Neratinib (HKI-272)HER2/EGFR inhibitor,potent and irreversible CAS# 698387-09-6 |
- AG-18
Catalog No.:BCC1051
CAS No.:118409-57-7
- Icotinib Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1639
CAS No.:1204313-51-8
- AZD-9291
Catalog No.:BCC4120
CAS No.:1421373-65-0
- OSI-420
Catalog No.:BCC4472
CAS No.:183320-51-6
- Lapatinib Ditosylate
Catalog No.:BCC2083
CAS No.:388082-78-8
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 698387-09-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 9915743 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C30H29ClN6O3 | M.Wt | 557.04 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | HKI-272 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 20 mg/mL (35.90 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||
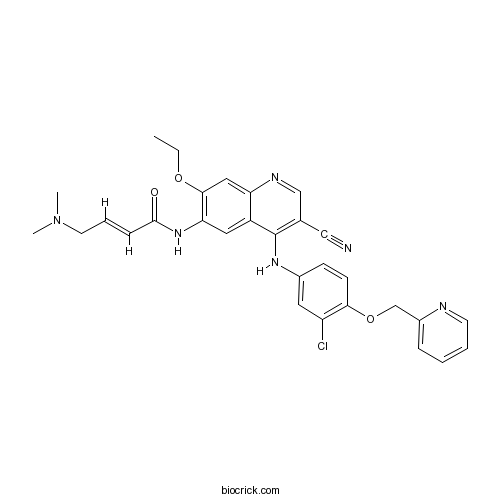
| Chemical Name | (E)-N-[4-[3-chloro-4-(pyridin-2-ylmethoxy)anilino]-3-cyano-7-ethoxyquinolin-6-yl]-4-(dimethylamino)but-2-enamide | ||
| SMILES | CCOC1=C(C=C2C(=C1)N=CC(=C2NC3=CC(=C(C=C3)OCC4=CC=CC=N4)Cl)C#N)NC(=O)C=CCN(C)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | JWNPDZNEKVCWMY-VQHVLOKHSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C30H29ClN6O3/c1-4-39-28-16-25-23(15-26(28)36-29(38)9-7-13-37(2)3)30(20(17-32)18-34-25)35-21-10-11-27(24(31)14-21)40-19-22-8-5-6-12-33-22/h5-12,14-16,18H,4,13,19H2,1-3H3,(H,34,35)(H,36,38)/b9-7+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Neratinib (HKI-272) is a highly selective inhibitor of HER2 and EGFR with IC50 of 59 nM and 92 nM, respectively. | |||||
| Targets | HER2 | EGFR | ||||
| IC50 | 59 nM | 92 nM | ||||

Neratinib (HKI-272) Dilution Calculator

Neratinib (HKI-272) Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.7952 mL | 8.976 mL | 17.952 mL | 35.9041 mL | 44.8801 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.359 mL | 1.7952 mL | 3.5904 mL | 7.1808 mL | 8.976 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1795 mL | 0.8976 mL | 1.7952 mL | 3.5904 mL | 4.488 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0359 mL | 0.1795 mL | 0.359 mL | 0.7181 mL | 0.8976 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.018 mL | 0.0898 mL | 0.1795 mL | 0.359 mL | 0.4488 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
IC50: 59 nM (Her-2); 92 nM (EGFR)
HER-2 belongs to the ErbB family of receptor tyrosine kinases, which has been implicated in a variety of cancers. Overexpression of HER-2 is seen in 25–30% of breast cancer patients and predicts a poor outcome in patients with primary disease. Neratinib (HKI-272) is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor under investigation for the treatment breast cancer and other solid tumours.
In vitro: Neratinib (HKI-272) is a potent inhibitor of HER-2 and is highly active against HER-2-overexpressing human breast cancer cell lines in vitro. It also inhibits the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) kinase and the proliferation of EGFR-dependent cells. Neratinib reduces HER-2 receptor autophosphorylation in cells at doses consistent with inhibition of cell proliferation and functions as an irreversible binding inhibitor, most likely by targeting a cysteine residue in the ATP-binding pocket of the receptor. In agreement with the predicted effects of HER-2 inactivation, Neratinib treatment of cells results in inhibition of downstream signal transduction events and cell cycle regulatory pathways. This leads to arrest at the G1-S (Gap 1/DNA synthesis)-phase transition of the cell division cycle, ultimately resulting in decreased cell proliferation [1].
In vivo: In vivo, Neratinib is active in HER-2- and EGFR-dependent tumor xenograft models when dosed orally on a once daily schedule. On the basis of its favorable preclinical pharmacological profile, Neratinib has been selected as a candidate for additional development as an antitumor agent in breast and other HER-2-dependent cancers [1].
Clinical trial: Neratinib is in development for the treatment of early- and late-stage HER2-positive breast cancer. Neratanib is being developed by Puma Biotechnology. It will be included in the forthcoming I-SPY2 breast cancer trial (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neratinib).
Reference:
[1] Rabindran SK, Discafani CM, Rosfjord EC, Baxter M, Floyd MB, Golas J, Hallett WA, Johnson BD, Nilakantan R, Overbeek E, Reich MF, Shen R, Shi X, Tsou HR, Wang YF, Wissner A. Antitumor activity of HKI-272, an orally active, irreversible inhibitor of the HER-2 tyrosine kinase. Cancer Res. 2004;64(11):3958-65.
- Noradrenaline Bitartrate
Catalog No.:BCC8343
CAS No.:51-40-1
- Agarotetrol
Catalog No.:BCN6763
CAS No.:69809-22-9
- 2,7-Dihydroxy-2H-1,4-benzoxazin-3(4H)-one
Catalog No.:BCN1374
CAS No.:69804-59-7
- Swertiajaponin
Catalog No.:BCN2791
CAS No.:6980-25-2
- UAMC 00039 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6340
CAS No.:697797-51-6
- Elvitegravir (GS-9137)
Catalog No.:BCC2134
CAS No.:697761-98-1
- Antibiotic BU 2313A
Catalog No.:BCN1846
CAS No.:69774-86-3
- 4-(3,4-Dimethoxyphenyl)-3-buten-1-ol
Catalog No.:BCN4258
CAS No.:69768-97-4
- W-9 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6623
CAS No.:69762-85-2
- BIS-TRIS
Catalog No.:BCC8028
CAS No.:6976-37-0
- CRSP-1
Catalog No.:BCC6043
CAS No.:697327-12-1
- Silvestrol
Catalog No.:BCC1948
CAS No.:697235-38-4
- Bourjotinolone A
Catalog No.:BCN4259
CAS No.:6985-35-9
- Boc-Glu(OtBu)-ONp
Catalog No.:BCC3393
CAS No.:69876-58-0
- Petunidin-3-O-glucoside chloride
Catalog No.:BCN3025
CAS No.:6988-81-4
- Pseudoginsenoside F11
Catalog No.:BCN1062
CAS No.:69884-00-0
- Atractylone
Catalog No.:BCN3048
CAS No.:6989-21-5
- Bayogenin
Catalog No.:BCN2458
CAS No.:6989-24-8
- Evodine
Catalog No.:BCN2630
CAS No.:6989-38-4
- (+)-Isoajmaline
Catalog No.:BCN3425
CAS No.:6989-79-3
- Rhapontisterone B
Catalog No.:BCN2664
CAS No.:698975-64-3
- Immethridine dihydrobromide
Catalog No.:BCC7328
CAS No.:699020-93-4
- Cinalbicol
Catalog No.:BCN7464
CAS No.:69904-85-4
- Cyanopindolol hemifumarate
Catalog No.:BCC6880
CAS No.:69906-86-1
Safety, efficacy and pharmacokinetics of neratinib (HKI-272) in Japanese patients with advanced solid tumors: a Phase 1 dose-escalation study.[Pubmed:22371427]
Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2012 Apr;42(4):278-86.
OBJECTIVE: Neratinib (HKI-272), a potent, irreversible, small-molecule, orally administered, pan-ErbB inhibitor that blocks signal transduction via inhibition of three epidermal growth factor receptors [ErbB1, ErbB2 (Her2) and ErbB4], is being developed for the treatment of solid tumors, including breast cancer. This Phase 1 dose-escalation study assessed the safety, tolerability, maximum-tolerated dose, antitumor activity and pharmacokinetics of neratinib in Japanese patients with advanced solid tumors. METHODS: Patients received neratinib 80, 160, 240 or 320 mg orally; each patient enrolled in only one dose cohort. Patients received a single dose in week 1, followed by daily continuous doses. Blood samples collected were on days 1 and 21 for pharmacokinetic analyses. RESULTS: Twenty-one patients were enrolled (3 breast cancer; 17 colorectal cancer; 1 gastric cancer). Neratinib-related adverse events (all grades) included diarrhea (20 patients), fatigue (14 patients), nausea and abdominal pain (9 patients each) and anorexia (8 patients). Grade >/=3 neratinib-related adverse events in two or more patients were diarrhea and anorexia (two patients each). Dose-limiting toxicities were diarrhea and anorexia (two patients, 320 mg dose). The maximum-tolerated dose and recommended dose was neratinib 240 mg once daily. Of 21 evaluable patients, 2 with breast cancer had partial response, 3 had stable disease >/=24 weeks, 7 had stable disease >/=16 weeks and 9 had progressive disease. Pharmacokinetic analyses indicated that neratinib exposures increased with dose. CONCLUSIONS: The safety, efficacy and pharmacokinetic profiles of neratinib are consistent with those reported for non-Japanese patients and warrant further investigation of neratinib in Japanese patients with solid tumors.
Neratinib (HKI-272) in the treatment of breast cancer.[Pubmed:22764764]
Future Oncol. 2012 Jun;8(6):671-81.
Neratinib is an orally available, small, irreversible, pan-HER kinase inhibitor. HER-2-positive breast cancer is a breast cancer subtype with an increasing body of knowledge regarding potential targeted drug combinations that are significantly improving outcomes through a biologically tailored therapy approach; neratinib emerges as a promising tool in this context. This article reviews the molecular and clinical development of neratinib, an example of a covalent drug, from preclinical models to Phase III clinical trials, focusing on breast cancer treatment. The potential combinations of neratinib with chemotherapy in the metastatic, adjuvant and even neoadjuvant settings are appraised. These results and future perspectives will be discussed.
Combination neratinib (HKI-272) and paclitaxel therapy in patients with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer.[Pubmed:23632474]
Br J Cancer. 2013 May 28;108(10):1985-93.
INTRODUCTION: Neratinib is a potent irreversible pan-ErbB tyrosine kinase inhibitor that has demonstrated antitumour activity and an acceptable safety profile in patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor (HER)-2-positive breast cancer and other solid tumours. METHODS: This was a phase I/II, open-label, two-part study. Part 1 was a dose-escalation study to determine the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) of neratinib plus paclitaxel in patients with solid tumours. Part 2 evaluated the safety, efficacy, and pharmacokinetics of the combination at the MTD in patients with HER2-positive breast cancer. RESULTS: Eight patients were included in the dose-escalation study; no dose-limiting toxicities were observed, and an MTD of oral neratinib 240 mg once daily plus intravenous paclitaxel 80 mg m(-2) on days 1, 8, and 15 of each 28-day cycle was determined. A total of 102 patients with HER2-positive breast cancer were enrolled in part 2. The overall median treatment duration was 47.9 weeks (range: 0.1-147.3 weeks). Common treatment-emergent adverse events (all grades/grade >/=3) included diarrhoea (92%/29%; none grade 4), peripheral sensory neuropathy (51%/3%), neutropenia (50%/20%), alopecia (46%/0%), leukopenia (41%/18%), anaemia (37%/8%), and nausea (34%/1%). Three (3%) patients discontinued treatment due to an adverse event (mouth ulceration, left ventricular ejection fraction reduction, and acute renal failure). Among the 99 evaluable patients in part 2 of the study, the overall response rate (ORR) was 73% (95% confidence interval (CI): 62.9-81.2%), including 7 (7%) patients who achieved a complete response; an additional 9 (9%) patients achieved stable disease for at least 24 weeks. ORR was 71% among patients with 0/1 prior chemotherapy regimen for metastatic disease and no prior lapatinib, and 77% among those with 2/3 prior chemotherapy regimens for metastatic disease with prior lapatinib permitted. Kaplan-Meier median progression-free survival was 57.0 weeks (95% CI: 47.7-81.6 weeks). Pharmacokinetic analyses indicated no interaction between neratinib and paclitaxel. CONCLUSION: The combination of neratinib and paclitaxel was associated with higher toxicity than that of neratinib as a single agent, but was manageable with antidiarrhoeal agents and dose reductions in general. The combination therapy also demonstrated a high rate of response in patients with HER2-positive breast cancer. A phase III trial is ongoing to assess the benefit and risk of this combination in the first-line setting.
Safety and efficacy of neratinib (HKI-272) plus vinorelbine in the treatment of patients with ErbB2-positive metastatic breast cancer pretreated with anti-HER2 therapy.[Pubmed:22967996]
Ann Oncol. 2013 Jan;24(1):109-16.
BACKGROUND: Neratinib (HKI-272) is a potent irreversible pan-ErbB tyrosine kinase inhibitor with clinical activity in patients with ErbB2/HER2-positive breast cancer. PATIENTS AND METHODS: Phase I of this open-label, phase I/II study investigated the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) of oral neratinib (160 or 240 mg/day) plus vinorelbine (25 mg/m2; days 1 and 8 of each 21-day cycle) in patients with solid tumors. Phase II assessed the safety, clinical activity, and pharmacokinetics of the combination in patients with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer; the primary efficacy end point was objective response (OR). RESULTS: In phase I (n=12), neratinib (240 mg) plus vinorelbine (25 mg/m2) was established as the MTD. In phase II, 79 patients with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer were treated at the MTD. The most common treatment-related adverse events were diarrhea (96%), neutropenia (54%), and nausea (50%). Three patients discontinued treatment due to diarrhea. No clinically important skin side-effects were observed. The OR rate in assessable phase II patients was 41% (no prior lapatinib) and 8% (prior lapatinib). There was no evidence of pharmacokinetic interaction between neratinib and vinorelbine. CONCLUSION: Neratinib plus vinorelbine showed promising antitumor activity and no unexpected toxic effects in HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer patients. Trial registration ClinicalTrials.gov #NCT00706030.


