PNU 74654CAS# 113906-27-7 |
- PF-562271
Catalog No.:BCC3674
CAS No.:717907-75-0
- TAE226 (NVP-TAE226)
Catalog No.:BCC3885
CAS No.:761437-28-9
- PF-573228
Catalog No.:BCC4496
CAS No.:869288-64-2
- PF-00562271
Catalog No.:BCC3684
CAS No.:939791-38-5
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 113906-27-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 9836739 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C19H16N2O3 | M.Wt | 320.34 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 30 mg/mL (93.65 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
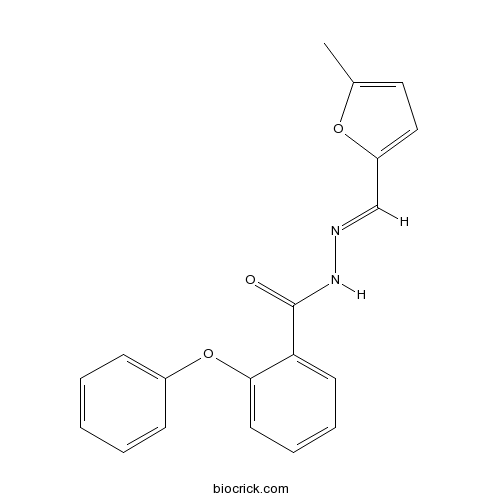
| Chemical Name | N-[(E)-(5-methylfuran-2-yl)methylideneamino]-2-phenoxybenzamide | ||
| SMILES | CC1=CC=C(O1)C=NNC(=O)C2=CC=CC=C2OC3=CC=CC=C3 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | JJEDWBQZCRESJL-DEDYPNTBSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C19H16N2O3/c1-14-11-12-16(23-14)13-20-21-19(22)17-9-5-6-10-18(17)24-15-7-3-2-4-8-15/h2-13H,1H3,(H,21,22)/b20-13+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Binds to β-catenin (KD = 450 nM). Inhibits the interaction between β-catenin and T cell factor 4 (Tcf4) and disrupts the Wnt signaling pathway. |

PNU 74654 Dilution Calculator

PNU 74654 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.1217 mL | 15.6084 mL | 31.2168 mL | 62.4337 mL | 78.0421 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6243 mL | 3.1217 mL | 6.2434 mL | 12.4867 mL | 15.6084 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3122 mL | 1.5608 mL | 3.1217 mL | 6.2434 mL | 7.8042 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0624 mL | 0.3122 mL | 0.6243 mL | 1.2487 mL | 1.5608 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0312 mL | 0.1561 mL | 0.3122 mL | 0.6243 mL | 0.7804 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
PNU-74654 is an inhibitor of Wnt/β-catenin pathway with an IC50 of 129.8 μM in NCI-H295 cell.
In Vitro:PNU-74654 binds to β-catenin with a KD of 450 nM. The Tcf3/Tcf4-binding surface on β-catenin contains a well-defined hot spot around residues K435 and R469. The binding mode of PNU-74654 involves the two narrow pockets on either side of this hot spot[2]. In NCI-H295 cells,PNU-74654 significantly decreases cell proliferation 96 h after treatment, increases early and late apoptosis, decreases nuclear beta-catenin accumulation, impairs CTNNB1/beta-catenin expression and increases beta-catenin target genes 48 h after treatment. No effects are observed on HeLa cells. In NCI-H295 cells, PNU-74654 decreases cortisol, testosterone and androstenedione secretion 24 and 48 h after treatment. The SF1 and CYP21A2 mRNA expression as well as the protein levels of STAR and aldosterone synthase are decreased in NCI-H295 cells after 48 h PNU-74654 treatment. In Y1 cells, PNU-74654 impairs corticosterone secretion 24 h after treatment but does not decrease cell viability[1].
References:
[1]. Leal LF, et al. Inhibition of the Tcf/beta-catenin complex increases apoptosis and impairs adrenocortical tumor cell proliferation and adrenal steroidogenesis. Oncotarget. 2015 Dec 15;6(40):43016-32.
[2]. Trosset JY, et al. Inhibition of protein-protein interactions: the discovery of druglike beta-catenin inhibitors by combining virtual and biophysical screening. Proteins. 2006 Jul 1;64(1):60-7.
- Koumine N-oxide
Catalog No.:BCN4807
CAS No.:113900-75-7
- Caryophyllene oxide
Catalog No.:BCN6019
CAS No.:1139-30-6
- Cinnamyl 3-aminobut-2-enoate
Catalog No.:BCC8914
CAS No.:113898-97-8
- CX-5461
Catalog No.:BCC3700
CAS No.:1138549-36-6
- Cidofovir
Catalog No.:BCC2546
CAS No.:113852-37-2
- N-p-coumaroyl-N'-caffeoylputrescine
Catalog No.:BCN6018
CAS No.:1138156-77-0
- N1,N12-Diethylspermine tetrahydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6669
CAS No.:113812-15-0
- Picrasidine T
Catalog No.:BCN6017
CAS No.:113808-03-0
- Z-Gly-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2770
CAS No.:1138-80-3
- (Z)-FeCP-oxindole
Catalog No.:BCC6079
CAS No.:1137967-28-2
- TAK960
Catalog No.:BCC6411
CAS No.:1137868-52-0
- MDL 72832 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6637
CAS No.:113777-40-5
- PMPA (NMDA antagonist)
Catalog No.:BCC7308
CAS No.:113919-36-1
- Andrographidine C
Catalog No.:BCN4730
CAS No.:113963-39-6
- Andrographidine E
Catalog No.:BCN4729
CAS No.:113963-41-0
- (Z)-Akuammidine
Catalog No.:BCN6020
CAS No.:113973-31-2
- Cefozopran hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC8909
CAS No.:113981-44-5
- 5-Hydroxy-7,8-dimethoxyflavanone
Catalog No.:BCN6021
CAS No.:113981-49-0
- Golgicide A
Catalog No.:BCC4373
CAS No.:1139889-93-2
- Erythromycin
Catalog No.:BCC4778
CAS No.:114-07-8
- Scopolamine hydrobromide
Catalog No.:BCN1199
CAS No.:114-49-8
- Neostigmine Bromide
Catalog No.:BCC4563
CAS No.:114-80-7
- Phenformin
Catalog No.:BCC9120
CAS No.:114-86-3
- Phaclofen
Catalog No.:BCC6562
CAS No.:114012-12-3
Virtual Cross-Linking of the Active Nemorubicin Metabolite PNU-159682 to Double-Stranded DNA.[Pubmed:28068470]
Chem Res Toxicol. 2017 Feb 20;30(2):614-624.
The DNA alkylating mechanism of PNU-159682 (PNU), a highly potent metabolite of the anthracycline nemorubicin, was investigated by gel-electrophoretic, HPLC-UV, and micro-HPLC/mass spectrometry (MS) measurements. PNU quickly reacted with double-stranded oligonucleotides, but not with single-stranded sequences, to form covalent adducts which were detectable by denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (DPAGE). Ion-pair reverse-phase HPLC-UV analysis on CG rich duplex sequences having a 5'-CCCGGG-3' central core showed the formation of two types of adducts with PNU, which were stable and could be characterized by micro-HPLC/MS. The first type contained one alkylated species (and possibly one reversibly bound species), and the second contained two alkylated species per duplex DNA. The covalent adducts were found to produce effective bridging of DNA complementary strands through the formation of virtual cross-links reminiscent of those produced by classical anthracyclines in the presence of formaldehyde. Furthermore, the absence of reactivity of PNU with CG-rich sequence containing a TA core (CGTACG), and the minor reactivity between PNU and CGC sequences (TACGCG.CGCGTA) pointed out the importance of guanine sequence context in modulating DNA alkylation.
Alpha7 Nicotine Acetylcholine Receptor Agonist PNU-282987 Attenuates Acute Lung Injury in a Cardiopulmonary Bypass Model in Rats.[Pubmed:27661000]
Shock. 2017 Apr;47(4):474-479.
OBJECTIVE: Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) carries a risk of lung ischemia-reperfusion, leading to acute lung injury (ALI). Alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (alpha7nAChR) has been implicated in the release of high mobility group box1 (HMGB1), which promotes systemic inflammation in response to ischemia-reperfusion injury. However, the specific role of alpha7nAChR in CPB is poorly understood. This study employed the alpha7nAChR agonist PNU-282987 and a rat model of CPB to determine whether alpha7nAChR was associated with CPB-induced lung damage. METHODS: Thirty Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly divided into five groups as follows: normal group, sham group, CPB group, PNU-282987 plus CPB group, and PNU-282987 plus sham group. Rats were subjected to CPB under anesthesia for 60 min. PNU-282987 (4.8 mg/kg) was administered via arterial inflow. Two hours post-CPB, samples of blood, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF), and lung tissues were processed for investigations. RESULTS: In CPB rats, structural damage in the lung was marked. Density of alpha7nAChR of the lung in the CPB group was significantly less than all other groups, while lung edema, inflammatory markers in serum and lung, protein concentrations in BALF were significantly higher. In the PNU-282987 plus CPB group, by all the above measures the CPB-associated effects were significantly ameliorated but were not identical to the control groups. CONCLUSION: Our results suggest that PNU-282987 affords protective effect against CPB-induced ALI, and inhibits HMGB1 release.
Acute lung injury is reduced by the alpha7nAChR agonist PNU-282987 through changes in the macrophage profile.[Pubmed:27729414]
FASEB J. 2017 Jan;31(1):320-332.
Nicotinic alpha-7 acetylcholine receptor (nAChRalpha7) is a critical regulator of cholinergic anti-inflammatory actions in several diseases, including acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Given the potential importance of alpha7nAChR as a therapeutic target, we evaluated whether PNU-282987, an alpha7nAChR agonist, is effective in protecting the lung against inflammation. We performed intratracheal instillation of LPS to generate acute lung injury (ALI) in C57BL/6 mice. PNU-282987 treatment, either before or after ALI induction, reduced neutrophil recruitment and IL-1beta, TNF-alpha, IL-6, keratinocyte chemoattractant (KC), and IL-10 cytokine levels in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (P < 0.05). In addition, lung NF-kappaB phosphorylation decreased, along with collagen fiber deposition and the number of matrix metalloproteinase-9(+) and -2(+) cells, whereas the number of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1(+) cells increased (P < 0.05). PNU-282987 treatment also reduced lung mRNA levels and the frequency of M1 macrophages, whereas cells expressing the M2-related markers CD206 and IL-10 increased, suggesting changes in the macrophage profile. Finally, PNU-282987 improved lung function in LPS-treated animals. The collective results suggest that PNU-282987, an agonist of alpha7nAChR, reduces LPS-induced experimental ALI, thus supporting the notion that drugs that act on alpha7nAChRs should be explored for ARDS treatment in humans.-Pinheiro, N. M., Santana, F. P. R., Almeida, R. R., Guerreiro, M., Martins, M. A., Caperuto, L. C., Camara, N. O. S., Wensing, L. A., Prado, V. F., Tiberio, I. F. L. C., Prado, M. A. M., Prado, C. M. Acute lung injury is reduced by the alpha7nAChR agonist PNU-282987 through changes in the macrophage profile.
Synthesis of Linezolid Metabolites PNU-142300 and PNU-142586 toward the Exploration of Metabolite-Related Events.[Pubmed:28154311]
Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2017;65(2):194-199.
Linezolid (1) is an oxazolidinone antibiotic that is partially metabolized in vivo via ring cleavage of its morpholine moiety to mainly form two metabolites, PNU-142300 (2) and PNU-142586 (3). It is supposed that accumulation of 2 and 3 in patients with renal insufficiency may cause thrombocytopenia, one of the adverse effects of linezolid. However, the poor availability of 2 and 3 has hindered further investigation of the clinical significance of the accumulation of these metabolites. In this paper, we synthesized metabolites 2 and 3 via a common synthetic intermediate, 4; this will encourage further exploration of events related to these metabolites and lead to improved clinical use of linezolid.
Reaching for high-hanging fruit in drug discovery at protein-protein interfaces.[Pubmed:18075579]
Nature. 2007 Dec 13;450(7172):1001-9.
Targeting the interfaces between proteins has huge therapeutic potential, but discovering small-molecule drugs that disrupt protein-protein interactions is an enormous challenge. Several recent success stories, however, indicate that protein-protein interfaces might be more tractable than has been thought. These studies discovered small molecules that bind with drug-like potencies to 'hotspots' on the contact surfaces involved in protein-protein interactions. Remarkably, these small molecules bind deeper within the contact surface of the target protein, and bind with much higher efficiencies, than do the contact atoms of the natural protein partner. Some of these small molecules are now making their way through clinical trials, so this high-hanging fruit might not be far out of reach.
Inhibition of protein-protein interactions: the discovery of druglike beta-catenin inhibitors by combining virtual and biophysical screening.[Pubmed:16568448]
Proteins. 2006 Jul 1;64(1):60-7.
The interaction between beta-catenin and Tcf family members is crucial for the Wnt signal transduction pathway, which is commonly mutated in cancer. This interaction extends over a very large surface area (4800 A(2)), and inhibiting such interactions using low molecular weight inhibitors is a challenge. However, protein surfaces frequently contain "hot spots," small patches that are the main mediators of binding affinity. By making tight interactions with a hot spot, a small molecule can compete with a protein. The Tcf3/Tcf4-binding surface on beta-catenin contains a well-defined hot spot around residues K435 and R469. A 17,700 compounds subset of the Pharmacia corporate collection was docked to this hot spot with the QXP program; 22 of the best scoring compounds were put into a biophysical (NMR and ITC) screening funnel, where specific binding to beta-catenin, competition with Tcf4 and finally binding constants were determined. This process led to the discovery of three druglike, low molecular weight Tcf4-competitive compounds with the tightest binder having a K(D) of 450 nM. Our approach can be used in several situations (e.g., when selecting compounds from external collections, when no biochemical functional assay is available, or when no HTS is envisioned), and it may be generally applicable to the identification of inhibitors of protein-protein interactions.


