Q-VD-OPh hydrateCell-permeable, irreversible pan-caspase inhibitor CAS# 1135695-98-5 |
- Cisplatin
Catalog No.:BCN1552
CAS No.:14283-03-5
- Z-VAD-FMK
Catalog No.:BCC1126
CAS No.:187389-52-2
- Ac-LEHD-AFC
Catalog No.:BCC2359
CAS No.:210345-03-2
- AZ 10417808
Catalog No.:BCC2356
CAS No.:331645-84-2
- Betulin
Catalog No.:BCN5528
CAS No.:473-98-3
- Apoptosis Activator 2
Catalog No.:BCC2099
CAS No.:79183-19-0
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1135695-98-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 24794416 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C26H25F2N3O6 | M.Wt | 513.49 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | QVD-OPH; Quinoline-Val-Asp-Difluorophenoxymethylketone | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 93.33 mg/mL (181.76 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
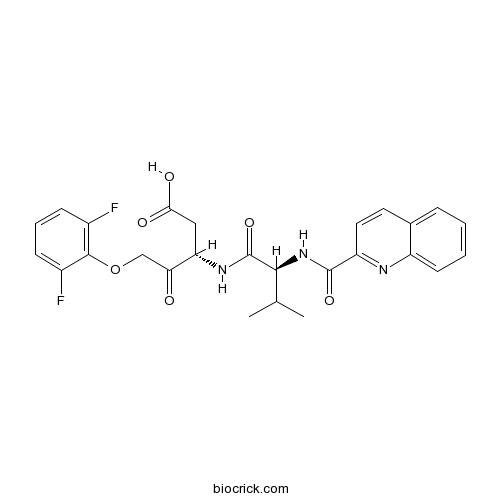
| Chemical Name | (3S)-5-(2,6-difluorophenoxy)-3-[[(2S)-3-methyl-2-(quinoline-2-carbonylamino)butanoyl]amino]-4-oxopentanoic acid | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)C(C(=O)NC(CC(=O)O)C(=O)COC1=C(C=CC=C1F)F)NC(=O)C2=NC3=CC=CC=C3C=C2 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | OOBJCYKITXPCNS-REWPJTCUSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C26H25F2N3O6/c1-14(2)23(31-25(35)19-11-10-15-6-3-4-9-18(15)29-19)26(36)30-20(12-22(33)34)21(32)13-37-24-16(27)7-5-8-17(24)28/h3-11,14,20,23H,12-13H2,1-2H3,(H,30,36)(H,31,35)(H,33,34)/t20-,23-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Q-VD-OPH is a selective, brain and cell permeable, highly potent and irreversible inhibitor of caspase-3 ( IC50=25nm), caspase-1 (IC50=50nM), caspase-8 (IC50=100nM) and caspase-9 (IC50=430nM). | ||||||
| Targets | caspase-1 | caspase-3 | caspase-8 | caspase-9 | |||
| IC50 | 50nM | 25nm | 100nM | 430nM | |||
| Cell experiment[1]: | |
| Cell lines | JURL-MK1 and HL60 cell |
| Preparation method | The solubility of this compound in DMSO is >10 mM. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37 °C for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20°C for several months. |
| Reacting condition | No specific suggestion |
| Applications | Q-VD-OPh largely inhibited caspase-3 and 7 activity at 0.05 mM. Caspase-8 was also inhibited by Q-VD-OPh at very low concentration. Q-VD-OPh prevented the cleavage of PARP-1 at 10 mM . Q-VD-OPh inhibited DNA fragmentation and disruption of the cell membrane functionality at 2 mM, and the drug-induced loss of cellular adhesivity to fibronectin need 10 mM Q-VD-OPh. |
| Animal experiment [2]: | |
| Animal models | TgCRND8 mice in 3 months-old |
| Dosage form | Intraperitoneally Injected with 10 mg/kg QVD-OPh at 3 times a week for 3 months |
| Application | Q-VD-OPh inhibited caspase-7 activation and limited the pathological changes of tau and caspase cleavage in chronic treatment of Alzheimer disease. |
| Other notes | Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
| References: 1. Kuželová K1, Grebeňová D, Brodská B.Dose-dependent effects of the caspase inhibitor Q-VD-OPh on different apoptosis-related processes. J Cell Biochem. 2011 Nov;112(11):3334-42. 2. Rohn TT, Kokoulina P, Eaton CR et al. Caspase activation in transgenic mice with Alzheimer-like pathology: results from a pilot study utilizing the caspase inhibitor, Q-VD-OPh. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2009 Nov 5;2(4):300-8. | |

Q-VD-OPh hydrate Dilution Calculator

Q-VD-OPh hydrate Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.9475 mL | 9.7373 mL | 19.4746 mL | 38.9492 mL | 48.6864 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3895 mL | 1.9475 mL | 3.8949 mL | 7.7898 mL | 9.7373 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1947 mL | 0.9737 mL | 1.9475 mL | 3.8949 mL | 4.8686 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0389 mL | 0.1947 mL | 0.3895 mL | 0.779 mL | 0.9737 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0195 mL | 0.0974 mL | 0.1947 mL | 0.3895 mL | 0.4869 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
The broad spectrum caspase inhibitor, QVD-OPh, provides a cost effective, non toxic, and highly specific means of apoptotic inhibition and provides new insight into the design of new inhibitors1.
Actinomycin D rapidly induced apoptosis and this was dramatically inhibited by the caspase inhibitor, Q-VD-OPh (quinolyl-valyl-O-methylaspartyl-[-2, 6-difluorophenoxy]-methyl ketone). Q-VD-OPh was significantly more effective in preventing apoptosis than the widely used inhibitors, ZVAD-fmk and Boc-D-fmk. Q-VD-OPh was also equally effective in preventing apoptosis mediated by the three major apoptotic pathways, caspase 9/3, caspase 8/10, and caspase 12. In addition to the increased effectiveness, Q-VD-OPh was not toxic to cells, even at high concentrations.
Q-VD-OPh was equally effective at inhibiting the three major apoptotic pathways, was functional in different cell types and species (human, mouse, and rat) and prevented terminal caspase activation, substrate cleavage, and DNA ladder formation associated with apoptosis. Q-VD-OPh can inhibit recombinant caspases 1, 3, 8, and 9 with IC50 values ranging from 25 to 400 nM2. The effectiveness of Q-VD-OPh as an apoptotic inhibitor is evidenced by the complete suppression of an apoptotic inducer capable of inducing substantial cell death in less than 4 hours.
Q-VD-OPh protected against the substantial apoptosis induced by actinomycin D. In addition, Q-VD-OPh alone exhibited little or no toxicity, even at extremely high concentrations.
The effective concentration of Q-VD-OPh may provide a unique reagent when trying to revive hard to propagate cell lines from liquid nitrogen. The addition of this inhibitor to thawed cells would give the cells adequate time to recover, even in the presence of standard DMSO concentrations (10%), from the stress of thawing and begin to proliferate in the absence of toxicity. Q-VD-OPh is stable in solution for several months and is effective in culture for at least 2.5 days. This would provide an ideal time frame for cell recovery; whereas, the subsequent decrease in effectiveness over time would be fortuitous in that the cells would return to standard culture conditions with minimal manipulation1.
References:
1. T. M. Caserta, A. N. Smith, A. D. Gultice, M. A. Reedy and T. L. Brown, Q-VD-OPh, a broad spectrum caspase inhibitor with potent antiapoptotic properties, Apoptosis 2003; 8: 345–352
2. Yin XM. Signal transduction mediated by Bid, a pro-death Bcl-2 family proteins, connects the death receptor and mitochondria apoptosis pathways. Cell Res 2000; 10: 161–167
- E-4031 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7182
CAS No.:113559-13-0
- Baohuoside I
Catalog No.:BCN5350
CAS No.:113558-15-9
- Ikarisoside F
Catalog No.:BCN2284
CAS No.:113558-14-8
- 1,2,3,19-Tetrahydroxy-12-ursen-28-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1615
CAS No.:113558-03-5
- Magnoloside A
Catalog No.:BCN6013
CAS No.:113557-95-2
- Ac-IEPD-AFC
Catalog No.:BCC2358
CAS No.:1135417-31-0
- 25(S)-Hydroxyprotopanaxatriol
Catalog No.:BCN2495
CAS No.:113539-03-0
- 6-Bnz-cAMP sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC8043
CAS No.:1135306-29-4
- Altanserin hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7183
CAS No.:1135280-78-2
- KN-92 phosphate
Catalog No.:BCC1682
CAS No.:1135280-28-2
- 3'-Fluorobenzylspiperone maleate
Catalog No.:BCC6752
CAS No.:1135278-61-3
- CGP 78608 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7087
CAS No.:1135278-54-4
- Tigecycline mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC4229
CAS No.:1135871-27-0
- Orbifloxacin
Catalog No.:BCC4689
CAS No.:113617-63-3
- 6beta-(Hexa-2,4-dienoyloxy)-9alpha,12-dihydroxydrimenol
Catalog No.:BCN7277
CAS No.:1136245-81-2
- Metasequoic acid A
Catalog No.:BCN6652
CAS No.:113626-22-5
- Stigmast-4-ene-3,6-diol
Catalog No.:BCN6014
CAS No.:113626-76-9
- IDE 2
Catalog No.:BCC6099
CAS No.:1136466-93-7
- Ustusolate A
Catalog No.:BCN6756
CAS No.:1136611-58-9
- Neuropeptide Y 13-36 (porcine)
Catalog No.:BCC6959
CAS No.:113662-54-7
- 3-(hydroxymethyl)cyclopentanone
Catalog No.:BCN6015
CAS No.:113681-11-1
- Shizukanolide H
Catalog No.:BCN6016
CAS No.:1136932-34-7
- 4-Aminobenzophenone
Catalog No.:BCC8684
CAS No.:1137-41-3
- BOC-D-ARG-OH.HCL.H2O
Catalog No.:BCC3069
CAS No.:113712-06-4


