BAY 80-6946 (Copanlisib)PI3K inhibitor CAS# 1032568-63-0 |
- Celastrol
Catalog No.:BCN5986
CAS No.:34157-83-0
- BMS-345541
Catalog No.:BCC1423
CAS No.:547757-23-3
- Bay 65-1942 free base
Catalog No.:BCC1408
CAS No.:600734-02-9
- Bay 65-1942 HCl salt
Catalog No.:BCC1409
CAS No.:600734-06-3
- Choline Fenofibrate
Catalog No.:BCC1478
CAS No.:856676-23-8
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1032568-63-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 24989044 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C23H28N8O4 | M.Wt | 480.52 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Copanlisib | ||
| Solubility | 1M HCl : 100 mg/mL (208.11 mM; Need ultrasonic) DMSO : < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||
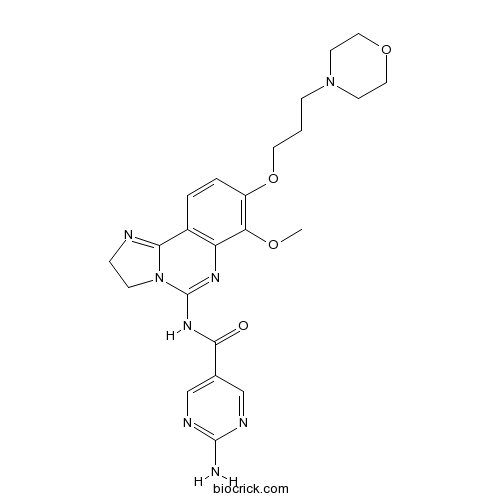
| Chemical Name | 2-amino-N-[7-methoxy-8-(3-morpholin-4-ylpropoxy)-2,3-dihydroimidazo[1,2-c]quinazolin-5-yl]pyrimidine-5-carboxamide | ||
| SMILES | COC1=C(C=CC2=C1N=C(N3C2=NCC3)NC(=O)C4=CN=C(N=C4)N)OCCCN5CCOCC5 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | PZBCKZWLPGJMAO-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C23H28N8O4/c1-33-19-17(35-10-2-6-30-8-11-34-12-9-30)4-3-16-18(19)28-23(31-7-5-25-20(16)31)29-21(32)15-13-26-22(24)27-14-15/h3-4,13-14H,2,5-12H2,1H3,(H2,24,26,27)(H,28,29,32) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | BAY 80-6946 is an ATP-competitive selective class-I PI3 kinases inhibitor, with IC50s of 0.5, 0.7, 3.7 and 6.4 nM for
PI3Kα, PI3Kδ, PI3Kβ and PI3Kγ, and much less active against mTOR (IC50=45 nM) and other PIKs (no inhibition at 1 μM).In Vitro:BAY 80-6946 potently inhibits the catalytic activity of the class I PI3Kα, β, γ, and δ isoforms with IC50s of 0.5, 3.7, 6.4, and 0.7 nM, respectively. BAY 80-6946 shows significantly weaker activity against mTOR with an IC50 of 45 nM. In KPL4 cells, BAY 80-6946 reduces basal levels of AKT phosphorylation at both Thr308 and Ser473 with IC50 values of 0.4 and 0.6 nM, respectively. BAY 80-6946 has mean IC50 values of 19 nM against cell lines with PIK3CA-activating mutations (n = 9) and 17 nM against HER2-positive cell lines (n=7), whereas the activity in PIK3CA wild-type and HER2-negative cells is about 40-fold less potent (average IC50=774 nM; n=11)[1].In Vivo:BAY 80-6946 is highly efficacious in a variety of human tumor xenograft models derived from different tumor indications that exhibit an activated PI3K pathway. BAY 80-6946 is administered at 0.5 to 6 mg/kg i.v. every second day for a total of five doses starting on day 14, following tumor cell implantation. On day 25, 3 days after the last dose, TGI rates of 77%, 84%, 99%, and 100% are observed with BAY 80-6946 at doses of 0.5, 1, 3, and 6 mg/kg, respectively. Complete tumor regression is shown in 10 of 10 rats in the 3 and 6 mg/kg groups, and all rats remained tumor free at the termination of the study on day 73. Tumor growth delays more than 25 days are observed in the 0.5 and 1 mg/kg dose groups[1]. References: | |||||

BAY 80-6946 (Copanlisib) Dilution Calculator

BAY 80-6946 (Copanlisib) Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0811 mL | 10.4054 mL | 20.8108 mL | 41.6216 mL | 52.027 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4162 mL | 2.0811 mL | 4.1622 mL | 8.3243 mL | 10.4054 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2081 mL | 1.0405 mL | 2.0811 mL | 4.1622 mL | 5.2027 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0416 mL | 0.2081 mL | 0.4162 mL | 0.8324 mL | 1.0405 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0208 mL | 0.1041 mL | 0.2081 mL | 0.4162 mL | 0.5203 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Several phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitors are being investigated as a treatment for patients with B-cell malignancies. Such agents prevent activation of PI3K enzymes that are hyperactive in many B-cell malignancies and associated with tumor progression. Copanlisib is a novel pan-Class I phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitor with potent preclinical inhibitory activity against both PI3K-d and PI3K-α isoforms.
In vitro: BAY 80-6946 is a phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitor with potential antineoplastic activity, which inhibits proliferation with IC50 of 147 nM in HuCCT-1 (KRASG12D ) and 137 nM in EGI-1 (KRASG12D ) cell lines [1].
In vivo: BAY 80-6946 is generally well tolerated through the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) of 0.8 mg/kg. pharmacokinetics (PK) results support dosing weekly. Grade 2 or 3 hyperglycemia in the first 24 hrs after receiving a MTD dose. Pharmacokinetics, clinical SD as well as FDG-PET data are consistent with effective exposure and PI3K pathway inhibition. [2].
Clinical trial: Copanlisib (BAY 80-6946), developed by Bayer, is a selective Class I phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitor which has shown promise in Phase I/II clinical trials for the treatment of non-Hodgkin lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Phase II study shows that Copanlisib is active as a single-agent in heavily pretreated, advanced refractory/relapsed FL, MZL, , CLL and SLL. Copanlisib exhibited an acceptable toxicity profile, which was consistent with previous findings (https://ash.confex.com/ash/2014/webprogram/Paper70672.html).
References:
[1] Patnaik A, et al. J Clin Oncol, 29, 2011, (suppl, abstr 3035)
[2] Andrea H, et al. Cancer Res, 2012; 72(8), (suppl, Abstract 869)
- L-655,240
Catalog No.:BCC7156
CAS No.:103253-15-2
- MK-2206 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1274
CAS No.:1032350-13-2
- D-Arabinose
Catalog No.:BCN3791
CAS No.:10323-20-3
- A939572
Catalog No.:BCC5305
CAS No.:1032229-33-6
- Fmoc-Cys(Trt)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3479
CAS No.:103213-32-7
- Fmoc-Tyr(3,5-I2)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3264
CAS No.:103213-31-6
- Pranlukast
Catalog No.:BCC4827
CAS No.:103177-37-3
- 14-Norpseurotin A
Catalog No.:BCN7262
CAS No.:1031727-34-0
- UNC 3230
Catalog No.:BCC5618
CAS No.:1031602-63-7
- 4-(4-(Dimethylamino)-1-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-hydroxybutyl)-3-(hydroxymethyl)benzonitrile hydrobromide
Catalog No.:BCC8648
CAS No.:103146-26-5
- ABT-046
Catalog No.:BCC1326
CAS No.:1031336-60-3
- Kinetensin (human)
Catalog No.:BCC5845
CAS No.:103131-69-7
- GNE-477
Catalog No.:BCC8049
CAS No.:1032754-81-6
- GDC-0980 (RG7422)
Catalog No.:BCC4992
CAS No.:1032754-93-0
- PTIQ
Catalog No.:BCC7953
CAS No.:1032822-42-6
- GSK1292263
Catalog No.:BCC3786
CAS No.:1032823-75-8
- LDK378
Catalog No.:BCC3691
CAS No.:1032900-25-6
- Taltirelin
Catalog No.:BCC5271
CAS No.:103300-74-9
- Pre-schisanartanin B
Catalog No.:BCN5846
CAS No.:1033288-92-4
- 3-Oxo-4-aza-5-alpha-androstane-17β-carboxylic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8641
CAS No.:103335-55-3
- L-364,373
Catalog No.:BCC7445
CAS No.:103342-82-1
- 1-Methyl-L-4,5-dihydroorotic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8472
CAS No.:103365-69-1
- GNE-493
Catalog No.:BCC8048
CAS No.:1033735-94-2
- Itol A
Catalog No.:BCN5847
CAS No.:1033747-78-2
First-in-human phase I study of copanlisib (BAY 80-6946), an intravenous pan-class I phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid tumors and non-Hodgkin's lymphomas.[Pubmed:27672108]
Ann Oncol. 2016 Oct;27(10):1928-40.
BACKGROUND: To evaluate the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and maximum tolerated dose (MTD) of copanlisib, a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid tumors or non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL). PATIENTS AND METHODS: Phase I dose-escalation study including patients with advanced solid tumors or NHL, and a cohort of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Patients received three weekly intravenous infusions of copanlisib per 28-day cycle over the dose range 0.1-1.2 mg/kg. Plasma copanlisib levels were analyzed for pharmacokinetics. Biomarker analysis included PIK3CA, KRAS, BRAF, and PTEN mutational status and PTEN immunohistochemistry. Whole-body [(18)F]-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography ((18)FDG-PET) was carried out at baseline and following the first dose to assess early pharmacodynamic effects. Plasma glucose and insulin levels were evaluated serially. RESULTS: Fifty-seven patients received treatment. The MTD was 0.8 mg/kg copanlisib. The most frequent treatment-related adverse events were nausea and transient hyperglycemia. Copanlisib exposure was dose-proportional with no accumulation; peak exposure positively correlated with transient hyperglycemia post-infusion. Sixteen of 20 patients treated at the MTD had reduced (18)FDG-PET uptake; 7 (33%) had a reduction >25%. One patient achieved a complete response (CR; endometrial carcinoma exhibiting both PIK3CA and PTEN mutations and complete PTEN loss) and two had a partial response (PR; both metastatic breast cancer). Among the nine NHL patients, all six with follicular lymphoma (FL) responded (one CR and five PRs) and one patient with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma had a PR by investigator assessment; two patients with FL who achieved CR (per post hoc independent radiologic review) were on treatment >3 years. CONCLUSION: Copanlisib, dosed intermittently on days 1, 8, and 15 of a 28-day cycle, was well tolerated and the MTD was determined to be 0.8 mg/kg. Copanlisib exhibited dose-proportional pharmacokinetics and promising anti-tumor activity, particularly in patients with NHL. CLINICALTRIALSGOV: NCT00962611; https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00962611.
Discovery and SAR of Novel 2,3-Dihydroimidazo[1,2-c]quinazoline PI3K Inhibitors: Identification of Copanlisib (BAY 80-6946).[Pubmed:27310202]
ChemMedChem. 2016 Jul 19;11(14):1517-30.
The phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) pathway is aberrantly activated in many disease states, including tumor cells, either by growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases or by the genetic mutation and amplification of key pathway components. A variety of PI3K isoforms play differential roles in cancers. As such, the development of PI3K inhibitors from novel compound classes should lead to differential pharmacological and pharmacokinetic profiles and allow exploration in various indications, combinations, and dosing regimens. A screening effort aimed at the identification of PI3Kgamma inhibitors for the treatment of inflammatory diseases led to the discovery of the novel 2,3-dihydroimidazo[1,2-c]quinazoline class of PI3K inhibitors. A subsequent lead optimization program targeting cancer therapy focused on inhibition of PI3Kalpha and PI3Kbeta. Herein, initial structure-activity relationship findings for this class and the optimization that led to the identification of copanlisib (BAY 80-6946) as a clinical candidate for the treatment of solid and hematological tumors are described.


