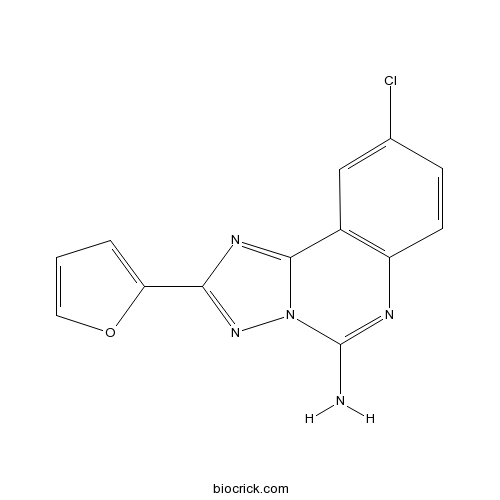
CGS 15943Potent adenosine receptor antagonist CAS# 104615-18-1 |
- LY2835219
Catalog No.:BCC1113
CAS No.:1231930-82-7
- Roscovitine (Seliciclib,CYC202)
Catalog No.:BCC1105
CAS No.:186692-46-6
- Nu 6027
Catalog No.:BCC1154
CAS No.:220036-08-8
- SNS-032 (BMS-387032)
Catalog No.:BCC1152
CAS No.:345627-80-7
- AT7519 Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1376
CAS No.:902135-91-5
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 104615-18-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 2690 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C13H8ClN5O | M.Wt | 285.69 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 5 mM in DMSO | ||
| Chemical Name | 9-chloro-2-(furan-2-yl)-[1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-c]quinazolin-5-amine | ||
| SMILES | C1=COC(=C1)C2=NN3C(=N2)C4=C(C=CC(=C4)Cl)N=C3N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | MSJODEOZODDVGW-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C13H8ClN5O/c14-7-3-4-9-8(6-7)12-17-11(10-2-1-5-20-10)18-19(12)13(15)16-9/h1-6H,(H2,15,16) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent adenosine receptor antagonist (Ki values are 3.5, 4.2, 16 and 51 nM for human A1, A2A, A2B and A3 receptors respectively). Orally active in vivo. |

CGS 15943 Dilution Calculator

CGS 15943 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.5003 mL | 17.5015 mL | 35.003 mL | 70.006 mL | 87.5074 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.7001 mL | 3.5003 mL | 7.0006 mL | 14.0012 mL | 17.5015 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.35 mL | 1.7501 mL | 3.5003 mL | 7.0006 mL | 8.7507 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.07 mL | 0.35 mL | 0.7001 mL | 1.4001 mL | 1.7501 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.035 mL | 0.175 mL | 0.35 mL | 0.7001 mL | 0.8751 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Caffeic acid phenethyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN2695
CAS No.:104594-70-9
- p-Menthan-3-one
Catalog No.:BCN3850
CAS No.:10458-14-7
- CAY10603
Catalog No.:BCC5542
CAS No.:1045792-66-2
- EC 23
Catalog No.:BCC6097
CAS No.:104561-41-3
- Bayogenin 3-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN7868
CAS No.:104513-86-2
- Testosterone acetate
Catalog No.:BCC9165
CAS No.:1045-69-8
- RVX-208
Catalog No.:BCC4475
CAS No.:1044870-39-4
- 3'-Methylflavokawin
Catalog No.:BCN3990
CAS No.:1044743-35-2
- Typhaneoside
Catalog No.:BCN4994
CAS No.:104472-68-6
- L803-mts
Catalog No.:BCC5889
CAS No.:1043881-55-5
- RU-SKI 43
Catalog No.:BCC5441
CAS No.:1043797-53-0
- Tetrahydroxysqualene
Catalog No.:BCN5858
CAS No.:1043629-23-7
- Pramipexole dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCN2181
CAS No.:104632-25-9
- Pramipexole
Catalog No.:BCC4467
CAS No.:104632-26-0
- Dexpramipexole dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1528
CAS No.:104632-27-1
- Dexpramipexole
Catalog No.:BCC1527
CAS No.:104632-28-2
- H-Ile-NH2.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2962
CAS No.:10466-56-5
- 7,3'-Di-O-methylorobol
Catalog No.:BCN6831
CAS No.:104668-88-4
- Iriflophenone 3-C-beta-D-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN1635
CAS No.:104669-02-5
- Lupiwighteone
Catalog No.:BCN4045
CAS No.:104691-86-3
- Ganoderic acid K
Catalog No.:BCN3039
CAS No.:104700-95-0
- Ganoderol B
Catalog No.:BCN5859
CAS No.:104700-96-1
- Ganoderol A
Catalog No.:BCN5860
CAS No.:104700-97-2
- Ganoderal A
Catalog No.:BCN2451
CAS No.:104700-98-3
Comparison of CGS 15943, ZM 241385 and SCH 58261 as antagonists at human adenosine receptors.[Pubmed:9933143]
Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1999 Jan;359(1):7-10.
Three structurally related non-xanthine compounds, CGS 15943, ZM 241385 and SCH 58261, are potent A2A adenosine receptor antagonists and have been used as tools in many pharmacological studies. We have now characterized their affinity and selectivity profile on human adenosine receptors stably transfected into either CHO cells (A1 and A2B receptors) or HEK-293 cells (A2A and A3 receptors). In binding studies using [3H]SCH 58261 as a radioligand, the three compounds were equally potent at A2A receptors, their K(i) value being less than 1 nM. Affinity for A1 and A3 receptors was measured using [3H]DPCPX and [125I]AB-MECA as radioligands. Given the lack of selective ligands, interaction with A2B receptors was assessed using the cAMP accumulation assay following stimulation by the adenosine receptor agonist N-ethylcarboxamidoadenosine (NECA). CGS 15943 was almost as potent at A1 receptors (K(i)3.5 nM) as at A2A receptors, showed moderate affinity for A3 receptors (K(i) 95 nM) and also interacted with A2B receptors (K(i) 44 nM; pA2 7.5). ZM 241385 showed little affinity for A1 receptors (K(i) 255 nM), and did not interact with A3 receptors (K(i)>10 microM); however, it displayed moderate affinity for A2B receptors (K(i) 50 nM; pA2 7.3). SCH 58261 had weak affinity for A1 receptors (K(i) 287 nM), no interaction with A3 receptors (K(i)>10 microM), and showed negligible interaction with A2B receptors (K(i) 5 microM; pA2 6.0). These data indicate that SCH 58261 is the most selective A2A antagonist currently available. Moreover, the different receptor selectivity of these three chemically related compounds provides useful information to progress with structure-activity relationship studies.
Caffeine and the analog CGS 15943 inhibit cancer cell growth by targeting the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway.[Pubmed:24521981]
Cancer Biol Ther. 2014 May;15(5):524-32.
Caffeine is a naturally occurring methylxanthine that acts as a non-selective adenosine receptor antagonist. Epidemiological studies demonstrated habitual coffee drinking to be significantly associated with liver cancer survival. We aimed to investigate the effects of caffeine and its analog CGS 15943 on hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and pancreatic cancer adenocarcinoma (PDAC). We demonstrate that caffeine and CGS 15943 block proliferation in HCC and PDAC cell lines by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt pathway. Importantly a kinase profiling assay reveals that CGS 15943 targets specifically the catalytic subunit of the class IB PI3K isoform (p110gamma). These data give mechanistic insight into the action of caffeine and its analogs and they identify these compounds as promising lead compounds to develop drugs that can specifically target this PI3K isoform whose key role in cancer progression is emerging.
Discriminative effects of CGS 15943, a competitive adenosine receptor antagonist, have a dopamine component in monkeys.[Pubmed:10440083]
Eur J Pharmacol. 1999 Jul 2;376(1-2):7-15.
9-Chloro-2-(2-furyl)[1,2,4]triazolol[1,5-c]quinazolin-5-amin e (CGS 15943), like caffeine, is an antagonist at adenosine A1 and A2A receptors and a behavioral stimulant in animals. The two drugs have overlapping discriminative effects. Enhancement of dopamine-mediated neurotransmission appears to contribute to the behavioral effects of caffeine. This study was conducted to determine if there is a dopamine component to the discriminative effects of CGS 15943. Squirrel monkeys discriminating between i.m. injections of 1.0 mg/kg CGS 15943 and vehicle generalized dose-dependently and completely to eight dopamine receptor agonists that encompass a variety of mechanisms and sites of action, both pre- and postsynaptic. The discriminative effects of the training dose of CGS 15943 were blocked dose-dependently and completely by the dopamine receptor antagonists R(+)-7-chloro-8-hydroxy-3-methyl-1-phenyl-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1H-3-benzaz epine (SCH 23390; D1) and eticlopride (D2). Thus, the discriminative effects of CGS 15943 have a dopamine component that appears to be mediated by both the D1 and D2 families of dopamine receptors. The monkeys also generalized to selective inhibitors of the neuronal transporters of norepinephrine (nisoxetine) and serotonin (fluoxetine), indicating that monoamines other than dopamine also contribute to the discriminative effects of CGS 15943.
Derivatives of the triazoloquinazoline adenosine antagonist (CGS 15943) having high potency at the human A2B and A3 receptor subtypes.[Pubmed:9667972]
J Med Chem. 1998 Jul 16;41(15):2835-45.
The adenosine antagonist 9-chloro-2-(2-furanyl)[1,2,4]triazolo[1, 5-c]quinazolin-5-amine (CGS 15943) binds nonselectively to human A1, A2A, and A3 receptors with high affinity. Acylated derivatives and one alkyl derivative of the 5-amino group and other modifications were prepared in an effort to enhance A2B or A3 subtype potency. In general, distal modifications of the N5-substituent were highly modulatory to potency and selectivity at adenosine receptors, as determined in radioligand binding assays at rat brain A1 and A2A receptors and at recombinant human A3 receptors. In Chinese hamster ovary cells stably transfected with human A2B receptor cDNA, inhibition of agonist-induced cyclic AMP production was measured. An N5-(2-iodophenyl)acetyl derivative was highly selective for A2A receptors. An (R)-N5-alpha-methyl(phenylacetyl) derivative was the most potent derivative at A3 receptors, with a Ki value of 0.36 nM. A bulky N5-diphenylacetyl derivative, 13, displayed a Ki value of 0. 59 nM at human A3 receptors and was moderately selective for that subtype. Thus, a large, nondiscriminating hydrophobic region occurs in the A3 receptor in proximity to the N5-substituent. A series of straight-chain N5-aminoalkylacyl derivatives demonstrated that for A2B receptors the optimal chain length occurs with three methylene groups, i.e., the N5-gamma-aminobutyryl derivative 27 which had a pA2 value of 8.0 but was not selective for A2B receptors. At A1, A2A, and A3 receptors however the optimum occurs with four methylene groups. An N5-pivaloyl derivative, which was less potent than 27 at A1, A2A, and A3 receptors, retained moderate potency at A2B receptors. A molecular model of the 27-A2B receptor complex based on the structure of rhodopsin utilizing a "cross-docking" procedure was developed in order to visualize the environment of the ligand binding site.
Adenosine receptors and their ligands.[Pubmed:11111832]
Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2000 Nov;362(4-5):382-91.
The regulatory actions of adenosine are mediated via four subtypes of G protein-coupled receptors distinguished as A1, A2A, A2B and A3 receptors. Their presence on basically every cell makes them an interesting target for the pharmacological intervention in many pathophysiological situations. A large number of ligands have been synthesized over the last two decades and provide agonists and antagonists that are more or less selective for the known receptor subtypes. In addition, many radioligands are available in tritiated or radioiodinated form. The comparative pharmacological characterization of all four human adenosine receptor subtypes revealed that some of the compounds thought to be selective from data in other species have unexpected potencies at human receptors. As a result, compounds that exhibit high affinity to only one subtype are an exception. Although the selection of ligands is immense, it is less than satisfying for most subtypes of adenosine receptors.
Pharmacological characterization of CGS 15943A: a novel nonxanthine adenosine antagonist.[Pubmed:3656113]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Sep;242(3):784-90.
CGS 15943A is a potent adenosine receptor antagonist with a novel nonxanthine heterocyclic ring structure. In vitro, CGS 15943A competitively inhibited the 2-chloroadenosine-induced A2 receptor-mediated relaxation of dog coronary artery strips contracted with KCl (25 mM). Similarly, CGS 15943A blocked 2-chloroadenosine- and N-ethylcarboxamideadenosine-induced A2 receptor-mediated relaxation of histamine-contracted guinea pig tracheal strips. Schild analysis of these results yielded pA2 values of 10.8 and 10.1 for the coronary arteries and the tracheal smooth muscle strips, respectively. In comparison, 8-phenyltheophylline blocked 2-chloroadenosine-induced tracheal response with a pA2 value of 7.0. CGS 15943A was devoid of intrinsic activity, and did not affect either histamine- or KCl-induced contractions of the smooth muscle strips. In the electrically stimulated guinea pig left atrial preparation, CGS 15943A antagonized the A1 receptor-mediated negative inotropic effects of R-phenylisopropyladenosine with a pA2 value of 7.4. In vivo, i.v. administration of CGS 15943A blocked the vasodepressor response to 2-chloradenosine in anesthetized normotensive rats with an ID50 of 0.024 mg/kg. In addition, p.o. administration of CGS 15943A (4.0 mg/kg) to conscious rats inhibited 2-chloroadenosine-induced decreases in diastolic blood pressure; maximal effects were observed 30 min after dosing, with a T1/2 of approximately 103 min. Therefore suggesting that CGS 15943A is an orally active antagonist of adenosine receptors. These results indicate that CGS 15943A antagonized both A1 and A2 receptor-mediated responses with a greater affinity toward the A2 than the A1 receptor subtype.
Biochemical characterization of the triazoloquinazoline, CGS 15943, a novel, non-xanthine adenosine antagonist.[Pubmed:2883298]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 May;241(2):415-20.
CGS 15943A, a triazoloquinazoline, is a potent and selective adenosine receptor antagonist as assessed by its effects on radioligand binding and adenosine-stimulated adenylate cyclase activity in guinea pig synaptoneurosomes. At the adenosine A-1 receptor labeled with [3H]cyclohexyladenosine, CGS 15943A had an IC50 value of 20 nM. At the striatal A-2 receptor labeled with [3H]5'-N-ethylcarboxamidoadenosine in the presence of a low concentration of cyclopentyladenosine to block A-1 receptors labeled by this nonselective adenosine agonist, CGS 15943A had an IC50 value of 3 nM, indicating that the compound had some degree of selectivity for the A-2 receptor. Analysis of the effect of the compound on the saturation isotherms for each of the receptors indicated that it was a competitive antagonist at the brain A-1 receptor but that it was noncompetitive at the striatal A-2 receptor. CGS 15943A was a potent adenosine antagonist in the adenosine-stimulated adenylate cyclase system in guinea pig synaptoneurosomes, where the compound was found to have an IC50 value of 30 to 70 nM against the increase in cyclic AMP evoked by 5 microM adenosine. CGS 15943A had no effect on the binding of [3H]nitrobenzylthioinosine, a ligand thought to bind to adenosine uptake sites, and, at a concentration of 10 microM, had no effect on beef heart type III phosphodiesterase activity.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)


