CAY10603CAS# 1045792-66-2 |
- CI994 (Tacedinaline)
Catalog No.:BCC2159
CAS No.:112522-64-2
- Tubastatin A HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3877
CAS No.:1310693-92-5
- M344
Catalog No.:BCC2162
CAS No.:251456-60-7
- AR-42 (OSU-HDAC42)
Catalog No.:BCC2161
CAS No.:935881-37-1
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1045792-66-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 24951314 | Appearance | Powder |
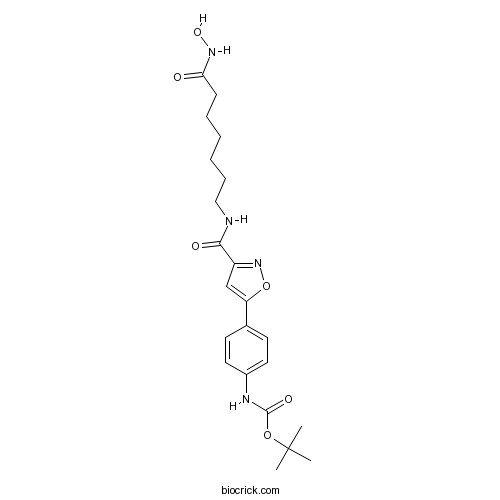
| Formula | C22H30N4O6 | M.Wt | 446.5 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 50 mg/mL (111.98 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | tert-butyl N-[4-[3-[[7-(hydroxyamino)-7-oxoheptyl]carbamoyl]-1,2-oxazol-5-yl]phenyl]carbamate | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)(C)OC(=O)NC1=CC=C(C=C1)C2=CC(=NO2)C(=O)NCCCCCCC(=O)NO | ||
| Standard InChIKey | WWGBHDIHIVGYLZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C22H30N4O6/c1-22(2,3)31-21(29)24-16-11-9-15(10-12-16)18-14-17(26-32-18)20(28)23-13-7-5-4-6-8-19(27)25-30/h9-12,14,30H,4-8,13H2,1-3H3,(H,23,28)(H,24,29)(H,25,27) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

CAY10603 Dilution Calculator

CAY10603 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2396 mL | 11.1982 mL | 22.3964 mL | 44.7928 mL | 55.991 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4479 mL | 2.2396 mL | 4.4793 mL | 8.9586 mL | 11.1982 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.224 mL | 1.1198 mL | 2.2396 mL | 4.4793 mL | 5.5991 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0448 mL | 0.224 mL | 0.4479 mL | 0.8959 mL | 1.1198 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0224 mL | 0.112 mL | 0.224 mL | 0.4479 mL | 0.5599 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
CAY10603 is a potent and selective HDAC6 inhibitor, with an IC50 of 2 pM; CAY10603 also inhibits HDAC1, HDAC2, HDAC3, HDAC8, HDAC10, with IC50s of 271, 252, 0.42, 6851, 90.7 nM.
In Vitro:CAY10603 (Compound 7) shows potent inhibitory activities against pancreatic cancer cell lines, with IC50s of 1, 0.3, 0.1, 0.1, 0.6, <1, 0.5 μM for BxPC-3, HupT3, Mia Paca-2, Panc 04.03, SU.86.86, HMEC, HPDE6c7, respectively. CAY10603 (100 nM, 200-300 nM) is active against both the Mia Paca-2 and Panc04.03 cell lines[1]. CAY10603 inhibits HDAC6 deacetylase activity, and supresses the proliferation of lung adenocarcinoma cells. CAY10603 also induces apoptosis of lung adenocarcinoma cells. Furthermore, CAY10603 synergizes with gefitinib to induce apoptosis in lung adenocarcinoma cell lines, partly through the destabilization of EGFR and inactivation of the EGFR pathway[2].
References:
[1]. Kozikowski AP, et al. Use of the nitrile oxide cycloaddition (NOC) reaction for molecular probe generation: a new class of enzyme selective histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACIs) showing picomolar activity at HDAC6. J Med Chem. 2008 Aug 14;51(15):4370-3.
[2]. Wang Z, et al. HDAC6 promotes cell proliferation and confers resistance to gefitinib in lung adenocarcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2016 Jul;36(1):589-97.
- EC 23
Catalog No.:BCC6097
CAS No.:104561-41-3
- Bayogenin 3-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN7868
CAS No.:104513-86-2
- Testosterone acetate
Catalog No.:BCC9165
CAS No.:1045-69-8
- RVX-208
Catalog No.:BCC4475
CAS No.:1044870-39-4
- 3'-Methylflavokawin
Catalog No.:BCN3990
CAS No.:1044743-35-2
- Typhaneoside
Catalog No.:BCN4994
CAS No.:104472-68-6
- L803-mts
Catalog No.:BCC5889
CAS No.:1043881-55-5
- RU-SKI 43
Catalog No.:BCC5441
CAS No.:1043797-53-0
- Tetrahydroxysqualene
Catalog No.:BCN5858
CAS No.:1043629-23-7
- Bisoprolol fumarate
Catalog No.:BCC4344
CAS No.:104344-23-2
- IRAK inhibitor 6
Catalog No.:BCC1658
CAS No.:1042672-97-8
- Famciclovir
Catalog No.:BCC4780
CAS No.:104227-87-4
- p-Menthan-3-one
Catalog No.:BCN3850
CAS No.:10458-14-7
- Caffeic acid phenethyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN2695
CAS No.:104594-70-9
- CGS 15943
Catalog No.:BCC7157
CAS No.:104615-18-1
- Pramipexole dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCN2181
CAS No.:104632-25-9
- Pramipexole
Catalog No.:BCC4467
CAS No.:104632-26-0
- Dexpramipexole dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1528
CAS No.:104632-27-1
- Dexpramipexole
Catalog No.:BCC1527
CAS No.:104632-28-2
- H-Ile-NH2.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2962
CAS No.:10466-56-5
- 7,3'-Di-O-methylorobol
Catalog No.:BCN6831
CAS No.:104668-88-4
- Iriflophenone 3-C-beta-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN1635
CAS No.:104669-02-5
- Lupiwighteone
Catalog No.:BCN4045
CAS No.:104691-86-3
- Ganoderic acid K
Catalog No.:BCN3039
CAS No.:104700-95-0
HDAC6 inhibition blocks inflammatory signaling and caspase-1 activation in LPS-induced acute lung injury.[Pubmed:30910594]
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2019 May 1;370:178-183.
HDAC6 is a member of the class II histone deacetylase. HDAC6 inhibition possesses anti-inflammatory effects. However, the effects of HDAC6 inhibition in acute lung inflammation have not been studied. Here, we investigated the effects of a highly selective and potent HDAC6 inhibitor CAY10603 in LPS-induced acute inflammatory lung injury. We also conducted a series of experiments including immunoblotting, ELISA, and histological assays to explore the inflammatory signaling pathways modulated by the selective HDAC6 inhibition. We observed that HDAC6 activity was increased in the lung tissues after LPS challenge, which was associated with a decreased level of a-tubulin acetylation in the lung tissues. HDAC6 inhibition by CAY10603 prevented LPS-induced a-tubulin deacetylation in the lung tissues. HDAC6 inhibition also exhibited protective effects against LPS-induced acute lung inflammation, which was demonstrated by the reduced production of pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-alpha, IL-1beta, and IL-6 and decreased leukocyte infiltration. Furthermore, HDAC6 inhibition blocked the decrease of E-cadherin level and inhibited the increase of MMP9 expression in the lung tissues, which could prevent the destruction of the lung architecture in LPS-induced inflammatory injury. Given the important roles of NFkB and inflammasome activation in inflammatory responses, we investigated their regulation by HDAC6 inhibition in LPS-induced lung injury. Our results showed that HDAC6 inhibition blocked the activation of NFkB by inhibiting IkB phosphorylation in LPS-induced acute lung injury, and LPS-induced-inflammasome activity was reduced by HDAC6 inhibition as demonstrated by the decreased IL-1beta and caspase-1 cleavage and activation. Collectively, our data suggest that selective HDAC6 inhibition suppresses inflammatory signaling pathways and alleviates LPS-induced acute lung inflammation.
Structural and energetic basis for the inhibitory selectivity of both catalytic domains of dimeric HDAC6.[Pubmed:30558483]
J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2018 Dec 17:1-20.
HDAC6 is a protein involved in cancer, neurodegenerative disease and inflammatory disorders. To date, the full three-dimensional (3D) structure of human HDAC6 has not been elucidated; however, there are some experimental 3D structural homologs to HDAC6 that can be used as templates. In this work, we utilized molecular modeling procedures to model both of the catalytic domains of HDAC6 connected by the linker region where DMB region is placed. Once the 3D structure of human HDAC6 was obtained, it was structurally evaluated and submitted to docking and molecular dynamic (MD) simulations along with Molecular Mechanics/Generalized Born Surface Area (MM/GBSA) method to explore the stability and the binding free energy properties of the HDAC6-ligand complexes. In addition, its structural and energetic behavior was explored with each one of the catalytic domains in the molecular recognition of six selective HDAC6 inhibitors, HPOB, CAY10603, Nexturastat, Rocilinostat, Tubacin and Tubastatin A for DD2, and with the so-called 9-peptide which is DD1-HDAC6 selective substrate. The use of the whole system (DD1-DMB-DD2) showed a tendency toward the ligand affinity of DD2, CAY10603> Tubacin > Rocilinostat > Nexturastat > HPOB > Tubastatin > 9-peptide, which is in line with experimental reports. However, 9-peptide showed a higher affinity for DD1, which agrees with experimental reports elsewhere. Principal component analysis provided important information about the structural changes linked to the molecular recognition process, whereas per-residue decomposition analysis revealed the energetic contribution of the key residues in the molecular binding and structural characteristics that could assist in drug design.
HDAC6 promotes cell proliferation and confers resistance to gefitinib in lung adenocarcinoma.[Pubmed:27221381]
Oncol Rep. 2016 Jul;36(1):589-97.
Histone deacetylases (HDACs) are promising targets for cancer therapy, and first-generation HDAC inhibitors are currently in clinical trials for the treatment of cancer patients. HDAC6, which is a key regulator of many signaling pathways that are linked to cancer, has recently emerged as an attractive target for the treatment of cancer. In the present study, HDAC6 was found to be overexpressed in lung adenocarcinoma cell lines and was negatively correlated with the prognosis of patients with lung adenocarcinoma. Overexpression of HDAC6 promoted the proliferation of lung adenocarcinoma cells in a deacetylase activity-dependent manner. HDAC6 overexpression conferred resistance to gefitinib via the stabilization of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). The inhibition of HDAC6 by CAY10603, a potent and selective inhibitor of HDAC6, inhibited the proliferation of lung adenocarcinoma cells and induced apoptosis. CAY10603 downregulated the levels of EGFR protein, which in turn inhibited activation of the EGFR signaling pathway. Moreover, CAY10603 synergized with gefitinib to induce apoptosis of the lung adenocarcinoma cell lines via the destabilization of EGFR. Taken together, our results suggest that the inhibition of HDAC6 may be a promising strategy for the treatment of lung adenocarcinoma.


