Vibralactone BCAS# 1093230-95-5 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1093230-95-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 102473701 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C12H16O4 | M.Wt | 224.26 |
| Type of Compound | Sesquiterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
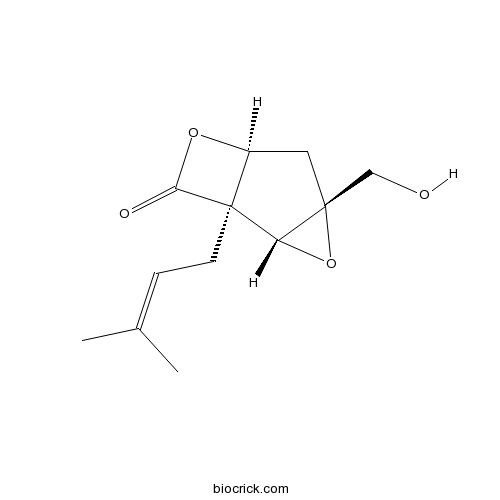
| SMILES | CC(=CCC12C(CC3(C1O3)CO)OC2=O)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | NOIVROLINHAPPT-XPXLGCRWSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C12H16O4/c1-7(2)3-4-12-8(15-10(12)14)5-11(6-13)9(12)16-11/h3,8-9,13H,4-6H2,1-2H3/t8-,9-,11+,12-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Vibralactone B shows antibacterial activity, it can inhibit significantly the growth of E. coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, with MBC values of 50 and 100 ug/mL, respectively. |
| Targets | Antifection |

Vibralactone B Dilution Calculator

Vibralactone B Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.4591 mL | 22.2955 mL | 44.5911 mL | 89.1822 mL | 111.4777 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.8918 mL | 4.4591 mL | 8.9182 mL | 17.8364 mL | 22.2955 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4459 mL | 2.2296 mL | 4.4591 mL | 8.9182 mL | 11.1478 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0892 mL | 0.4459 mL | 0.8918 mL | 1.7836 mL | 2.2296 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0446 mL | 0.223 mL | 0.4459 mL | 0.8918 mL | 1.1148 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- LKB1 (AAK1 dual inhibitor)
Catalog No.:BCC1705
CAS No.:1093222-27-5
- 3-Hydroxy-4,15-dinor-1(5)-xanthen-12,8-olide
Catalog No.:BCN1625
CAS No.:1093207-99-8
- HNGF6A
Catalog No.:BCC8021
CAS No.:1093111-54-6
- B-Raf inhibitor 1
Catalog No.:BCC4182
CAS No.:1093100-40-3
- PLpro inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC5302
CAS No.:1093070-14-4
- Angelol M
Catalog No.:BCN8271
CAS No.:1092952-64-1
- 7,2',4'-Trihydroxy-5-methoxy-3-phenylcoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN1626
CAS No.:1092952-62-9
- Ruxolitinib phosphate
Catalog No.:BCC1912
CAS No.:1092939-17-7
- Ruxolitinib sulfate
Catalog No.:BCC1913
CAS No.:1092939-16-6
- PP121
Catalog No.:BCC4980
CAS No.:1092788-83-4
- IT1t dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6234
CAS No.:1092776-63-0
- WAY 100635 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5061
CAS No.:146714-97-8
- SRT2104 (GSK2245840)
Catalog No.:BCC1950
CAS No.:1093403-33-8
- VU 0155041
Catalog No.:BCC7615
CAS No.:1093757-42-6
- gamma-secretase modulator 2
Catalog No.:BCC1584
CAS No.:1093978-89-2
- CYM 5442 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7722
CAS No.:1094042-01-9
- SCH-1473759
Catalog No.:BCC1934
CAS No.:1094069-99-4
- Fmoc-His(Trt)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3501
CAS No.:109425-51-6
- Fmoc-Orn(Boc)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3533
CAS No.:109425-55-0
- Fmoc-His(Trt)-OPfp
Catalog No.:BCC3502
CAS No.:109434-24-4
- BIX 02188
Catalog No.:BCC2550
CAS No.:1094614-84-2
- BIX 02189
Catalog No.:BCC2549
CAS No.:1094614-85-3
- 3'-Methyl-4-O-methylhelichrysetin
Catalog No.:BCN4062
CAS No.:109471-13-8
- JNJ-31020028
Catalog No.:BCC5516
CAS No.:1094873-14-9
Bioactive compounds isolated from submerged fermentations of the Chilean fungus Stereum rameale.[Pubmed:26020559]
Z Naturforsch C. 2015;70(3-4):97-102.
Liquid fermentations of the fungus Stereum rameale (N degrees 2511) yielded extracts with antibacterial activity. The antibacterial activity reached its peak after 216 h of stirring. Bioassay-guided fractionation methods were employed for the isolation of the bioactive metabolites. Three known compounds were identified: MS-3 (1), vibralactone (2) and Vibralactone B (3). The three compounds showed antibacterial activity as a function of their concentration. Minimal bactericidal concentrations (MBC) of compound 1 against Gram-positive bacteria were as follows: Bacillus cereus (50 mug/mL), Bacillus subtilis (10 mug/mL) and Staphylococcus aureus (100 mug/mL). Compounds 2 and 3 were active only against Gram-negative bacteria. The MBC of compound 2 against Escherichia coli was 200 mug/mL. Compound 3 inhibited significantly the growth of E. coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, with MBC values of 50 and 100 mug/mL, respectively.
Derivatives of vibralactone from cultures of the basidiomycete Boreostereum vibrans.[Pubmed:18758102]
Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2008 Sep;56(9):1286-8.
Four new natural products possessing vibralactone skeleton, 1,5-secovibralactone (1), Vibralactone B (2), vibralactone C (3) and acetylated vibralactone (4), together with known compound vibralactone (5), had been isolated from cultures of the basidiomycete Boreostereum vibrans. The structures of 1-4 were elucidated on the basis of spectroscopic methods. The absolute configuration of 1 was suggested to be S by computational methods.
Antifungal activities of secondary metabolites isolated from liquid fermentations of Stereum hirsutum (Sh134-11) against Botrytis cinerea (grey mould agent).[Pubmed:28528973]
Food Chem Toxicol. 2017 Nov;109(Pt 2):1048-1054.
Extracts obtained from liquid mycelial fermentations of the Chilean fungus Stereum hirsutum (Sh134-11) showed antifungal activity against Botrytis cinerea. Two types of extracts were obtained: EtOAc-extract (liquid phase) and MeOH-extract (mycelial phase). Plate diffusion assay showed that EtOAc-extracts were more active than MeOH-extracts. A large-scale fermentation of Sh134-11 and chromatographic methods allowed to isolated four compounds: MS-3, Vibralactone, Vibralactone B and Sterenin D. Only Sterenin D showed antifungal activity against B. cinerea in the tests performed. Effects on the mycelial growth of B. cinerea showed that Sterenin D showed inhibition at 1000-2000 mug/mL reaching 67% and 76% respectively. Sterenin D was more effective to control the sporogenesis, inhibiting in 96% the sporulation at 500 mug/mL. Assays showed that Sterenin D exhibited a minimal fungicidal concentration (MFC) of 50 mug/mL and minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) at 20 mug/mL. Our study indicated that submerged fermentations of Chilean S. hirsutum (Sh134-11) produced extracts with antifungal activity and Sterenin D is responsible for this activity, which could be used as possible biofungicides alternative to synthetic fungicides.


