Ruxolitinib phosphateJAK1/JAK2 inhibitor CAS# 1092939-17-7 |
- BMN-673 8R,9S
Catalog No.:BCC1422
CAS No.:1207456-00-5
- ME0328
Catalog No.:BCC3995
CAS No.:1445251-22-8
- Rucaparib (free base)
Catalog No.:BCC4012
CAS No.:283173-50-2
- PJ34 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC2210
CAS No.:344458-15-7
- Olaparib (AZD2281, Ku-0059436)
Catalog No.:BCC2206
CAS No.:763113-22-0
- NU 1025
Catalog No.:BCC2454
CAS No.:90417-38-2
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1092939-17-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 25127112 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C17H21N6O4P | M.Wt | 404.36 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | INCB018424 phosphate | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 31 mg/mL (76.66 mM) H2O : 5.4 mg/mL (13.35 mM; Need ultrasonic and warming) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
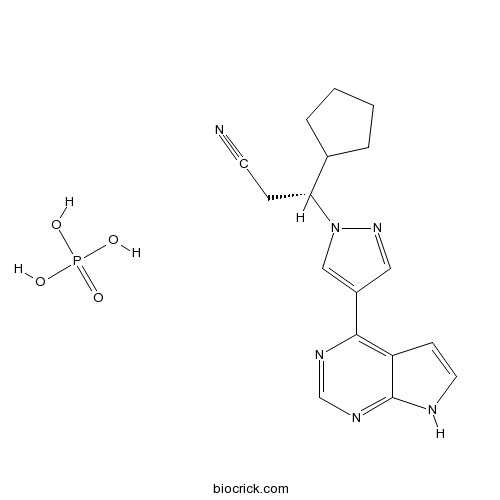
| Chemical Name | (3R)-3-cyclopentyl-3-[4-(7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)pyrazol-1-yl]propanenitrile;phosphoric acid | ||
| SMILES | C1CCC(C1)C(CC#N)N2C=C(C=N2)C3=C4C=CNC4=NC=N3.OP(=O)(O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | JFMWPOCYMYGEDM-XFULWGLBSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C17H18N6.H3O4P/c18-7-5-15(12-3-1-2-4-12)23-10-13(9-22-23)16-14-6-8-19-17(14)21-11-20-16;1-5(2,3)4/h6,8-12,15H,1-5H2,(H,19,20,21);(H3,1,2,3,4)/t15-;/m1./s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Ruxolitinib (phosphate) is the first potent JAK1/2 inhibitor with IC50 values of 3.3 nM/2.8 nM, more than 130-fold selectivity for JAK1/2 versus JAK3.In Vitro:Ruxolitinib (INCB018424) potently and selectively inhibits JAK2V617F-mediated signaling and proliferation. Ruxolitinib inhibits the growth of HEL cells with EC50 of 186 nM. Ruxolitinib markedly increases apoptosis in Ba/F3-EpoR-JAK2V617F cell system, and inhibits hematopoietic progenitor cell proliferation in primary MPN patient samples[1].In Vivo:Ruxolitinib (180 mg/kg, p.o.) reduces the tumor burden of mice inoculated with JAK2V617F-expressing cells without causing anemia or lymphopenia[1]. References: | |||||

Ruxolitinib phosphate Dilution Calculator

Ruxolitinib phosphate Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.473 mL | 12.3652 mL | 24.7304 mL | 49.4609 mL | 61.8261 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4946 mL | 2.473 mL | 4.9461 mL | 9.8922 mL | 12.3652 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2473 mL | 1.2365 mL | 2.473 mL | 4.9461 mL | 6.1826 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0495 mL | 0.2473 mL | 0.4946 mL | 0.9892 mL | 1.2365 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0247 mL | 0.1237 mL | 0.2473 mL | 0.4946 mL | 0.6183 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
INCB018424 (Ruxolitinib) is an orally bioavailable JAK inhibitor .(IC50 values for JAK1, JAK2 and JAK3 are 3, 5 and 332 nM, respectively).INCB018424 is useful for rheumatoid arthritis.
- Ruxolitinib sulfate
Catalog No.:BCC1913
CAS No.:1092939-16-6
- PP121
Catalog No.:BCC4980
CAS No.:1092788-83-4
- IT1t dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6234
CAS No.:1092776-63-0
- WAY 100635 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5061
CAS No.:146714-97-8
- (3S,4R)-Tofacitinib
Catalog No.:BCC4267
CAS No.:1092578-48-7
- (3S,4S)-Tofacitinib
Catalog No.:BCC4052
CAS No.:1092578-47-6
- (3R,4S)-Tofacitinib
Catalog No.:BCC4268
CAS No.:1092578-46-5
- Paxiphylline E
Catalog No.:BCN5886
CAS No.:1092555-03-7
- Paxiphylline D
Catalog No.:BCN5885
CAS No.:1092555-02-6
- Deuterated Atazanivir-D3-1
Catalog No.:BCC2115
CAS No.:1092540-56-1
- Deuterated Atazanivir-D3-3
Catalog No.:BCC2117
CAS No.:1092540-52-7
- Deuterated Atazanivir-D3-2
Catalog No.:BCC2116
CAS No.:1092540-51-6
- 7,2',4'-Trihydroxy-5-methoxy-3-phenylcoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN1626
CAS No.:1092952-62-9
- Angelol M
Catalog No.:BCN8271
CAS No.:1092952-64-1
- PLpro inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC5302
CAS No.:1093070-14-4
- B-Raf inhibitor 1
Catalog No.:BCC4182
CAS No.:1093100-40-3
- HNGF6A
Catalog No.:BCC8021
CAS No.:1093111-54-6
- 3-Hydroxy-4,15-dinor-1(5)-xanthen-12,8-olide
Catalog No.:BCN1625
CAS No.:1093207-99-8
- LKB1 (AAK1 dual inhibitor)
Catalog No.:BCC1705
CAS No.:1093222-27-5
- Vibralactone B
Catalog No.:BCN6748
CAS No.:1093230-95-5
- SRT2104 (GSK2245840)
Catalog No.:BCC1950
CAS No.:1093403-33-8
- VU 0155041
Catalog No.:BCC7615
CAS No.:1093757-42-6
- gamma-secretase modulator 2
Catalog No.:BCC1584
CAS No.:1093978-89-2
- CYM 5442 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7722
CAS No.:1094042-01-9
Population pharmacokinetic analysis of orally-administered ruxolitinib (INCB018424 Phosphate) in patients with primary myelofibrosis (PMF), post-polycythemia vera myelofibrosis (PPV-MF) or post-essential thrombocythemia myelofibrosis (PET MF).[Pubmed:23677817]
J Clin Pharmacol. 2013 Jul;53(7):721-30.
Ruxolitinib is a selective inhibitor of Janus kinase 1 and 2, which is approved to treat intermediate or high-risk myelofibrosis. The population pharmacokinetics for ruxolitinib were characterized by a modeling dataset of 272 subjects from a Phase 2 and a Phase 3 study and validated by an external validation dataset of 142 subjects from a second Phase 3 study. The PK of ruxolitinib was adequately described by a two-compartment disposition model with first-order absorption and linear elimination. All model parameters were estimated with good precision. Gender and body weight were identified as covariates for oral clearance (CL/F) and volume of distribution for central compartment (Vc/F), respectively. Apparent oral clearance was 22.1 and 17.7 L/h for a typical male and female subject, respectively, with 39.1% unexplained inter-individual variability (IIV). The typical Vc /F for a subject with a median weight of 72.9 kg was estimated to be 58.6 L, with 28% unexplained IIV. The model predictive performance was validated by visual predictive check (VPC) and the external validation dataset. This analysis suggests that effects of gender and body weight on ruxolitinib PK are not clinically significant and hence no dose adjustment is needed based on gender and weight.
Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of orally administered ruxolitinib (INCB018424 phosphate) in renal and hepatic impairment patients.[Pubmed:27128228]
Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 2014 Jan;3(1):34-42.
Hepatic and renal impairment studies were conducted with ruxolitinib, a JAK1&2 inhibitor that is cleared predominantly by metabolism. Both studies were open label, single-dose studies. Ruxolitinib area under the curve (AUC) was increased by 87%, 28%, and 65%, respectively, in subjects with mild, moderate, and severe hepatic impairment compared to healthy subjects with no correlation between exposure of ruxolitinib and the degree of hepatic impairment. The pharmacodynamics (PD) data were consistent with ruxolitinib pharmacokinetics (PK). The renal impairment study showed a surprising finding. While there was no change in ruxolitinib PK with varying degrees of renal impairment, the PD showed increasing pharmacological activity with increased severity of renal impairment. Analysis of the metabolite exposures revealed that active metabolites contributed to the observed incremental increase in PD activity. The recovery of ruxolitinib in dialysate was negligible. The starting dose of ruxolitinib in subjects with any hepatic impairment or moderate or severe renal impairment should be decreased to 10 mg twice daily (BID) if their platelet counts are between 100 x 10(9) /L and 150 x 10(9) /L. Subjects on dialysis should initiate dosing with a single dose of 15 or 20 mg, based on platelet counts, with dosing only on the days of dialysis.
The effect of CYP3A4 inhibition or induction on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of orally administered ruxolitinib (INCB018424 phosphate) in healthy volunteers.[Pubmed:21602517]
J Clin Pharmacol. 2012 Jun;52(6):809-18.
Ruxolitinib, a selective Janus kinase (JAK) 1&2 inhibitor in development for the treatment of myeloproliferative neoplasms, is primarily metabolized by CYP3A4. The effects of inhibition or induction of CYP3A4 on single oral dose ruxolitinib pharmacokinetics (PK) and pharmacodynamics (PD) were evaluated in healthy volunteers. Coadministration of ketoconazole (a potent CYP3A4 inhibitor) and erythromycin (a moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor) increased total ruxolitinib plasma exposure (AUC(0-infinity)) by 91% and 27%, respectively, and ruxolitinib PD, as measured by the inhibition of interleukin (IL)-6-stimulated STAT3 phosphorylation in whole blood, was generally consistent with the PK observed. Pretreatment with rifampin, a potent CYP3A4 inducer, decreased ruxolitinib AUC(0-infinity) by 71% while resulting in only a 10% decrease in the overall PD activity. This apparent PK/PD discrepancy may be explained, in part, by an increase in the relative abundance of ruxolitinib active metabolites with the rifampin coadministration. The collective PK/PD data suggest that starting doses of ruxolitinib should be reduced by 50% if coadministered with a potent CYP3A4 inhibitor, whereas adjustments in ruxolitinib starting doses may not be needed when coadministered with inducers or mild/moderate inhibitors of CYP3A4. All study doses of ruxolitinib were generally safe and well tolerated when given alone and in combination with ketoconazole, erythromycin, or rifampin.


