Sodium bicarbonateCAS# 144-55-8 |
- Tiratricol
Catalog No.:BCC4738
CAS No.:51-24-1
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 144-55-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 516892 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | NaHCO3 | M.Wt | 84.01 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 1000 mM in water | ||
| Chemical Name | sodium;hydrogen carbonate | ||
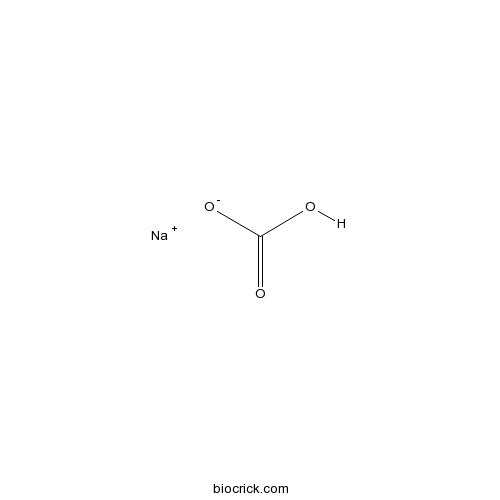
| SMILES | C(=O)(O)[O-].[Na+] | ||
| Standard InChIKey | UIIMBOGNXHQVGW-UHFFFAOYSA-M | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/CH2O3.Na/c2-1(3)4;/h(H2,2,3,4);/q;+1/p-1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Commonly used laboratory reagent |

Sodium bicarbonate Dilution Calculator

Sodium bicarbonate Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 11.9033 mL | 59.5167 mL | 119.0334 mL | 238.0669 mL | 297.5836 mL |
| 5 mM | 2.3807 mL | 11.9033 mL | 23.8067 mL | 47.6134 mL | 59.5167 mL |
| 10 mM | 1.1903 mL | 5.9517 mL | 11.9033 mL | 23.8067 mL | 29.7584 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.2381 mL | 1.1903 mL | 2.3807 mL | 4.7613 mL | 5.9517 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.119 mL | 0.5952 mL | 1.1903 mL | 2.3807 mL | 2.9758 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Sodium barbital
Catalog No.:BCN2160
CAS No.:144-02-5
- CTX0294885
Catalog No.:BCC6396
CAS No.:1439934-41-4
- Jaceidin triacetate
Catalog No.:BCN6245
CAS No.:14397-69-4
- CB-839
Catalog No.:BCC5493
CAS No.:1439399-58-2
- M40
Catalog No.:BCC7686
CAS No.:143896-17-7
- Elacridar hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1547
CAS No.:143851-98-3
- CC-401 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1458
CAS No.:1438391-30-0
- 2,24-Dihydroxyursolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN6244
CAS No.:143839-02-5
- Fmoc-Trp(Boc)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3558
CAS No.:143824-78-6
- 22-Dehydroclerosterol glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN6243
CAS No.:143815-99-0
- 13-Epimanool
Catalog No.:BCN4862
CAS No.:1438-62-6
- SB 200646 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5751
CAS No.:143797-62-0
- Oxalic acid
Catalog No.:BCN8515
CAS No.:144-62-7
- Zeaxanthin
Catalog No.:BCN2380
CAS No.:144-68-3
- Sulfathiazole sodium
Catalog No.:BCC5207
CAS No.:144-74-1
- Sulfamethizole
Catalog No.:BCC4856
CAS No.:144-82-1
- Sulfapyridine
Catalog No.:BCC4729
CAS No.:144-83-2
- Sodium Nitroprusside
Catalog No.:BCC4844
CAS No.:14402-89-2
- BRD73954
Catalog No.:BCC5652
CAS No.:1440209-96-0
- Piclamilast
Catalog No.:BCC6215
CAS No.:144035-83-6
- 6-O-Syringoylajugol
Catalog No.:BCN6246
CAS No.:144049-72-9
- Febuxostat
Catalog No.:BCC2556
CAS No.:144060-53-7
- Deltarasin
Catalog No.:BCC1524
CAS No.:1440898-61-2
- Deltarasin hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4270
CAS No.:1440898-82-7
The Reproducibility of Blood Acid Base Responses in Male Collegiate Athletes Following Individualised Doses of Sodium Bicarbonate: A Randomised Controlled Crossover Study.[Pubmed:28229390]
Sports Med. 2017 Oct;47(10):2117-2127.
BACKGROUND: Current evidence suggests Sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) should be ingested based upon the individualised alkalotic peak of either blood pH or bicarbonate (HCO3(-)) because of large inter-individual variations (10-180 min). If such a strategy is to be practical, the blood analyte response needs to be reproducible. OBJECTIVE: This study aimed to evaluate the degree of reproducibility of both time to peak (TTP) and absolute change in blood pH, HCO3(-) and sodium (Na(+)) following acute NaHCO3 ingestion. METHODS: Male participants (n = 15) with backgrounds in rugby, football or sprinting completed six randomised treatments entailing ingestion of two doses of 0.2 g.kg(-1) body mass (BM) NaHCO3 (SBC2a and b), two doses of 0.3 g.kg(-1) BM NaHCO3 (SBC3a and b) or two control treatments (CON1a and b) on separate days. Blood analysis included pH, HCO3(-) and Na(+) prior to and at regular time points following NaHCO3 ingestion over a 3-h period. RESULTS: HCO3(-) displayed greater reproducibility than pH in intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) analysis for both TTP (HCO3(-) SBC2 r = 0.77, P = 0.003; SBC3 r = 0.94, P < 0.001; pH SBC2 r = 0.62, P = 0.044; SBC3 r = 0.71, P = 0.016) and absolute change (HCO3(-) SBC2 r = 0.89, P < 0.001; SBC3 r = 0.76, P = 0.008; pH SBC2 r = 0.84, P = 0.001; SBC3 r = 0.62, P = 0.041). CONCLUSION: Our results indicate that both TTP and absolute change in HCO3(-) is more reliable than pH. As such, these data provide support for an individualised NaHCO3 ingestion strategy to consistently elicit peak alkalosis before exercise. Future work should utilise an individualised NaHCO3 ingestion strategy based on HCO3(-) responses and evaluate effects on exercise performance.
Effectiveness of sodium bicarbonate combined with hydrogen peroxide and CPP-ACPF in whitening and microhardness of enamel.[Pubmed:28298972]
J Clin Exp Dent. 2017 Mar 1;9(3):e344-e350.
BACKGROUND: This study investigated the effects of Sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) combined with 1.5% hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and casein phosphopeptide amorphous calcium phosphate fluoride (CPP-ACPF) on color and microhardness of enamel. MATERIAL AND METHODS: Seventy-five bovine incisors were immersed in a tea solution for 7.5 days. The specimens were randomly divided into five groups according to the whitening agent applied: 1) 94% NaHCO3, 2) a blend of 94% NaHCO3 and CPP-ACPF, 3) a blend of 94% NaHCO3 and 1.5% H2O2, 4) a blend of 94% NaHCO3, 1.5% H2O2 and CPP-ACPF, 5) control. The whitening procedure was performed for 10 times over 10 days. At each day, the buccal surfaces were covered with whitening agents for 5 minutes and then brushed for 30 seconds. After the 10 days, the teeth were again immersed in a tea solution for 10 minutes. Color assessment was performed at baseline (T1), after the first staining process (T2), after the whitening procedure (T3), and after the second staining process (T4). Finally, the specimens were subjected to microhardness test. RESULTS: There was a statistically significant difference in the color change between T2 and T3 stages among the study groups (p<0.05), with the greatest improvement observed in group 4. Microhardness was significantly greater in groups 2 and 4, as compared to the other groups (p<0.05). CONCLUSIONS: The combination of 94% NaHCO3, 1.5% H2O2 and CPP-ACPF was effective in improving color and microhardness of teeth with extrinsic stains and could be recommended in the clinical situation.
Cardiotoxicity of tricyclic antidepressant treated by 2650 mEq sodium bicarbonate: A case report.[Pubmed:28228939]
JRSM Cardiovasc Dis. 2016 Dec 1;5:2048004016682178.
Poisoning with tricyclic antidepressants is an important cause of drug-related self-poisoning in the developed world and a very common cause of poisoning and mortality in developing countries. Electrocardiographic manifestations of most tricyclic antidepressant-poisoned patients resolve by the administration of 1-2 mEq/kg of Sodium bicarbonate. Some rare cases have been reported who have been resistant to the long-term or high doses of bicarbonate administration. We present a case of acute tricyclic antidepressant toxicity referring with status epilepticus, hypotension, and refractory QRS complex widening that resolved after the intravenous administration of 2650 mEq Sodium bicarbonate.
Molecular characterization of Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) sodium bicarbonate cotransporter (NBC) and its role in response to pH stress.[Pubmed:28257848]
Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017 May;64:226-233.
The Sodium bicarbonate cotransporter (NBC) is an integral membrane ion transporter that can transport HCO3(-) (or a related species, such as CO3(2-)) across the plasma membrane. Previous researches revealed that NBC might play an important role in the regulation of intracellular pH in vertebrates. In the present study, an NBC cDNA was identified from Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) and designated as Lv-NBC. The full-length Lv-NBC cDNA is 4479 bp in size, containing a 5'-untranslated region (UTR) of 59 bp, a 3'-UTR of 835 bp and an open reading frame (ORF) of 3585 bp that encodes a protein of 1194 amino acids with a deduced molecular weight of 134.34 kDa. The Lv-NBC protein contains two functional domains (Band_3_cyto and HCO3_cotransp) and twelve transmembrane (TM) domains. Expression of the Lv-NBC mRNA was ubiquitously detected in all selected tissues, with the highest level in the gill. By in situ hybridization (ISH) with Digoxigenin-labeled probe, the Lv-NBC positive cells were shown mainly located in the secondary gill filaments. After low or high pH challenge, the transcript levels of Lv-NBC in the gill were found to be up-regulated. After knockdown of the Lv-NBC level by siRNA, the mortality of shrimp significantly increased under pH stress. Our study, as a whole, may provide evidences for the role of NBC in shrimp responding to pH stress, and give a new insight of the acid/base homeostasis mechanism in crustaceans.


