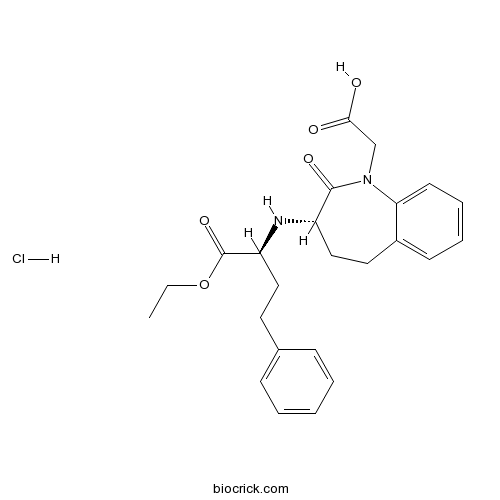
Benazepril HClAngiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor CAS# 86541-74-4 |
- M344
Catalog No.:BCC2162
CAS No.:251456-60-7
- NSC 3852
Catalog No.:BCC2423
CAS No.:3565-26-2
- LAQ824 (NVP-LAQ824,Dacinostat)
Catalog No.:BCC2160
CAS No.:404951-53-7
- JNJ-26481585
Catalog No.:BCC2147
CAS No.:875320-29-9
- AR-42 (OSU-HDAC42)
Catalog No.:BCC2161
CAS No.:935881-37-1
- KD 5170
Catalog No.:BCC2420
CAS No.:940943-37-3
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 86541-74-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5362123 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C24H29ClN2O5 | M.Wt | 460.95 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | CGS 14824A | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 100 mg/mL (216.94 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : 10 mg/mL (21.69 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
| Chemical Name | 2-[(3S)-3-[[(2S)-1-ethoxy-1-oxo-4-phenylbutan-2-yl]amino]-2-oxo-4,5-dihydro-3H-1-benzazepin-1-yl]acetic acid;hydrochloride | ||
| SMILES | CCOC(=O)C(CCC1=CC=CC=C1)NC2CCC3=CC=CC=C3N(C2=O)CC(=O)O.Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | VPSRQEHTHIMDQM-FKLPMGAJSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C24H28N2O5.ClH/c1-2-31-24(30)20(14-12-17-8-4-3-5-9-17)25-19-15-13-18-10-6-7-11-21(18)26(23(19)29)16-22(27)28;/h3-11,19-20,25H,2,12-16H2,1H3,(H,27,28);1H/t19-,20-;/m0./s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Non-peptide angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor. Reduces blood pressure and myocardial hypertrophy in spontaneous hypertensive rats. |

Benazepril HCl Dilution Calculator

Benazepril HCl Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1694 mL | 10.8472 mL | 21.6943 mL | 43.3887 mL | 54.2358 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4339 mL | 2.1694 mL | 4.3389 mL | 8.6777 mL | 10.8472 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2169 mL | 1.0847 mL | 2.1694 mL | 4.3389 mL | 5.4236 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0434 mL | 0.2169 mL | 0.4339 mL | 0.8678 mL | 1.0847 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0217 mL | 0.1085 mL | 0.2169 mL | 0.4339 mL | 0.5424 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Benazepril hydrochloride, an angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor, which is a medication used to treat high blood pressure.
- N-Methylcalycinine
Catalog No.:BCN4412
CAS No.:86537-66-8
- FR 180204
Catalog No.:BCC3669
CAS No.:865362-74-9
- 4,5-dihydroxy-3,8-dimethylnaphthalene-1,2-dione
Catalog No.:BCN8422
CAS No.:86533-36-0
- AMG837
Catalog No.:BCC6387
CAS No.:865231-46-5
- Gelsempervine A
Catalog No.:BCN3929
CAS No.:865187-17-3
- Vinblastine
Catalog No.:BCN2376
CAS No.:865-21-4
- BMS-663068 Tris
Catalog No.:BCC1429
CAS No.:864953-39-9
- BMS-663068
Catalog No.:BCC1428
CAS No.:864953-29-7
- Leojaponin
Catalog No.:BCN7381
CAS No.:864817-63-0
- Resminostat (RAS2410)
Catalog No.:BCC2165
CAS No.:864814-88-0
- Gnetucleistol C
Catalog No.:BCN3395
CAS No.:864763-61-1
- Gnetucleistol B
Catalog No.:BCN3585
CAS No.:864763-60-0
- Benazepril
Catalog No.:BCC4286
CAS No.:86541-75-5
- apigenin 7-O-(6〃-O-malonyl)-β-D-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN8399
CAS No.:86546-87-4
- Narlaprevir
Catalog No.:BCC1785
CAS No.:865466-24-6
- Bisisorhapontigenin A
Catalog No.:BCN3501
CAS No.:865474-98-2
- 5-R-Rivaroxaban
Catalog No.:BCC1313
CAS No.:865479-71-6
- Junipediol A
Catalog No.:BCN6912
CAS No.:86548-91-6
- Ganoderic acid SZ
Catalog No.:BCN4413
CAS No.:865543-37-9
- TC-E 5001
Catalog No.:BCC6355
CAS No.:865565-29-3
- 2-[(6-Chloro-3,4-dihydro-3-methyl-2,4-dioxo-1(2H)-pyrimidinyl)methyl]benzonitrile
Catalog No.:BCC8506
CAS No.:865758-96-9
- Trelagliptin
Catalog No.:BCC2014
CAS No.:865759-25-7
- PF-03084014
Catalog No.:BCC1848
CAS No.:865773-15-5
- Cytochrome c - pigeon (88-104)
Catalog No.:BCC1038
CAS No.:86579-06-8
A randomized, double-blind trial comparing the effects of amlodipine besylate/benazepril HCl vs amlodipine on endothelial function and blood pressure.[Pubmed:17028482]
J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2006 Oct;8(10):692-8.
Evidence suggests that renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibition ameliorates endothelial dysfunction. The authors examined the effect of amlodipine besylate/Benazepril HCl combination treatment compared with amlodipine besylate monotherapy in modulating endothelial dysfunction. This multicenter, double-blind, 12-week study randomized 70 hypertensive subjects with at least one other endothelial dysfunction risk factor to amlodipine besylate/Benazepril HCl (5/20 mg/d force-titrated to 5/40 mg/d) or amlodipine besylate monotherapy (5 mg/d force-titrated to 10 mg/d). Both the combination and monotherapy produced significant median increases from baseline in percentage flow-mediated vasodilation (2.0% and 1.2%, respectively) and percentage change in percent flow-mediated vasodilation (25% and 16%, respectively). These improvements were numerically larger with combination treatment, but between-group differences did not achieve statistical significance. Reductions in systolic and diastolic blood pressure were significantly greater (P=.0452/P=.0297) with combination treatment (-18.6/-12.3 mm Hg) than with monotherapy (-14.8/-9.1 mm Hg). A highly positive correlation between change in systolic blood pressure and change in percent of flow-mediated vasodilation was demonstrated only for combination treatment.
Formal synthesis of the ACE inhibitor benazepril x HCl via an asymmetric aza-Michael reaction.[Pubmed:17971736]
Molecules. 2006 Aug 23;11(8):641-8.
A formal enantioselective synthesis of benazepril.HCl (4), an anti- hypertensive drug, is reported. Our synthesis employed an asymmetric aza-Michael addition of L-homophenylalanine ethyl ester (LHPE, 1) to 4-(2-nitrophenyl)-4-oxo- but-2-enoic acid methyl ester (6) as the key step to prepare (2S,3'S)-2-(2-oxo-2,3,4,5- tetrahydro-1H-benzo[b]azepin-3-ylamino)-4-phenylbutyric acid ethyl ester (8), which is the key intermediate leading to benazepril x HCl (4).
Adherence to antihypertensive therapy with fixed-dose amlodipine besylate/benazepril HCl versus comparable component-based therapy.[Pubmed:14688505]
Congest Heart Fail. 2003 Nov-Dec;9(6):324-32.
Adhering to medication regimens has the potential to significantly improve clinical outcomes for persons with high blood pressure. A patient-related factor likely to affect adherence to treatment is the convenience of the prescribed drug regimen. The authors hypothesized that medication adherence would be superior and cost benefits would accrue in subjects who receive a once-daily, single-capsule, fixed-dose combination product for blood pressure control, compared with subjects who receive a similar regimen of separate components. A managed care organization that provides benefits for members enrolled in various health plans provided the data for this retrospective analysis. The database was used to assess medication adherence patterns for two groups of hypertensive subjects. Group 1 included subjects who had been prescribed the single-capsule, fixed-dose combination of amlodipine besylate/Benazepril HCl. Group 2 comprised subjects who had been prescribed a regimen including an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor and a dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker as separate drugs. Adherence was measured by the medication possession ratio, and medical resource utilization by the two groups was assessed during the study period. Group 1 (n=2754) and Group 2 (n=2978) were balanced with regard to age (mean, 53 years; range, 18-64 years) and sex (men, 50%; women, 50%). The overall medication possession ratio for Group 1 was significantly higher than that for Group 2 (80.8% vs. 73.8%; p<0.001). The average annual cost of cardiovascular-related care per subject was significantly lower in Group 1 compared with Group 2 (p<0.001). Subjects receiving the once-daily, single-capsule, fixed-dose combination of amlodipine/Benazepril HCl demonstrated significantly better medication adherence and required fewer medical resources than did subjects receiving an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor and a dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker as separate components.
Kinetics of the acidic and enzymatic hydrolysis of benazepril HCl studied by LC.[Pubmed:11682216]
J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2002 Jan 1;27(1-2):107-16.
A reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatographic (HPLC) method was developed and validated for the kinetic investigation of the chemical and enzymatic hydrolysis of benazepril hydrochloride. Kinetic studies on the acidic hydrolysis of benazepril hydrochloride were carried out in 0.1 M hydrochloric acid solution at 50, 53, 58 and 63 degrees C. Benazepril hydrochloride appeared stable in a pH 7.4 phosphate buffered solution at 37 degrees C and showed susceptibility to undergoing in vitro enzymatic hydrolysis with porcine liver esterase (PLE) in a pH 7.4 buffered solution at 37 degrees C. Benazeprilat appeared to be the major degradation product in both (chemical and enzymatic) studies of hydrolysis. Statistical evaluation of the proposed HPLC methods revealed their good linearity and reproducibility. Relative standard deviation (R.S.D.) was less than 4.76, while detection limits for benazepril hydrochloride and benazeprilat were 13.0 x 10(-7) and 9.0 x 10(-7) M, respectively. Treatment of the kinetic data of the acidic hydrolysis was carried out by non-linear regression analysis and k values were determined. The kinetic parameters of the enzymatic hydrolysis were determined by non-linear regression analysis of the data using the equation of Michaelis-Menten.


