Baohuoside ICAS# 113558-15-9 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 113558-15-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5488822 | Appearance | Yellow powder |
| Formula | C27H30O10 | M.Wt | 514.52 |
| Type of Compound | Flavonoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Icariin-II; Icariside-II | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 32 mg/mL (62.19 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
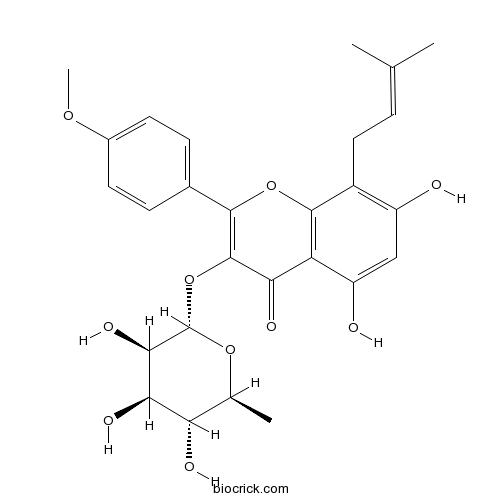
| Chemical Name | 5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-8-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)-3-[(2S,3R,4R,5R,6S)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxychromen-4-one | ||
| SMILES | CC1C(C(C(C(O1)OC2=C(OC3=C(C2=O)C(=CC(=C3CC=C(C)C)O)O)C4=CC=C(C=C4)OC)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | NGMYNFJANBHLKA-LVKFHIPRSA-N | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Baohuoside I is a novel immunosuppressive molecule, exhibits antimetastatic, anti-osteoporosis, anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer activities. Baohuoside I can inhibit the proliferation of Eca-109 cells, this effect associats with down-regulation expression of β-catenin,Cyclin D1,Survivin,and their proteins,which affects on the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. |
| Targets | CXCR | Wnt/β-catenin | ROS | Bcl-2/Bax | Caspase | JNK | p38MAPK |
| In vitro | Effect of baohuoside-I on Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway of human esophageal carcinoma cell Eca-109.[Reference: WebLink]Chinese Traditional & Herbal Drugs, 2011, 42(1):124-6.To study the effect of baohuoside-I extracted from Periplocae Cortex on proliferation and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway of human esophageal carcinoma cell Eca-109. Reactive oxygen species-mediated mitochondrial pathway is involved in Baohuoside I-induced apoptosis in human non-small cell lung cancer.[Pubmed: 22687635]Chem Biol Interact. 2012 Jul 30;199(1):9-17.Baohuoside I (also known as Icariside II) is a flavonoid isolated from Epimedium koreanum Nakai. Although Baohuoside I exhibits anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer activities, its molecular targets/pathways in human lung cancer cells are poorly understood. Therefore, in the present study, we investigated the usefulness of Baohuoside I as a potential apoptosis-inducing cytotoxic agent using human adenocarcinoma alveolar basal epithelial A549 cells as in vitro model.
Baohuoside-1, a novel immunosuppressive molecule, inhibits lymphocyte activation in vitro and in vivo.[Pubmed: 15385801]Transplantation. 2004 Sep 27;78(6):831-8.We evaluated the in vitro and in vivo immunosuppressive effects of Baohuoside I (B1), a novel flavonoid isolated from Epimedium davidii.
|
| Kinase Assay | Baohuoside I suppresses invasion of cervical and breast cancer cells through the downregulation of CXCR4 chemokine receptor expression.[Pubmed: 25407882]Biochemistry. 2014 Dec 9;53(48):7562-9.More than 90 percent of cancer-mediated deaths are due to metastasis, but the mechanisms that control metastasis remain poorly understood.
Thus, the therapy targeting this process has been challenged constantly, but no therapy has yet been approved. CXC chemokine receptor 4 (CXCR4), a Gi protein-coupled receptor for the CXC chemokine ligand (CXCL) 12/stromal cell derived factor (SDF) 1α, is known to be expressed in various tumors.
Recently, the CXCL12/CXCR4 axis has emerged as a key mediator of tumor metastasis; therefore, the possibility that identification of CXCR4 inhibitors can be a promising strategy for abrogating metastasis has been considered.
|
| Cell Research | The flavonoid Baohuoside-I inhibits cell growth and downregulates survivin and cyclin D1 expression in esophageal carcinoma via β-catenin-dependent signaling.[Pubmed: 21785828]Oncol Rep. 2011 Nov;26(5):1149-56.Esophageal cancer is one of the most common malignancies and is associated with a dismal prognosis. Although treatment options have increased for some patients, overall progress has been modest. Thus, there is a great need to develop new treatments. We found that Baohuoside I, a flavonoid extracted from a Chinese medicinal plant, exhibits anticancer activity.
|
| Animal Research | Two-dimensional zebrafish model combined with hyphenated chromatographic techniques for evaluation anti-osteoporosis activity of epimendin A and its metabolite baohuoside I.[Pubmed: 25212043]Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2014 Jun;49(6):932-7.This article firstly established a new efficient method for screening anti-osteoporosis ingredients, which used two-dimensional zebrafish model combined with hyphenated chromatographic techniques to evaluate anti-osteoporosis activities of epimedin A and its metabolite Baohuoside I.
|

Baohuoside I Dilution Calculator

Baohuoside I Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.9436 mL | 9.7178 mL | 19.4356 mL | 38.8712 mL | 48.589 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3887 mL | 1.9436 mL | 3.8871 mL | 7.7742 mL | 9.7178 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1944 mL | 0.9718 mL | 1.9436 mL | 3.8871 mL | 4.8589 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0389 mL | 0.1944 mL | 0.3887 mL | 0.7774 mL | 0.9718 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0194 mL | 0.0972 mL | 0.1944 mL | 0.3887 mL | 0.4859 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Baohuoside I (Icariside-II) is a component of Epimedium koreanum; a regulator of CXCR4 expression as well as function in cervical cancer and breast cancer cells; Apoptosis inducer. IC50 value: Target: CXCR4 expression regulator in vitro: Baohuoside I downregulated CXCR4 expression in a dose- and time-dependent manner in HeLa cells [1]. Treatment with a pharmacological proteasome and lysosomal inhibitors did not have a substantial effect on baohuoside I's ability to suppress CXCR4 expression [1]. Treatment with 50 μm IS resulted in an increased number of apoptotic cells mirrored by increases in cleaved caspase?9 and cleaved PARP. In addition, treatment with 50 μM Icariside-IIsignificantly inhibited the activation of the Janus kinase (JAK)STAT3 and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) ERK pathways, but promoted the activation of the PI3K?AKT pathway [2]. Treatment of A375 cells with IS resulted in an increased number of apoptotic cells ranging from 5.6% to 26.3% mirrored by increases in cleaved caspase-3 and a decrease in survivin expression. IS significantly inhibited the activation of the JAK-STAT3 and MAPK pathways but promoted an unsustained activation peak of the PI3K-AKT pathway [3]. Icariside-II in MCF7 cells produced a loss of mitochondrial membrane potential and release of cytochrome c and apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF), and activation of caspase-9 revealed the involvement of the intrinsic apoptosis pathway. In contrast, IcaS enhanced the expression level of Fas and the Fas-associated death domain (FADD), and activated caspase-8, suggesting the involvement of the extrinsic apoptosis pathway [4]. in vivo: IS administration (50 mg/kg) resulted in a 47.5% decreased tumor volume in A375 bearing mice. IS administration (50 mg/kg, 100 mg/kg) resulted in 41% and 49% decreased tumor volume in B16 bearing mice, respectively [3].
References:
[1]. Kim B, et al. Baohuoside I Suppresses Invasion of Cervical and Breast Cancer Cells through the Downregulation of CXCR4 Chemokine Receptor Expression. Biochemistry. 2014 Dec 9;53(48):7562-9.
[2]. Wu J, et al. Icariside II induces apoptosis via inhibition of the EGFR pathways in A431 human epidermoid carcinoma cells. Mol Med Rep. 2013 Aug;8(2):597-602.
[3]. Wu J, et al. Icariside II induces apoptosis of melanoma cells through the downregulation of survival pathways. Nutr Cancer. 2013;65(1):110-7.
[4]. Huang C, et al. Induction of apoptosis by Icariside II through extrinsic and intrinsic signaling pathways in human breast cancer MCF7 cells. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2012;76(7):1322-8.
- Ikarisoside F
Catalog No.:BCN2284
CAS No.:113558-14-8
- 1,2,3,19-Tetrahydroxy-12-ursen-28-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1615
CAS No.:113558-03-5
- Magnoloside A
Catalog No.:BCN6013
CAS No.:113557-95-2
- Ac-IEPD-AFC
Catalog No.:BCC2358
CAS No.:1135417-31-0
- 25(S)-Hydroxyprotopanaxatriol
Catalog No.:BCN2495
CAS No.:113539-03-0
- 6-Bnz-cAMP sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC8043
CAS No.:1135306-29-4
- Altanserin hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7183
CAS No.:1135280-78-2
- KN-92 phosphate
Catalog No.:BCC1682
CAS No.:1135280-28-2
- 3'-Fluorobenzylspiperone maleate
Catalog No.:BCC6752
CAS No.:1135278-61-3
- CGP 78608 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7087
CAS No.:1135278-54-4
- SR 59230A hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7094
CAS No.:1135278-41-9
- VU 0255035
Catalog No.:BCC7766
CAS No.:1135243-19-4
- E-4031 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7182
CAS No.:113559-13-0
- Q-VD-OPh hydrate
Catalog No.:BCC1125
CAS No.:1135695-98-5
- Tigecycline mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC4229
CAS No.:1135871-27-0
- Orbifloxacin
Catalog No.:BCC4689
CAS No.:113617-63-3
- 6beta-(Hexa-2,4-dienoyloxy)-9alpha,12-dihydroxydrimenol
Catalog No.:BCN7277
CAS No.:1136245-81-2
- Metasequoic acid A
Catalog No.:BCN6652
CAS No.:113626-22-5
- Stigmast-4-ene-3,6-diol
Catalog No.:BCN6014
CAS No.:113626-76-9
- IDE 2
Catalog No.:BCC6099
CAS No.:1136466-93-7
- Ustusolate A
Catalog No.:BCN6756
CAS No.:1136611-58-9
- Neuropeptide Y 13-36 (porcine)
Catalog No.:BCC6959
CAS No.:113662-54-7
- 3-(hydroxymethyl)cyclopentanone
Catalog No.:BCN6015
CAS No.:113681-11-1
- Shizukanolide H
Catalog No.:BCN6016
CAS No.:1136932-34-7
[Two-dimensional zebrafish model combined with hyphenated chromatographic techniques for evaluation anti-osteoporosis activity of epimendin A and its metabolite baohuoside I].[Pubmed:25212043]
Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2014 Jun;49(6):932-7.
This article firstly established a new efficient method for screening anti-osteoporosis ingredients, which used two-dimensional zebrafish model combined with hyphenated chromatographic techniques to evaluate anti-osteoporosis activities of epimedin A and its metabolite Baohuoside I. Adult zebrafish was used for metabolism of epimedin A in 0.5% DMSO, and LC-MS was used for analysis of the metabolite, which was captured by HPLC, and prednisolone-induced osteoporosis model of zebrafish was used to evaluate the anti-osteoporotic activities of trace amounts of epimedin A and Baohuoside I. The results indicated that epimedin A and Baohuoside I can prevent prednisolone-induced osteoporosis in zebrafish. The developed method in this paper enables the separation, enrichment and analysis of micro-amount metabolite of epimedin A, and anti-osteoporosis activities in vivo of epimedin A and Baohuoside I was simple and efficient screening resorting to zebrafish osteoporosis mode. This paper would provide new ideas and methods for a rapid and early discovery of anti-osteoporosis activities of micro-ingredients and its metabolite of traditional Chinese medicine.
The flavonoid Baohuoside-I inhibits cell growth and downregulates survivin and cyclin D1 expression in esophageal carcinoma via beta-catenin-dependent signaling.[Pubmed:21785828]
Oncol Rep. 2011 Nov;26(5):1149-56.
Esophageal cancer is one of the most common malignancies and is associated with a dismal prognosis. Although treatment options have increased for some patients, overall progress has been modest. Thus, there is a great need to develop new treatments. We found that Baohuoside-I, a flavonoid extracted from a Chinese medicinal plant, exhibits anticancer activity. Here, we demonstrated that Baohuoside-I significantly inhibited Eca109 human esophageal squamous carcinoma cell proliferation and induced Eca109 cell apoptosis in vitro and in vivo. The growth inhibitory effect of Baohuoside-I on the Eca109 tumor cell line was examined by MTT assay; the induction of apoptosis was analyzed by flow cytometry. Eca109-luc cells were injected into the subcutaneous tissue of nude mice to establish xenograft tumors. Our results revealed that Baohuoside-I caused a dose- and time-dependent inhibition of cell growth and an induction of apoptosis. Furthermore, Baohuoside-I-treated cells were characterized by decreased expression of the beta-catenin gene and protein in the total cell lysates. Thus, the gene and protein expression of the downstream elements survivin and cyclin D1 was downregulated. To determine the precise inhibitory mechanisms involved, further in-depth in vivo studies of Baohuoside-I are warranted. Our study provides the first evidence that Baohuoside-I inhibits tumor growth and induces apoptosis by inhibiting beta-catenin-dependent signaling pathways. Thus, Baohuoside-I is a potential candidate in ESCC disease therapy.
Baohuoside-1, a novel immunosuppressive molecule, inhibits lymphocyte activation in vitro and in vivo.[Pubmed:15385801]
Transplantation. 2004 Sep 27;78(6):831-8.
BACKGROUND: We evaluated the in vitro and in vivo immunosuppressive effects of baohuoside-1 (B1), a novel flavonoid isolated from Epimedium davidii. METHODS: Proliferation assay was used to determine the antiproliferative properties on T-cell and B-cell proliferation. Flow cytometry analysis was applied to detect changes of phenotypes on activated cells. RESULTS: B1 inhibits the lymphocyte proliferation activated by polyclonal mitogens and mixed lymphocyte reaction with a 50% inhibitory concentration of low micromolar concentration. Also, B1 suppressed T-cell activation in T cell receptor/CD3-mediated signaling pathways in a dose- and time-dependent manner. The suppression of B1 was not simply a result of a toxic effect and was recovered by withdrawing the drug. B1 down-regulated the expression of some phenotype molecules. In Ca(2+)-independent or -dependent antigen stimulation, although B1 had different inhibitive patterns on CD69 expression stimulated by phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) or Ca2+ ionophore, it inhibited T-cell proliferation induced by CD3/CD28 or PMA/ionomycin and partially blocked that induced by PMA/CD28. Interestingly, an additive inhibition between B1 and tacrolimus (FK506) was found in the CD69 expression stimulated by PMA/CD28 and PMA/ionomycin. Similarly, this immunosuppression by combination therapy was observed in a heart transplantation model in vivo and might act through an immunosuppressive mechanism different from FK506. CONCLUSIONS: B1, whose mechanism of action is not similar to that of FK506, has selectively immunosuppressive effects on T-cell and B-cell activation in vitro and effectively prevents rat heart allograft rejection in vivo.
Reactive oxygen species-mediated mitochondrial pathway is involved in Baohuoside I-induced apoptosis in human non-small cell lung cancer.[Pubmed:22687635]
Chem Biol Interact. 2012 Jul 30;199(1):9-17.
Baohuoside I (also known as Icariside II) is a flavonoid isolated from Epimedium koreanum Nakai. Although Baohuoside I exhibits anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer activities, its molecular targets/pathways in human lung cancer cells are poorly understood. Therefore, in the present study, we investigated the usefulness of Baohuoside I as a potential apoptosis-inducing cytotoxic agent using human adenocarcinoma alveolar basal epithelial A549 cells as in vitro model. The apoptosis induced by Baohuoside I in A549 cells was confirmed by annexin V/propidium iodide double staining, cell cycle analysis and dUTP nick end labeling. Further research revealed that Baohuoside I accelerated apoptosis through the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway, involving the increment of BAX/Bcl-2 ratio, dissipation of mitochondrial membrane potential, transposition of cytochrome c, caspase 3 and caspase 9 activation, degradation of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase and the over-production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). A pan-caspase inhibitor, Z-VAD-FMK, only partially prevented apoptosis induced by Baohuoside I, while NAC, a scavenger of ROS, diminished its effect more potently. In addition, the apoptotic effect of Baohuoside I was dependent on the activation of ROS downstream effectors, JNK and p38(MAPK), which could be almost abrogated by using inhibitors SB203580 (an inhibitor of p38(MAPK)) and SP600125 (an inhibitor of JNK). These findings suggested that Baohuoside I might exert its cytotoxic effect via the ROS/MAPK pathway.


