Tenuifoliside ACAS# 139726-35-5 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 139726-35-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 46933844 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C31H38O17 | M.Wt | 682.6 |
| Type of Compound | Phenylpropanoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
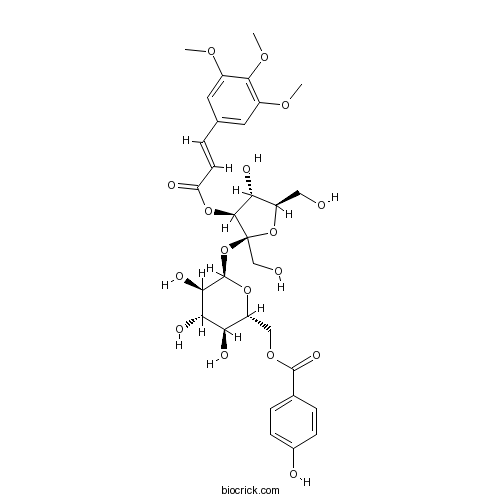
| Chemical Name | [(2R,3S,4S,5R,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-[(2S,3S,4R,5R)-4-hydroxy-2,5-bis(hydroxymethyl)-3-[(E)-3-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-enoyl]oxyoxolan-2-yl]oxyoxan-2-yl]methyl 4-hydroxybenzoate | ||
| SMILES | COC1=CC(=CC(=C1OC)OC)C=CC(=O)OC2C(C(OC2(CO)OC3C(C(C(C(O3)COC(=O)C4=CC=C(C=C4)O)O)O)O)CO)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | BBUQNXDJRVCZTI-FNUXIAMKSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C31H38O17/c1-41-18-10-15(11-19(42-2)27(18)43-3)4-9-22(35)46-28-24(37)20(12-32)47-31(28,14-33)48-30-26(39)25(38)23(36)21(45-30)13-44-29(40)16-5-7-17(34)8-6-16/h4-11,20-21,23-26,28,30,32-34,36-39H,12-14H2,1-3H3/b9-4+/t20-,21-,23-,24-,25+,26-,28+,30-,31+/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Tenuifoliside A has anti-apoptotic,neuroprotective,and anti-inflammatory effects, it inhibits the NF-κB and MAPK pathways. |
| Targets | NO | NOS | PGE | COX | TNF-α | p65 | NF-kB | IkB | MAPK | JNK | ERK | PI3K | Akt | IKK |
| In vitro | The inhibition of JNK MAPK and NF-κB signaling by tenuifoliside A isolated from Polygala tenuifolia in lipopolysaccharide-induced macrophages is associated with its anti-inflammatory effect.[Pubmed: 24076326]Eur J Pharmacol. 2013 Dec 5;721(1-3):267-76.The root of Polygala tenuifolia Willd. (Polygalaceae) is well known for its use in the treatment of neurasthenia, amnesia, and inflammation. Plant-derived natural medicines for the management of depression: an overview of mechanisms of action.[Pubmed: 25719303]Rev Neurosci. 2015;26(3):305-21.Depression is a serious widespread psychiatric disorder that affects approximately 17% of people all over the world. Exploring the neurological mechanisms of the antidepressant activity of plant-derived agents could have a crucial role in developing natural drugs for the management of depression. |
| In vivo | Potential antidepressant properties of Radix Polygalae (Yuan Zhi).[Pubmed: 20541923]Phytomedicine. 2010 Aug;17(10):794-9.Radix Polygalae ("Yuan Zhi", the roots of Polygala tenuifolia Willd., YZ) is an important herb used in traditional Chinese medicine to mediate depression. |
| Kinase Assay | Effect of Tenuifoliside A isolated from Polygala tenuifolia on the ERK and PI3K pathways in C6 glioma cells.[Pubmed: 24877714]Phytomedicine. 2014 Sep 15;21(10):1178-88.Tenuifoliside A (TFSA) is a bioactive oligosaccharide ester component of Polygala tenuifolia Wild, a traditional Chinese medicine which was used to manage mental disorders effectively. The neuroprotective and anti-apoptotic effects of Tenuifoliside A have been demonstrated in our previous studies. |

Tenuifoliside A Dilution Calculator

Tenuifoliside A Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.465 mL | 7.3249 mL | 14.6499 mL | 29.2997 mL | 36.6247 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.293 mL | 1.465 mL | 2.93 mL | 5.8599 mL | 7.3249 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1465 mL | 0.7325 mL | 1.465 mL | 2.93 mL | 3.6625 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0293 mL | 0.1465 mL | 0.293 mL | 0.586 mL | 0.7325 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0146 mL | 0.0732 mL | 0.1465 mL | 0.293 mL | 0.3662 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Isodunnianol
Catalog No.:BCN6213
CAS No.:139726-30-0
- Dunnianol
Catalog No.:BCN6212
CAS No.:139726-29-7
- BS-181 HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2537
CAS No.:1397219-81-6
- Yunnanxane
Catalog No.:BCN6702
CAS No.:139713-81-8
- Amphotericin B
Catalog No.:BCN2564
CAS No.:1397-89-3
- Gardenine
Catalog No.:BCN6211
CAS No.:139682-36-3
- EPZ005687
Catalog No.:BCC2219
CAS No.:1396772-26-1
- CGP 52432
Catalog No.:BCC6989
CAS No.:139667-74-6
- PR 39 (porcine)
Catalog No.:BCC5856
CAS No.:139637-11-9
- Purotoxin 1
Catalog No.:BCC6333
CAS No.:1396322-38-5
- 3-Bromoisonicotinic Acid
Catalog No.:BCC8368
CAS No.:13959-02-9
- Epicannabidiol hydrate
Catalog No.:BCN6207
CAS No.:139561-95-8
- Tenuifoliside B
Catalog No.:BCC9251
CAS No.:139726-36-6
- tenuifoliside C
Catalog No.:BCN8299
CAS No.:139726-37-7
- Sildenafil
Catalog No.:BCC1947
CAS No.:139755-83-2
- Cucurbitacin E-2-O-Glucoside
Catalog No.:BCC8156
CAS No.:1398-78-3
- Milameline hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7427
CAS No.:139886-04-7
- 3,6'-Disinapoyl sucrose
Catalog No.:BCN2719
CAS No.:139891-98-8
- Globularin
Catalog No.:BCN6215
CAS No.:1399-49-1
- Drahebenine
Catalog No.:BCN7044
CAS No.:1399049-43-4
- Alpinone 3-acetate
Catalog No.:BCN7768
CAS No.:139906-49-3
- Palbinone
Catalog No.:BCN3930
CAS No.:139954-00-0
- Cinnamic acid
Catalog No.:BCN6217
CAS No.:140-10-3
- Nithiamide
Catalog No.:BCC4687
CAS No.:140-40-9
Effect of Tenuifoliside A isolated from Polygala tenuifolia on the ERK and PI3K pathways in C6 glioma cells.[Pubmed:24877714]
Phytomedicine. 2014 Sep 15;21(10):1178-88.
Tenuifoliside A (TFSA) is a bioactive oligosaccharide ester component of Polygala tenuifolia Wild, a traditional Chinese medicine which was used to manage mental disorders effectively. The neuroprotective and anti-apoptotic effects of TFSA have been demonstrated in our previous studies. The present work was designed to study the molecular mechanism of TFSA on promoting the viability of rat glioma cells C6. We exposed C6 cells to TFSA (or combined with ERK, PI3K and TrkB inhibitors) to examine the effects of TFSA on the cell viability and the expression and phosphorylation of key proteins in the ERK and PI3K signaling pathway. TFSA increased levels of phospho-ERK and phospho-Akt, enhanced release of BDNF, which were blocked by ERK and PI3K inhibitors, respectively (U0126 and LY294002). Moreover, the TFSA caused the enhanced phosphorylation of cyclic AMP response element binding protein (CREB) at Ser133 site, the effect was revoked by U0126, LY294002 and K252a. Furthermore, when C6 cells were pretreated with K252a, a TrkB antagonist, known to significantly inhibit the activity of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), blocked the levels of phospho-ERK, phospho-Akt and phosphor-CREB. Taking these results together, we suggested the neuroprotection of TFSA might be mediated through BDNF/TrkB-ERK/PI3K-CREB signaling pathway in C6 glioma cells.
Potential antidepressant properties of Radix Polygalae (Yuan Zhi).[Pubmed:20541923]
Phytomedicine. 2010 Aug;17(10):794-9.
Radix Polygalae ("Yuan Zhi", the roots of Polygala tenuifolia Willd., YZ) is an important herb used in traditional Chinese medicine to mediate depression. The present study was designed to verify the antidepressant effects of the standardized YZ ethanol extract (YZE) and its four fractions YZ-30, YZ-50, YZ-70 and YZ-90 on the tail suspension (TST) and forced swimming test (FST). Furthermore, the standardization of the fractions obtained from the separation procedures was carried out by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)-fingerprint. The YZ-50 fraction (Oligosaccharide esters--enriched, oral (200 mg/kg) showed a significant anti-immobility like effects. The data of YZ-50 on the corticosterone-induced injure of SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cell indicated that YZ-50 may have biological effects on neuroprotection. Proliferation of cell lines was assessed by dimethylthiazoldiphenyltetrazoliumbromide (MTT) and 5-bromo-2'-deoxyuridine (BrdU) incorporation assays. It was found that YZ-50 and its two bioactive compounds, 3,6'-di-o-sinapoyl-sucrose (DISS) and Tenuifoliside A(TEA) showed protection activities in SY5Y cells from the lesion. By using bioassay-screening methods, our results indicate that the presence of oligosaccharide esters such as DISS and TEA in this herb may be responsible for the cytoprotective activity effects.
Plant-derived natural medicines for the management of depression: an overview of mechanisms of action.[Pubmed:25719303]
Rev Neurosci. 2015;26(3):305-21.
Depression is a serious widespread psychiatric disorder that affects approximately 17% of people all over the world. Exploring the neurological mechanisms of the antidepressant activity of plant-derived agents could have a crucial role in developing natural drugs for the management of depression. The aim of the present study is to review the neurological mechanisms of action of antidepressant plants and their constituents. For this purpose, electronic databases, including PubMed, Science Direct, Scopus, and Cochrane Library, were searched from 1966 to October 2013. The results showed that several molecular mechanisms could be proposed for the antidepressant activity of medicinal plants and their constituents. Hypericum species could normalize brain serotonin level. Liquiritin and isoliquiritin from Glycyrrhiza uralensis rhizome act via the noradrenergic system. Rosmarinus officinalis and curcumin from Curcuma longa interact with D1 and D2 receptors as well as elevate the brain dopamine level. Sida tiagii and Aloysia gratissima involve gamma-aminobutyric acid and N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors, respectively. Fuzi polysaccharide-1 from Aconitum carmichaeli could affect brain-derived neurotrophic factor signaling pathways. Psoralidin from Psoralea corylifolia seed modulate the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. The total glycosides of Paeonia lactiflora demonstrate an inhibitory effect on both subtypes of monoamine oxidase. 3,6'-Di-o-sinapoyl-sucrose and Tenuifoliside A from Polygala tenuifolia exhibit cytoprotective effects on neuronal cells. Further preclinical and clinical trials evaluating their safety, bioefficacy, and bioavailability are suggested to prove the valuable role of natural drugs in the management of depressive disorders.
The inhibition of JNK MAPK and NF-kappaB signaling by tenuifoliside A isolated from Polygala tenuifolia in lipopolysaccharide-induced macrophages is associated with its anti-inflammatory effect.[Pubmed:24076326]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2013 Dec 5;721(1-3):267-76.
The root of Polygala tenuifolia Willd. (Polygalaceae) is well known for its use in the treatment of neurasthenia, amnesia, and inflammation. In this study, we isolated phenyl propanoid type metabolite Tenuifoliside A, one of the phenylpropanoids from P. tenuifolia, and investigated its anti-inflammatory effects in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated RAW264.7 and murine peritoneal macrophages. The results showed that Tenuifoliside A inhibited the production of nitric oxide (NO), inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), prostaglandin E2 (PG E2), and cyclooxygenase (COX)-2. In addition, Tenuifoliside A suppressed the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha and interleukin (IL)-1beta. We also evaluated the effects of Tenuifoliside A on the activation of nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB). Tenuifoliside A inhibited the translocation of the NF-kappaB subunit p65 into the nucleus by interrupting the phosphorylation and degradation of inhibitor kappa B (IkappaB)-alpha in LPS-stimulated murine peritoneal macrophages. Moreover, we confirmed that the suppression of the inflammatory process by Tenuifoliside A was mediated through the mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) pathway based on the fact that Tenuifoliside A significantly decreased p-c-Jun N-terminal kinase (p-JNK) protein expression in LPS-stimulated murine peritoneal macrophages. Taken together, the anti-inflammatory effects of Tenuifoliside A were mediated by the inhibition of the NF-kappaB and MAPK pathways. This study is the first report on the anti-inflammatory effects of Tenuifoliside A, and the strong anti-inflammatory effects of Tenuifoliside A provide potential compound to be developed as therapeutic for inflammatory diseases.


