TMP269HDAC 4/5/7/9 inhibitor CAS# 1314890-29-3 |
- Valproic acid sodium salt (Sodium valproate)
Catalog No.:BCC2156
CAS No.:1069-66-5
- Vorinostat (SAHA, MK0683)
Catalog No.:BCC2145
CAS No.:149647-78-9
- Resminostat (RAS2410)
Catalog No.:BCC2165
CAS No.:864814-88-0
- PCI-34051
Catalog No.:BCC2148
CAS No.:950762-95-5
- Droxinostat
Catalog No.:BCC2157
CAS No.:99873-43-5
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1314890-29-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 53344908 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C25H21F3N4O3S | M.Wt | 514.52 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 41 mg/mL (79.69 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
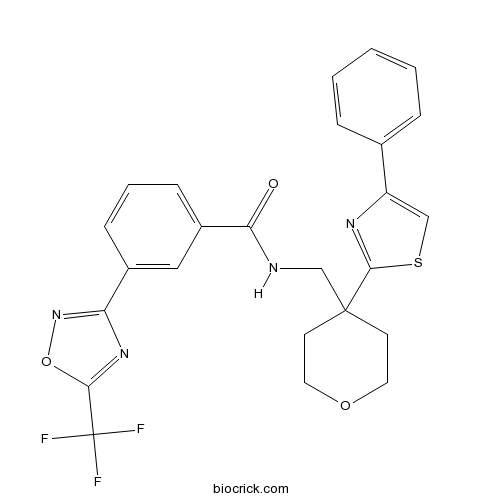
| Chemical Name | N-[[4-(4-phenyl-1,3-thiazol-2-yl)oxan-4-yl]methyl]-3-[5-(trifluoromethyl)-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl]benzamide | ||
| SMILES | C1COCCC1(CNC(=O)C2=CC=CC(=C2)C3=NOC(=N3)C(F)(F)F)C4=NC(=CS4)C5=CC=CC=C5 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | HORXBWNTEDOVKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C25H21F3N4O3S/c26-25(27,28)22-31-20(32-35-22)17-7-4-8-18(13-17)21(33)29-15-24(9-11-34-12-10-24)23-30-19(14-36-23)16-5-2-1-3-6-16/h1-8,13-14H,9-12,15H2,(H,29,33) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | TMP269 is a potent, selective inhibitor of class IIa HDAC with IC50 values of 157 nM, 97 nM, 43 nM and 23 nM for HDAC4, HDAC5, HDAC7 and HDAC9, respectively. | ||||||
| Targets | HDAC9 | HDAC7 | HDAC5 | HDAC4 | |||
| IC50 | 23 nM | 43 nM | 97 nM | 157 nM | |||

TMP269 Dilution Calculator

TMP269 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.9436 mL | 9.7178 mL | 19.4356 mL | 38.8712 mL | 48.589 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3887 mL | 1.9436 mL | 3.8871 mL | 7.7742 mL | 9.7178 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1944 mL | 0.9718 mL | 1.9436 mL | 3.8871 mL | 4.8589 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0389 mL | 0.1944 mL | 0.3887 mL | 0.7774 mL | 0.9718 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0194 mL | 0.0972 mL | 0.1944 mL | 0.3887 mL | 0.4859 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
TMP269 is a novel and selective inhibitor of class IIa histone deacetylase with IC50 values of 126, 80, 36, 9 nM for HDAC 4, 5, 7, 9, respectively [1].
Histone deacetylases (HADC) are a series of enzymes that remove acetyl groups from an ε-N-acetyl lysine amino acid on a histone and make the histones to wrap the DNA more tightly, which prevent transcription.
TMP269 is a novel and selective class IIa HDAC inhibitor. In MM cell lines, TMP269 induced modest cytotoxicity with IC50 values ranging from 22 to 38 μM in a dose-dependent way, which was associated with cleavage of caspase-3, -8, -9 and PARP. Also, TMP269 enhanced CFZ-induced apoptosis and increased the expression of activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4) and proapoptotic transcription factor C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP). In the presence of BMSCs or IL-6, TMP269 and CFZ also showed significant cytotoxicity [2]. In IEC-18 intestinal epithelial cells, TMP269 inhibited cell proliferation, cell cycle progression and DNA synthesis in response to G protein-coupled receptor/protein kinase D1 (PKD1) activation [3].
References:
[1]. Lobera M, Madauss KP, Pohlhaus DT, et al. Selective class IIa histone deacetylase inhibition via a nonchelating zinc-binding group. Nat Chem Biol, 2013, 9(5): 319-325.
[2]. Kikuchi S, Suzuki R, Ohguchi H, et al. Class IIa HDAC inhibition enhances ER stress-mediated cell death in multiple myeloma. Leukemia, 2015.
[3]. Sinnett-Smith J, Ni Y, Wang J, et al. Protein kinase D1 mediates class IIa histone deacetylase phosphorylation and nuclear extrusion in intestinal epithelial cells: role in mitogenic signaling. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol, 2014, 306(10): C961-71.
- Amyloid Beta-Peptide (1-40) (human)
Catalog No.:BCC1045
CAS No.:131438-79-4
- Cercosporamide
Catalog No.:BCC2438
CAS No.:131436-22-1
- UNC669
Catalog No.:BCC3997
CAS No.:1314241-44-5
- TC-N 22A
Catalog No.:BCC6150
CAS No.:1314140-00-5
- Hemopressin (human, mouse)
Catalog No.:BCC6065
CAS No.:1314035-51-2
- CBZ-Osu
Catalog No.:BCC2798
CAS No.:13139-17-8
- Boc-Ile-OH.1/2H2O
Catalog No.:BCC3406
CAS No.:13139-16-7
- Boc-Leu-OH.H2O
Catalog No.:BCC3408
CAS No.:13139-15-6
- Boc-Trp-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3455
CAS No.:13139-14-5
- Teijin compound 1
Catalog No.:BCC6057
CAS No.:1313730-14-1
- Periplocin
Catalog No.:BCN2655
CAS No.:13137-64-9
- erythro-Guaiacylglycerol beta-threo-syringylglycerol ether
Catalog No.:BCN7333
CAS No.:1313434-74-0
- HG6-64-1
Catalog No.:BCC5459
CAS No.:1315329-43-1
- B-Raf inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC1437
CAS No.:1315330-11-0
- NG25
Catalog No.:BCC1799
CAS No.:1315355-93-1
- pep2-EVKI
Catalog No.:BCC5786
CAS No.:1315378-67-6
- pep2-AVKI
Catalog No.:BCC5787
CAS No.:1315378-69-8
- TCS 184
Catalog No.:BCC5899
CAS No.:1315378-71-2
- Scrambled 10Panx
Catalog No.:BCC1246
CAS No.:1315378-72-3
- PDZ1 Domain inhibitor peptide
Catalog No.:BCC5883
CAS No.:1315378-73-4
- Bax inhibitor peptide, negative control
Catalog No.:BCC2395
CAS No.:1315378-74-5
- MNI caged kainic acid
Catalog No.:BCC7297
CAS No.:1315378-75-6
- pep2-SVKE
Catalog No.:BCC5785
CAS No.:1315378-76-7
- Rac1 Inhibitor F56, control peptide
Catalog No.:BCC5887
CAS No.:1315378-77-8
Suppression of triple-negative breast cancer metastasis by pan-DAC inhibitor panobinostat via inhibition of ZEB family of EMT master regulators.[Pubmed:24810497]
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2014 Jun;145(3):593-604.
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is a highly aggressive breast cancer subtype that lacks effective targeted therapies. The epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is a key contributor in the metastatic process. We previously showed the pan-deacetylase inhibitor LBH589 induces CDH1 expression in TNBC cells, suggesting regulation of EMT. The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of LBH589 on the metastatic qualities of TNBC cells and the role of EMT in this process. A panel of breast cancer cell lines (MCF-7, MDA-MB-231, and BT-549), drugged with LBH589, was examined for changes in cell morphology, migration, and invasion in vitro. The effect on in vivo metastasis was examined using immunofluorescent staining of lung sections. EMT gene expression profiling was used to determine LBH589-induced changes in TNBC cells. ZEB overexpression studies were conducted to validate requirement of ZEB in LBH589-mediated proliferation and tumorigenesis. Our results indicate a reversal of EMT by LBH589 as demonstrated by altered morphology and altered gene expression in TNBC. LBH589 was shown to be a more potent inhibitor of EMT than other HDAC inhibitors, SAHA and TMP269. Additionally, we found that LBH589 inhibits metastasis of MDA-MB-231 cells in vivo. These effects of LBH589 were mediated in part by inhibition of ZEB, as overexpression of ZEB1 or ZEB2 mitigated the effects of LBH589 on MDA-MB-231 EMT-associated gene expression, migration, invasion, CDH1 expression, and tumorigenesis. These data indicate therapeutic potential of LBH589 in targeting EMT and metastasis of TNBC.
Protein kinase D1 mediates class IIa histone deacetylase phosphorylation and nuclear extrusion in intestinal epithelial cells: role in mitogenic signaling.[Pubmed:24647541]
Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2014 May 15;306(10):C961-71.
We examined whether class IIa histone deacetylases (HDACs) play a role in mitogenic signaling mediated by protein kinase D1 (PKD1) in IEC-18 intestinal epithelial cells. Our results show that class IIa HDAC4, HDAC5, and HDAC7 are prominently expressed in these cells. Stimulation with ANG II, a potent mitogen for IEC-18 cells, induced a striking increase in phosphorylation of HDAC4 at Ser(246) and Ser(632), HDAC5 at Ser(259) and Ser(498), and HDAC7 at Ser(155). Treatment with the PKD family inhibitors kb NB 142-70 and CRT0066101 or small interfering RNA-mediated knockdown of PKD1 prevented ANG II-induced phosphorylation of HDAC4, HDAC5, and HDAC7. A variety of PKD1 activators in IEC-18 cells, including vasopressin, lysophosphatidic acid, and phorbol esters, also induced HDAC4, HDAC5, and HDAC7 phosphorylation. Using endogenously and ectopically expressed HDAC5, we show that PKD1-mediated phosphorylation of HDAC5 induces its nuclear extrusion into the cytoplasm. In contrast, HDAC5 with Ser(259) and Ser(498) mutated to Ala was localized to the nucleus in unstimulated and stimulated cells. Treatment of IEC-18 cells with specific inhibitors of class IIa HDACs, including MC1568 and TMP269, prevented cell cycle progression, DNA synthesis, and proliferation induced in response to G protein-coupled receptor/PKD1 activation. The PKD1-class IIa HDAC axis also functions in intestinal epithelial cells in vivo, since an increase in phosphorylation of HDAC4/5 and HDAC7 was demonstrated in lysates of crypt cells from PKD1 transgenic mice compared with matched nontransgenic littermates. Collectively, our results reveal a PKD1-class IIa HDAC axis in intestinal epithelial cells leading to mitogenic signaling.
Class IIa HDAC inhibition enhances ER stress-mediated cell death in multiple myeloma.[Pubmed:25801913]
Leukemia. 2015 Sep;29(9):1918-27.
Histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors have been extensively investigated as therapeutic agents in cancer. However, the biological role of class IIa HDACs (HDAC4, 5, 7 and 9) in cancer cells, including multiple myeloma (MM), remains unclear. Recent studies show HDAC4 interacts with activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4) and inhibits activation of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress-associated proapoptotic transcription factor C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP). In this study, we hypothesized that HDAC4 knockdown and/or inhibition could enhance apoptosis in MM cells under ER stress condition by upregulating ATF4, followed by CHOP. HDAC4 knockdown showed modest cell growth inhibition; however, it markedly enhanced cytotoxicity induced by either tunicamycin or carfilzomib (CFZ), associated with upregulating ATF4 and CHOP. For pharmacological inhibition of HDAC4, we employed a novel and selective class IIa HDAC inhibitor TMP269, alone and in combination with CFZ. As with HDAC4 knockdown, TMP269 significantly enhanced cytotoxicity induced by CFZ in MM cell lines, upregulating ATF4 and CHOP and inducing apoptosis. Conversely, enhanced cytotoxicity was abrogated by ATF4 knockdown, confirming that ATF4 has a pivotal role mediating cytotoxicity in this setting. These results provide the rationale for novel treatment strategies combining class IIa HDAC inhibitors with ER stressors, including proteasome inhibitors, to improve patient outcome in MM.


