HydroxyureaCAS# 127-07-1 |
- chroman 1
Catalog No.:BCC1480
CAS No.:1273579-40-0
- Y-27632 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1273
CAS No.:129830-38-2
- Hydroxyfasudil hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1636
CAS No.:155558-32-0
- H-1152
Catalog No.:BCC1615
CAS No.:451462-58-1
- H-1152 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1616
CAS No.:871543-07-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 127-07-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 3657 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | CH4N2O2 | M.Wt | 76.05 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Hydroxycarbamide | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 100 mg/mL (1314.92 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : 50 mg/mL (657.46 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
| Chemical Name | hydroxyurea | ||
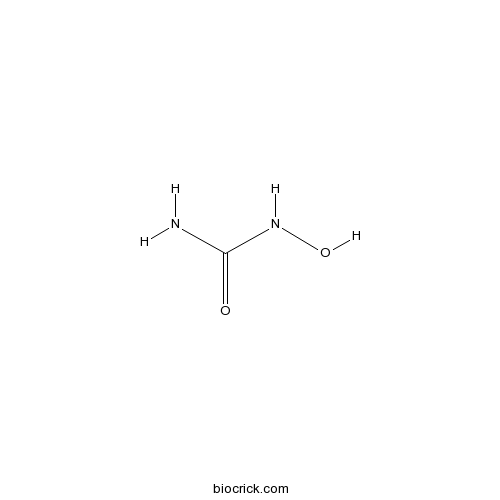
| SMILES | C(=O)(N)NO | ||
| Standard InChIKey | VSNHCAURESNICA-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/CH4N2O2/c2-1(4)3-5/h5H,(H3,2,3,4) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Hydroxyurea is a cell apoptosis inducer that inhibitDNA synthesis through inhibition of ribonucleotide reductase.In Vitro:Hydroxyurea is used in a number of myeloproliferative, neoplastic, HIV, and non-hematological diseases[1]. Treatment of cells in primary culture with 30 μM hydroxyurea for 96 hours significantly increases the fractional HbF content. The Gγ: Aγ-globin mRNA is induced 0.30- to 8-fold in vitro[2]. Hydroxyurea has been shown to block HIV-1 reverse transcription and/or replication in quiescent peripheral blood mononuclear cells and macrophages[3].In Vivo:Hydroxyurea therapy producs consistent reductions in WBC and ANC without improvement in anemia over 17 weeks. Hydroxyurea at 50mg/kg produces a reduced white blood cell count, absolute neutrophil count and no improvement in anemia compared to vehicle treated sickle cell mice[4]. References: | |||||

Hydroxyurea Dilution Calculator

Hydroxyurea Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 13.1492 mL | 65.7462 mL | 131.4924 mL | 262.9849 mL | 328.7311 mL |
| 5 mM | 2.6298 mL | 13.1492 mL | 26.2985 mL | 52.597 mL | 65.7462 mL |
| 10 mM | 1.3149 mL | 6.5746 mL | 13.1492 mL | 26.2985 mL | 32.8731 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.263 mL | 1.3149 mL | 2.6298 mL | 5.2597 mL | 6.5746 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.1315 mL | 0.6575 mL | 1.3149 mL | 2.6298 mL | 3.2873 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Hydroxyurea
- Locustatachykinin I
Catalog No.:BCC5926
CAS No.:126985-97-5
- 1-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-7-(4-hydroxyphenyl)heptane-3,5-diyl diacetate
Catalog No.:BCN6572
CAS No.:1269839-26-0
- 5-Hydroxy-1,7-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)heptan-3-yl acetate
Catalog No.:BCN6586
CAS No.:1269839-24-8
- CDK inhibitor II
Catalog No.:BCC1464
CAS No.:1269815-17-9
- Tetrahydro tanshinone I
Catalog No.:BCN2602
CAS No.:126979-84-8
- Methylenedihydrotanshinquinone
Catalog No.:BCN3221
CAS No.:126979-81-5
- Sar-[D-Phe8]-des-Arg9-Bradykinin
Catalog No.:BCC5996
CAS No.:126959-88-4
- LGX818
Catalog No.:BCC4184
CAS No.:1269440-17-6
- MK 1903
Catalog No.:BCC6242
CAS No.:1268882-43-4
- 3-Methoxy-5-heneicosylphenol
Catalog No.:BCN6147
CAS No.:126882-76-6
- Ssioriside
Catalog No.:BCN6146
CAS No.:126882-53-9
- MC 1046
Catalog No.:BCC1733
CAS No.:126860-83-1
- Sodium acetate
Catalog No.:BCC7587
CAS No.:127-09-3
- Taraxerol
Catalog No.:BCN6148
CAS No.:127-22-0
- Pimaric acid
Catalog No.:BCN6149
CAS No.:127-27-5
- Lasiocarpine N-oxide
Catalog No.:BCN2002
CAS No.:127-30-0
- Lutein
Catalog No.:BCN6151
CAS No.:127-40-2
- Vitamin A Acetate
Catalog No.:BCC4748
CAS No.:127-47-9
- 2,2-Bis(4-hydroxy-3-isopropylphenyl)propane
Catalog No.:BCC8494
CAS No.:127-54-8
- Sulfacetamide Sodium
Catalog No.:BCC4383
CAS No.:127-56-0
- Sulfamerazine sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC5205
CAS No.:127-58-2
- Sulfisoxazole
Catalog No.:BCC4860
CAS No.:127-69-5
- Sulfamerazine
Catalog No.:BCC4854
CAS No.:127-79-7
- Beta-Pinene
Catalog No.:BCC8302
CAS No.:127-91-3
Barriers to hydroxyurea adherence and health-related quality of life in adolescents and young adults with sickle cell disease.[Pubmed:28306171]
Eur J Haematol. 2017 Jun;98(6):608-614.
OBJECTIVES: To identify barriers to Hydroxyurea adherence (negative beliefs, access, and/or recall barriers), and their relationship to adherence rates and health-related quality of life (HRQOL) among adolescents and young adults (AYA) with sickle cell disease (SCD). METHODS: A cross-sectional survey was administered to 34 AYAs (12-22 years old) in SCD clinics from January to December 2015. Study measures included Brief Medication Questionnaire, Modified Morisky Adherence Scale 8-items, visual analog scale, and Patient Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System. RESULTS: Participants (59% male; 91% Black) had a median age of 13.5 years (IQR 12-18). Participants reported negative beliefs (32%), recall barriers (44%), and access barriers (32%). Participants with recall barriers reported worse pain (P=.02), fatigue (P=.05), and depression (P=.05). The number of adherence barriers inversely correlated with adherence level using (c)MMAS-8 (rs =-.38, P=.02) and VASdose (rs =-.25, P=.14) as well as MCV (rs =-.45, P=.01) and HbF% (rs =-.36, P=.05), suggesting higher Hydroxyurea adherence in patients with fewer barriers. CONCLUSIONS: Patients with fewer barriers to Hydroxyurea adherence were more likely to have higher adherence rates and better HRQOL scores. Routine assessment of Hydroxyurea adherence and its related barriers could provide actionable information to improve adherence rates, HRQOL, and other clinical outcomes.


