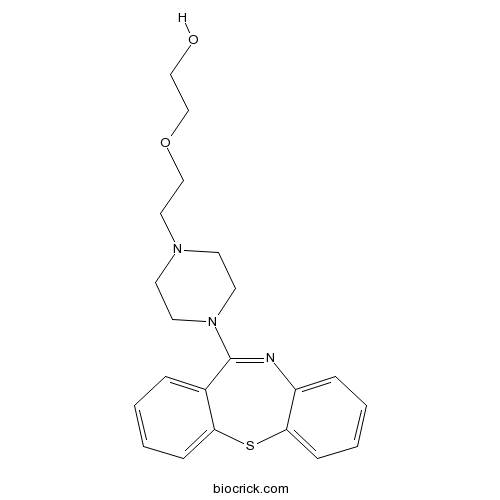
QuetiapineCAS# 111974-69-7 |
- Dexpramipexole dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1528
CAS No.:104632-27-1
- Dexpramipexole
Catalog No.:BCC1527
CAS No.:104632-28-2
- Cariprazine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1454
CAS No.:1083076-69-0
- Cariprazine
Catalog No.:BCC1453
CAS No.:839712-12-8
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 111974-69-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5002 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C21H25N3O2S | M.Wt | 383.51 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||
| Chemical Name | 2-[2-(4-benzo[b][1,4]benzothiazepin-6-ylpiperazin-1-yl)ethoxy]ethanol | ||
| SMILES | C1CN(CCN1CCOCCO)C2=NC3=CC=CC=C3SC4=CC=CC=C42 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | URKOMYMAXPYINW-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C21H25N3O2S/c25-14-16-26-15-13-23-9-11-24(12-10-23)21-17-5-1-3-7-19(17)27-20-8-4-2-6-18(20)22-21/h1-8,25H,9-16H2 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Quetiapine Dilution Calculator

Quetiapine Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6075 mL | 13.0375 mL | 26.0749 mL | 52.1499 mL | 65.1873 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5215 mL | 2.6075 mL | 5.215 mL | 10.43 mL | 13.0375 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2607 mL | 1.3037 mL | 2.6075 mL | 5.215 mL | 6.5187 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0521 mL | 0.2607 mL | 0.5215 mL | 1.043 mL | 1.3037 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0261 mL | 0.1304 mL | 0.2607 mL | 0.5215 mL | 0.6519 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Quetiapine is an atypical antipsychotic approved for the treatment of schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and as an add-on to treat depression. From Wikipedia
- Adenanthin
Catalog No.:BCN6000
CAS No.:111917-59-0
- Temocapril
Catalog No.:BCC5013
CAS No.:111902-57-9
- (1S,3R)-ACPD
Catalog No.:BCC6590
CAS No.:111900-32-4
- MitMAB
Catalog No.:BCC7892
CAS No.:1119-97-7
- 2-Guanidinoethanesulfinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1800
CAS No.:1119-54-6
- H-Arg-OH.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2857
CAS No.:1119-34-2
- H-Glu(OEt)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2930
CAS No.:1119-33-1
- KY 02111
Catalog No.:BCC3628
CAS No.:1118807-13-8
- 2,4-Dihydroxyphenylacetyl-L-asparagine
Catalog No.:BCC6585
CAS No.:111872-98-1
- BIM 23042
Catalog No.:BCC5998
CAS No.:111857-96-6
- UCPH 101
Catalog No.:BCC7692
CAS No.:1118460-77-7
- Hancinone C
Catalog No.:BCN4751
CAS No.:111843-10-8
- Quetiapine fumarate
Catalog No.:BCN5339
CAS No.:111974-72-2
- 2-Undecanone
Catalog No.:BCN8461
CAS No.:112-12-9
- Acetic acid octyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN8303
CAS No.:112-14-1
- Methyl hexadecanoate
Catalog No.:BCN8290
CAS No.:112-39-0
- Methyl Stearate
Catalog No.:BCN8309
CAS No.:112-61-8
- Methyl Oleate
Catalog No.:BCN8306
CAS No.:112-62-9
- Methyl linoleate
Catalog No.:BCN8137
CAS No.:112-63-0
- Oleic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7159
CAS No.:112-80-1
- Docosanoic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8952
CAS No.:112-85-6
- OctMAB
Catalog No.:BCC7893
CAS No.:1120-02-1
- p-Vinylphenyl O-[beta-D-apiofuranosyl-(1-6)]-beta-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN1619
CAS No.:112047-91-3
- Endoxifen
Catalog No.:BCC7761
CAS No.:112093-28-4
Reducing the rehospitalization risk after a manic episode: A population based cohort study of lithium, valproate, olanzapine, quetiapine and aripiprazole in monotherapy and combinations.[Pubmed:28364619]
J Affect Disord. 2017 Aug 1;217:16-23.
BACKGROUND: Data on real-world rehospitalization risks in patients using different drugs and combination therapies for relapse prevention after a manic episode is limited. METHODS: We conducted a nationwide population based cohort study using data from Swedish national registers. Swedish residents aged 18-75 years who were hospitalized for a manic episode between July 1, 2006 and December 2, 2014 were included. Prescription fills of lithium, valproate, olanzapine, Quetiapine and aripiprazole were recorded throughout the first four weeks after hospital discharge, after which the patients were followed for up to one year. General and treatment specific rehospitalization risks were determined and results were adjusted for clinical and sociodemographic factors. RESULTS: The study included follow-up data from 6 502 hospitalizations for mania. Pharmacologic relapse prevention was used after 78% of these hospitalizations. Monotherapies and combination therapies were equally common. The average one-year rehospitalization risk for patients who did versus did not initiate prophylactic treatment was 39% and 46%, respectively. The lowest rehospitalization risks were seen in patients on combination therapy with olanzapine and valproate or olanzapine and lithium, experiencing one year rehospitalization risks of 32% and 34% (adjusted hazard ratios 0.76 (95% confidence interval [CI] 0.62-0.93) and 0.83 (95% CI 0.70-0.98), compared to lithium monotherapy). LIMITATIONS: Register data does not provide information on all clinical parameters affecting treatment choices. CONCLUSIONS: One-year rehospitalization rates after a manic episode are considerable also for patients who initiate prophylactic treatment. Combination therapies including olanzapine and a classic mood-stabilizer may be beneficial for reducing rehospitalization risks after a manic episode.
Quetiapine Misuse and Abuse: Is it an Atypical Paradigm of Drug Seeking Behavior?[Pubmed:28331860]
J Res Pharm Pract. 2017 Jan-Mar;6(1):12-15.
Recent case reports in medical literatures suggest that more and more second-generation atypical antipsychotics (AAs) have been prescribed for off-label use; Quetiapine (Brand name: Seroquel((R))) showed increase in its trend for off-label use. Little is known about the reasons behind this trend, although historical sedative and hypnotic prescription patterns suggest that despite relatively superior safety profiles of Quetiapine (especially for movement disorders), it may be used for treating substance abuse disorder. In addition, recent studies have shown a strong potential for misuse and abuse (MUA) of Quetiapine beyond Food and Drug Administration-approved indications. This includes drug-seeking behaviors, such as feigning symptoms, motivated by Quetiapine and use of Quetiapine in conjunction with alcohol. Quetiapine appears to be the most documented AA with street values bartered illicitly on the street. A recent report from the Drug Abuse Warning Network has shown a high prevalence of Quetiapine-related emergency department visits involving MUA. Several other case studies have found that Quetiapine causes seeking behaviors observed in substance use disorder. In fact, the majority of Quetiapine MUA involved patients diagnosed with substance use disorder. In the absence of a definitive mechanism of action of Quetiapine's reinforcing properties, it is imperative to gather robust evidence to support or refute increasing off-label use of AAs.
Comparison of the Effects of Quetiapine XR and Lithium Monotherapy on Actigraphy-Measured Circadian Parameters in Patients With Bipolar II Depression.[Pubmed:28328790]
J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2017 Jun;37(3):351-354.
PURPOSE/BACKGROUND: The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of Quetiapine XR and lithium on actigraphy-measured circadian parameters in patients with bipolar II depression. METHODS/PROCEDURES: This was an 8-week, open-label, prospective, randomized comparative study. The assessments included the 17-item Hamilton Depression Rating Scale score and actigraphic measures concerning the previous 7 days, collected at each visit (weeks 0 [baseline], 1, 2, 4, 6, and 8); the actigraphic data were analyzed with a cosinor analysis. FINDINGS/RESULTS: Medication, time, and the interaction between medication and time were significantly associated with acrophase for the entire group (Ps = 0.003, 0.020, and 0.042, respectively). More specifically, acrophase was significantly delayed at weeks 1 and 6 (Ps = 0.004 and 0.039, respectively) in the Quetiapine XR group. The F statistics significantly increased over time for the entire group (P < 0.001), and there was a significant increase in F statistics on weeks 4 and 6 in the Quetiapine XR group (Ps = 0.016 and 0.020, respectively) and on weeks 4 and 8 in the lithium group (Ps = 0.001 and 0.016, respectively). In addition, scores on the 17-item Hamilton Depression Rating Scale were significantly associated with the F statistics during 8 weeks for the entire group (P = 0.008). IMPLICATIONS/CONCLUSIONS: Both Quetiapine XR and lithium affected several circadian parameters, including peak activity time and robustness of circadian rhythm, but exerted different effects on acrophase in patients with bipolar II depression. In particular, clinical depressive symptoms were associated with robustness of circadian rhythm during the course of the 8-week treatment.


