suppressing the peripheral blood naive and central memory T cells [1].
In vivo: In a study of in vivo toxicity in rats, Psora-4 was found not to show any signs of acute toxicity following five daily subcutaneous injections at 33 mg/kg body weight [1].
Clinical trial: N/A
Reference:
[1] Vennekamp J,Wulff H,Beeton C,Calabresi PA,Grissmer S,Hnsel W,Chandy KG. Kv1.3-blocking 5-phenylalkoxypsoralens: a new class of immunomodulators. Mol Pharmacol.2004 Jun;65(6):1364-74.
- Praeruptorin C
Catalog No.:BCN4991
CAS No.:72463-77-5
- 11-Hydroxytephrosin
Catalog No.:BCN4861
CAS No.:72458-85-6
- Aniracetam
Catalog No.:BCC4219
CAS No.:72432-10-1
- Miglitol
Catalog No.:BCC4921
CAS No.:72432-03-2
- Acifran
Catalog No.:BCC7170
CAS No.:72420-38-3
- Aflatoxin G2
Catalog No.:BCC9215
CAS No.:7241-98-7
- Meglumine Metrizoate
Catalog No.:BCC5631
CAS No.:7241-11-4
- 6-Methoxydihydrosanguinarine
Catalog No.:BCN7581
CAS No.:72401-54-8
- X-Gal
Catalog No.:BCC1211
CAS No.:7240-90-6
- Oxacillin sodium monohydrate
Catalog No.:BCC4816
CAS No.:7240-38-2
- Yuheinoside
Catalog No.:BCN4279
CAS No.:72396-01-1
- 2,3-Dihydrobellendine
Catalog No.:BCN1896
CAS No.:72362-47-1
- STF 31
Catalog No.:BCC7938
CAS No.:724741-75-7
- Pirarubicin
Catalog No.:BCC5092
CAS No.:72496-41-4
- Methyl vanillate glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN4033
CAS No.:72500-11-9
- Felodipine
Catalog No.:BCC4402
CAS No.:72509-76-3
- Lycobetaine
Catalog No.:BCN8313
CAS No.:72510-04-4
- Specioside
Catalog No.:BCN4280
CAS No.:72514-90-0
- Paeonolide
Catalog No.:BCN2805
CAS No.:72520-92-4
- XCT790
Catalog No.:BCC5121
CAS No.:725247-18-7
- Polygonal
Catalog No.:BCN4281
CAS No.:72537-20-3
- 6-chloro-9h-fluoren-2-amine
Catalog No.:BCC9231
CAS No.:7254-05-9
- GIP (1-39)
Catalog No.:BCC5890
CAS No.:725474-97-5
- Ceftazidime
Catalog No.:BCC5274
CAS No.:72558-82-8
Psora-4, a Kv1.3 Blocker, Enhances Differentiation and Maturation in Neural Progenitor Cells.[Pubmed:25976092]
CNS Neurosci Ther. 2015 Jul;21(7):558-67.
AIM: The self-repair ability of neural progenitor cells (NPCs) has been found to be activated and protected in several therapies helpful in multiple sclerosis (MS), an inflammatory demyelinating disease of the CNS. As a potential therapeutic target in MS, the role of the ion channel Kv1.3 in NPC self-repair has received limited attention. The aim of this study was to explore the effects of a selective Kv1.3 blocker on NPC neuronal differentiation and maturation. METHODS: A small-molecule selective blocker for Kv1.3, Psora-4, was added to the differentiation medium of cultured mouse NPCs to assess its effect on NPC differentiation efficiency. Both a polypeptide Kv1.3 blocker and Kv1.3-specific RNA interference were used in parallel experiments. Further, the maturity of newborn neurons in the presence of Psora-4 was measured both by morphological analysis and by whole-cell patch clamping. RESULTS: Psora-4 induced a significant increase in the percentage of neurons. Knockdown of Kv1.3 in NPCs also promoted neuronal differentiation. Both morphological and electrophysiological analyses suggested that NPC-derived neurons in the presence of Psora-4 were more mature. CONCLUSION: Our studies reveal a crucial role for the ion channel Kv1.3 in the regulation of NPC differentiation and maturation, making Psora-4 a promising candidate molecule for MS treatment.
Voltage-gated potassium channel Kv1.3 regulates GLUT4 trafficking to the plasma membrane via a Ca2+-dependent mechanism.[Pubmed:16403947]
Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2006 Feb;290(2):C345-51.
Kv1.3 is a voltage-gated K(+) channel expressed in insulin-sensitive tissues. We previously showed that gene inactivation or pharmacological inhibition of Kv1.3 channel activity increased peripheral insulin sensitivity independently of body weight by augmenting the amount of GLUT4 at the plasma membrane. In the present study, we further examined the effect Kv1.3 on GLUT4 trafficking and tested whether it occurred via an insulin-dependent pathway. We found that Kv1.3 inhibition by margatoxin (MgTX) stimulated glucose uptake in adipose tissue and skeletal muscle and that the effect of MgTX on glucose transport was additive to that of insulin. Furthermore, whereas the increase in uptake was wortmannin insensitive, it was completely inhibited by dantrolene, a blocker of Ca(2+) release from intracellular Ca(2+) stores. In white adipocytes in primary culture, channel inhibition by Psora-4 increased GLUT4 translocation to the plasma membrane. In these cells, GLUT4 protein translocation was unaffected by the addition of wortmannin but was significantly inhibited by dantrolene. Channel inhibition depolarized the membrane voltage and led to sustained, dantrolene-sensitive oscillations in intracellular Ca(2+) concentration. These results indicate that the apparent increase in insulin sensitivity observed in association with inhibition of Kv1.3 channel activity is mediated by an increase in GLUT4 protein at the plasma membrane, which occurs largely through a Ca(2+)-dependent process.
Design of PAP-1, a selective small molecule Kv1.3 blocker, for the suppression of effector memory T cells in autoimmune diseases.[Pubmed:16099841]
Mol Pharmacol. 2005 Nov;68(5):1254-70.
The lymphocyte K+ channel Kv1.3 constitutes an attractive pharmacological target for the selective suppression of terminally differentiated effector memory T (TEM) cells in T cell-mediated autoimmune diseases, such as multiple sclerosis and type 1 diabetes. Unfortunately, none of the existing small-molecule Kv1.3 blockers is selective, and many of them, such as correolide, 4-phenyl-4-[3-(methoxyphenyl)-3-oxo-2-azapropyl]cyclohexanone, and our own compound Psora-4 inhibit the cardiac K+ channel Kv1.5. By further exploring the structure-activity relationship around Psora-4 through a combination of traditional medicinal chemistry and whole-cell patch-clamp, we identified a series of new phenoxyalkoxypsoralens that exhibit 2- to 50-fold selectivity for Kv1.3 over Kv1.5, depending on their exact substitution pattern. The most potent and "drug-like" compound of this series, 5-(4-phenoxybutoxy)psoralen (PAP-1), blocks Kv1.3 in a use-dependent manner, with a Hill coefficient of 2 and an EC50 of 2 nM, by preferentially binding to the C-type inactivated state of the channel. PAP-1 is 23-fold selective over Kv1.5, 33- to 125-fold selective over other Kv1-family channels, and 500- to 7500-fold selective over Kv2.1, Kv3.1, Kv3.2, Kv4.2, HERG, calcium-activated K+ channels, Na+,Ca2+, and Cl- channels. PAP-1 does not exhibit cytotoxic or phototoxic effects, is negative in the Ames test, and affects cytochrome P450-dependent enzymes only at micromolar concentrations. PAP-1 potently inhibits the proliferation of human TEM cells and suppresses delayed type hypersensitivity, a TEM cell-mediated reaction, in rats. PAP-1 and several of its derivatives therefore constitute excellent new tools to further explore Kv1.3 as a target for immunosuppression and could potentially be developed into orally available immunomodulators.
Kv1.3-blocking 5-phenylalkoxypsoralens: a new class of immunomodulators.[Pubmed:15155830]
Mol Pharmacol. 2004 Jun;65(6):1364-74.
The lymphocyte potassium channel Kv1.3 is widely regarded as a promising new target for immunosuppression. To identify a potent small-molecule Kv1.3 blocker, we synthesized a series of 5-phenylalkoxypsoralens and tested them by whole-cell patch clamp. The most potent compound of this series, 5-(4-phenylbutoxy)psoralen (Psora-4), blocked Kv1.3 in a use-dependent manner, with a Hill coefficient of 2 and an EC50 value of 3 nM, by preferentially binding to the C-type inactivated state of the channel. Psora-4 is the most potent small-molecule Kv1.3 blocker known. It exhibited 17- to 70-fold selectivity for Kv1.3 over closely related Kv1-family channels (Kv1.1, Kv1.2, Kv1.4, and Kv1.7) with the exception of Kv1.5 (EC50, 7.7 nM) and showed no effect on human ether-a-go-go-related channel, Kv3.1, the calcium-activated K+ channels (IKCa1, SK1-SK3, and BKCa), or the neuronal NaV1.2 channel. In a test of in vivo toxicity in rats, Psora-4 did not display any signs of acute toxicity after five daily subcutaneous injections at 33 mg/kg body weight. Psora-4 selectively suppressed the proliferation of human and rat myelin-specific effector memory T cells with EC50 values of 25 and 60 nM, respectively, without persistently suppressing peripheral blood naive and central memory T cells. Because autoantigen-specific effector memory T cells contribute to the pathogenesis of T cell-mediated autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis, Psora-4 and other Kv1.3 blockers may be useful as immunomodulators for the therapy of autoimmune disorders.


