Amphotericin BCAS# 1397-89-3 |
- Tezampanel
Catalog No.:BCC1993
CAS No.:154652-83-2
- Noopept
Catalog No.:BCC1804
CAS No.:157115-85-0
- LY450108
Catalog No.:BCC1725
CAS No.:376594-67-1
- Perampanel
Catalog No.:BCC1847
CAS No.:380917-97-5
- Aniracetam
Catalog No.:BCC4219
CAS No.:72432-10-1
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1397-89-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 91827561 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C47H73NO17 | M.Wt | 924.07 |
| Type of Compound | Miscellaneous | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (108.22 mM) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
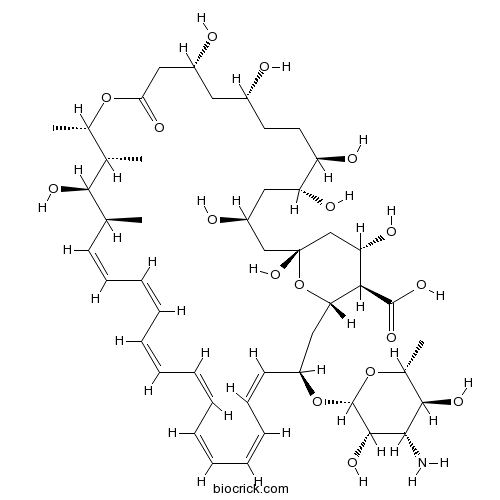
| Chemical Name | (1S,3R,4Z,6Z,8Z,10Z,12Z,14Z,16Z,18S,19R,20R,21S,25R,27R,30R,31R,33S,35R,37S,38R)-3-[(2R,3S,4S,5S,6R)-4-amino-3,5-dihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy-19,25,27,30,31,33,35,37-octahydroxy-18,20,21-trimethyl-23-oxo-22,39-dioxabicyclo[33.3.1]nonatriaconta-4,6,8,10,12,14,16-heptaene-38-carboxylic acid | ||
| SMILES | CC1C=CC=CC=CC=CC=CC=CC=CC(CC2C(C(CC(O2)(CC(CC(C(CCC(CC(CC(=O)OC(C(C1O)C)C)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)C(=O)O)OC3C(C(C(C(O3)C)O)N)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | APKFDSVGJQXUKY-ZNVUZQDLSA-N | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Amphotericin B is an antifungal agent. 2. Amphotericin B inhibits the A. actinomycetemcomitans-induced production of prostaglandin E2. 3. Amphotericin B can regulate inflammatory cytokines in host cells and regulate inflammatory responses in HGEC. 4. Amphotericin B inhibits the A. actinomycetemcomitans-induced phosphorylation of ERK and p38 MAP kinase. 5. The inhibition of the PKA signaling pathway can aid in reducing the degree of nephrotoxicity caused by Amphotericin B. 6. Treatment with Amphotericin B, particularly in combination with MCSF, increased the number of oligodendrocyte precursor cells and promoted remyelination within lesions. |
| Targets | NO | PKA | IL Receptor | TNF-α | p38MAPK | ERK | PGE |

Amphotericin B Dilution Calculator

Amphotericin B Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.0822 mL | 5.4108 mL | 10.8217 mL | 21.6434 mL | 27.0542 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.2164 mL | 1.0822 mL | 2.1643 mL | 4.3287 mL | 5.4108 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1082 mL | 0.5411 mL | 1.0822 mL | 2.1643 mL | 2.7054 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0216 mL | 0.1082 mL | 0.2164 mL | 0.4329 mL | 0.5411 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0108 mL | 0.0541 mL | 0.1082 mL | 0.2164 mL | 0.2705 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Amphotericin B is a polyene, antifungal antibiotic produced from a strain of Streptomyces nodosus. (IC50=0.028–0.290 μg/ml)
- Gardenine
Catalog No.:BCN6211
CAS No.:139682-36-3
- EPZ005687
Catalog No.:BCC2219
CAS No.:1396772-26-1
- CGP 52432
Catalog No.:BCC6989
CAS No.:139667-74-6
- PR 39 (porcine)
Catalog No.:BCC5856
CAS No.:139637-11-9
- Purotoxin 1
Catalog No.:BCC6333
CAS No.:1396322-38-5
- 3-Bromoisonicotinic Acid
Catalog No.:BCC8368
CAS No.:13959-02-9
- Epicannabidiol hydrate
Catalog No.:BCN6207
CAS No.:139561-95-8
- Serratriol
Catalog No.:BCN6210
CAS No.:13956-52-0
- Lycoclavanol
Catalog No.:BCN6209
CAS No.:13956-51-9
- Cannabidiol
Catalog No.:BCN6208
CAS No.:13956-29-1
- Fmoc-Leu-ol
Catalog No.:BCC2582
CAS No.:139551-83-0
- 2-(7-Methoxy-1-naphthyl)ethylamine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCN1574
CAS No.:139525-77-2
- Yunnanxane
Catalog No.:BCN6702
CAS No.:139713-81-8
- BS-181 HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2537
CAS No.:1397219-81-6
- Dunnianol
Catalog No.:BCN6212
CAS No.:139726-29-7
- Isodunnianol
Catalog No.:BCN6213
CAS No.:139726-30-0
- Tenuifoliside A
Catalog No.:BCN2893
CAS No.:139726-35-5
- Tenuifoliside B
Catalog No.:BCC9251
CAS No.:139726-36-6
- tenuifoliside C
Catalog No.:BCN8299
CAS No.:139726-37-7
- Sildenafil
Catalog No.:BCC1947
CAS No.:139755-83-2
- Cucurbitacin E-2-O-Glucoside
Catalog No.:BCC8156
CAS No.:1398-78-3
- Milameline hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7427
CAS No.:139886-04-7
- 3,6'-Disinapoyl sucrose
Catalog No.:BCN2719
CAS No.:139891-98-8
- Globularin
Catalog No.:BCN6215
CAS No.:1399-49-1
Alteration in cellular viability, pro-inflammatory cytokines and nitric oxide production in nephrotoxicity generation by Amphotericin B: involvement of PKA pathway signaling.[Pubmed:24105867]
J Appl Toxicol. 2014 Dec;34(12):1285-92.
Amphotericin B is one of the most effective antifungal agents; however, its use is often limited owing to adverse effects, especially nephrotoxicity. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of inhibiting the PKA signaling pathway in nephrotoxicity using Amphotericin B from the assessment of cell viability, pro-inflammatory cytokines and nitric oxide (NO) production in LLC-PK1 and MDCK cell lines. Amphotericin B proved to be cytotoxic for both cell lines, as assessed by the mitochondrial enzyme activity (MTT) assay; caused DNA fragmentation, determined by flow cytometry using the propidium iodide (PI) dye; and activated the PKA pathway (western blot assay). In MDCK cells, the inhibition of the PKA signaling pathway (using the H89 inhibitor) caused a significant reduction in DNA fragmentation. In both cells lines the production of interleukin-6 (IL)-6 proved to be a dependent PKA pathway, whereas tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) was not influenced by the inhibition of the PKA pathway. The NO production was increased when cells were pre-incubated with H89 followed by Amphotericin B, and this production produced a dependent PKA pathway in LLC-PK1 and MDCK cells lines. Therefore, considering the present study's results as a whole, it can be concluded that the inhibition of the PKA signaling pathway can aid in reducing the degree of nephrotoxicity caused by Amphotericin B.
Amphotericin B down-regulates Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans-induced production of IL-8 and IL-6 in human gingival epithelial cells.[Pubmed:25064453]
Cell Immunol. 2014 Aug;290(2):201-8.
Gingival epithelium is the primary barrier against microorganism invasion and produces inflammatory cytokines. Amphotericin B, a major antifungal drug, binds to cholesterol in the mammalian cell membrane in addition to fungal ergosterol. Amphotericin B has been shown to regulate inflammatory cytokines in host cells. To investigate the suppressive effect of Amphotericin B on the gingival epithelium, we examined the expression of interleukin (IL)-8 and IL-6 and involvement of MAP kinase in human gingival epithelial cells (HGEC) stimulated by Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans. Amphotericin B and the p38 MAP kinase inhibitor down-regulated the A. actinomycetemcomitans-induced increase in the expression of IL-8 and IL-6 at the mRNA. The ERK inhibitor suppressed the A. actinomycetemcomitans-induced IL-8 mRNA expression. Amphotericin B inhibited the A. actinomycetemcomitans-induced phosphorylation of ERK and p38 MAP kinase. Furthermore, Amphotericin B inhibited the A. actinomycetemcomitans-induced production of prostaglandin E2. These results suggest that Amphotericin B regulate inflammatory responses in HGEC.
Stimulation of monocytes, macrophages, and microglia by amphotericin B and macrophage colony-stimulating factor promotes remyelination.[Pubmed:25609628]
J Neurosci. 2015 Jan 21;35(3):1136-48.
Approaches to stimulate remyelination may lead to recovery from demyelinating injuries and protect axons. One such strategy is the activation of immune cells with clinically used medications, since a properly directed inflammatory response can have healing properties through mechanisms such as the provision of growth factors and the removal of cellular debris. We previously reported that the antifungal medication Amphotericin B is an activator of circulating monocytes, and their tissue-infiltrated counterparts and macrophages, and of microglia within the CNS. Here, we describe that Amphotericin B activates these cells through engaging MyD88/TRIF signaling. When mice were subjected to lysolecithin-induced demyelination of the spinal cord, systemic injections of nontoxic doses of Amphotericin B and another activator, macrophage colony-stimulating factor (MCSF), further elevated the representation of microglia/macrophages at the site of injury. Treatment with Amphotericin B, particularly in combination with MCSF, increased the number of oligodendrocyte precursor cells and promoted remyelination within lesions; these pro-regenerative effects were mitigated in mice treated with clodronate liposomes to reduce circulating monocytes and tissue-infiltrated macrophages. Our results have identified candidates among currently used medications as potential therapies for the repair of myelin.


